Pain & Spot-Free Skin with Pityriasis Rosea Treatment
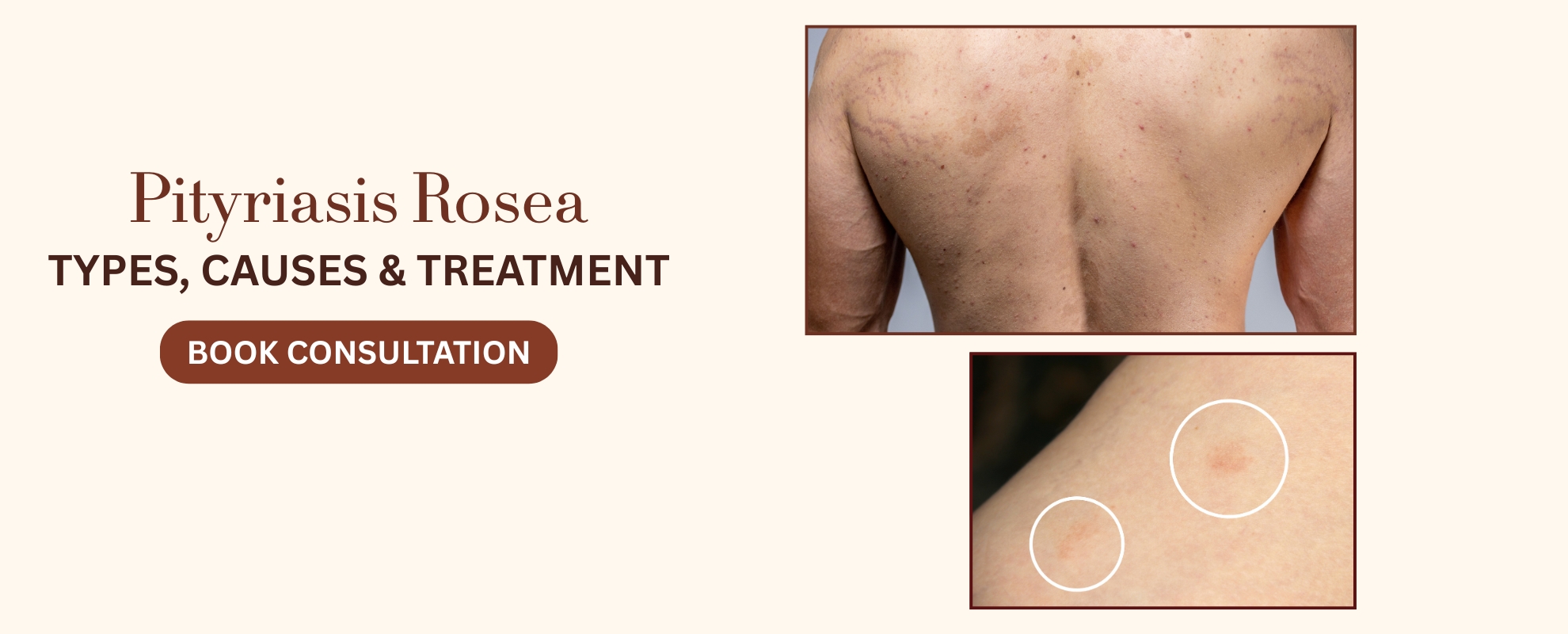
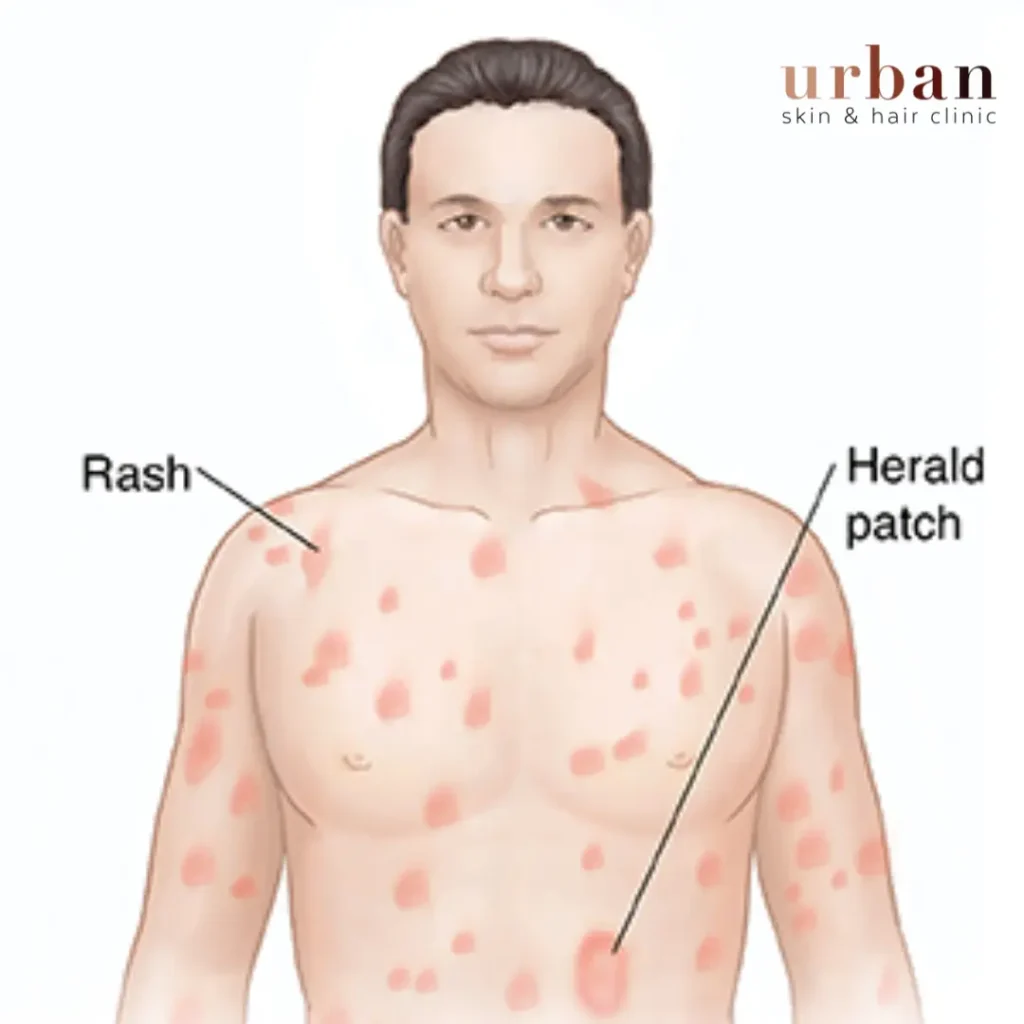
Pityriasis Rosea is a common and mild skin condition characterized by a distinctive rash. It starts with a single scaly patch known as the “herald patch” and is followed by smaller patches in a Christmas tree-like pattern on the back, chest, abdomen, and arms.
The rash is typically pink or red and may cause mild itching or discomfort. While the exact cause is unclear, it’s not contagious and often resolves on its own within weeks or months.
For any skin concerns, including Pityriasis Rosea, seek professional evaluation and personalized treatment for the best results.
Symptoms and Causes
signs & Symptoms Of Pityriasis Rosea?
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of Pityriasis Rosea is crucial in identifying this skin condition and seeking timely care. Here are the key indicators:
- Pink or Red Coloration: The rash typically exhibits pink or red coloration, which can be more apparent in lighter skin tones.
- Mild Itching or Discomfort: While not everyone with Pityriasis Rosea experiences symptoms, some individuals may notice mild itching.
- Other Symptoms: Apart from the characteristic rash and mild itching, Pityriasis Rosea does not typically cause severe symptoms.
- Fatigue: Some people with Pityriasis Rosea may feel more tired than usual, experiencing a sense of low energy or fatigue.
- Headache: Occasional headaches have been reported by a few individuals during the course of Pityriasis Rosea.
- Fever: While not common, a low-grade fever may accompany Pityriasis Rosea in rare instances.
- Loss of Appetite: A temporary loss of appetite has been observed in a small number of cases.
- Achiness: Mild body aches or discomfort may be present but are generally not severe.
- Nausea: Some individuals may experience mild nausea, though this symptom is infrequent.
- Trouble Sleeping: A few people with Pityriasis Rosea may encounter difficulties falling or staying asleep, but this is not a common symptom.

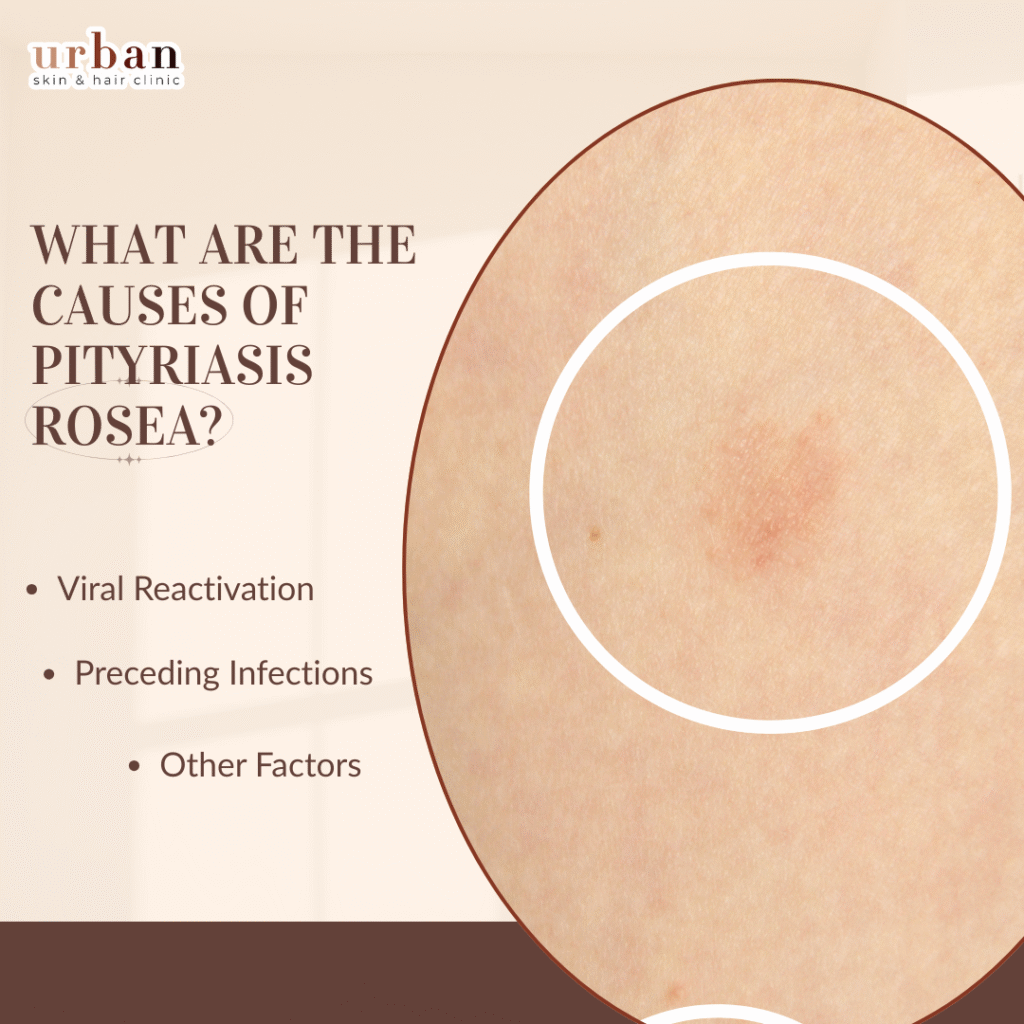
What are the Causes of Pityriasis Rosea?
Pityriasis rosea arises from an unclear etiology, but strong evidence points to reactivation of human herpesviruses 6 and 7 (HHV-6/7) as the primary trigger.
Viral Reactivation
HHV-6 and HHV-7, common latent viruses from childhood, reactivate due to immune fluctuations, causing the characteristic herald patch and Christmas tree rash pattern.
Preceding Infections
Upper respiratory infections, possibly streptococcal, often precede onset, suggesting bacterial superantigens or co-triggers amplify T-cell responses.
Other Factors
Certain medications (e.g., ACE inhibitors, metronidazole) and vaccinations provoke pityriasis rosea-like eruptions via hypersensitivity or molecular mimicry.
What are the Types of Pityriasis Rosea
Pityriasis Rosea primarily occurs in one main form, but it can exhibit slight variations in its presentation. Here are the key types:
- Classic Pityriasis Rosea: This is the most common type and follows the typical pattern. It begins with a single, larger “herald patch” and is followed by smaller patches spreading across the body in a symmetrical, Christmas tree-like pattern.
- Inverse Pityriasis Rosea: In this type, the rash appears in areas with skin folds, such as the armpits, groin, or under the breasts. It may be more challenging to diagnose due to its location, but it shares similar characteristics with the classic form.
- Giant Pityriasis Rosea: This type is relatively rare and involves larger and more pronounced patches than the classic form. The rash may be more extensive and take longer to resolve.
- Unilateral Pityriasis Rosea: Unlike the usual symmetrical distribution, this type affects only one side of the body. It is less common but follows the same course of self-resolution as other types.
While these variations exist, the underlying nature of Pityriasis Rosea remains generally benign and self-limiting.
Treatment For Pityriasis Rosea
Pityriasis Rosea is a self-limiting condition that typically resolves on its own without specific medical treatment. However, managing the symptoms and promoting comfort during the rash’s duration is essential. Here are some general treatment approaches that can be beneficial:
Keeping the skin well-moisturized can help reduce itching and discomfort. Using mild, fragrance-free moisturizers or emollients is recommended. Avoiding harsh soaps and hot water can also prevent further irritation.
In cases where itching or inflammation is bothersome, a dermatologist may prescribe topical corticosteroids. These medications can help reduce redness, swelling, and itching, promoting faster symptom relief.
Over-the-counter antihistamines can be used to alleviate itching and improve sleep quality if nighttime itching is a concern.
For individuals with severe or persistent Pityriasis Rosea, phototherapy (light therapy) may be considered. This treatment involves exposing the affected skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet (UV) light, which can help expedite the resolution of the rash.
If you suspect you have Pityriasis Rosea or any other skin condition, seeking professional evaluation from a qualified dermatologist is essential. They can confirm the diagnosis, rule out other skin conditions, and provide personalized recommendations for your specific situation.
However, with the right approach and expert guidance from Urban Skin & Hair Clinic, you can achieve healthy, hydrated, and lustrous locks. Don’t let dry frizzy hair hold you back – take the first step towards beautiful hair by scheduling a consultation with our experienced team today!
Pityriasis Rosea Treatment Results Before & After


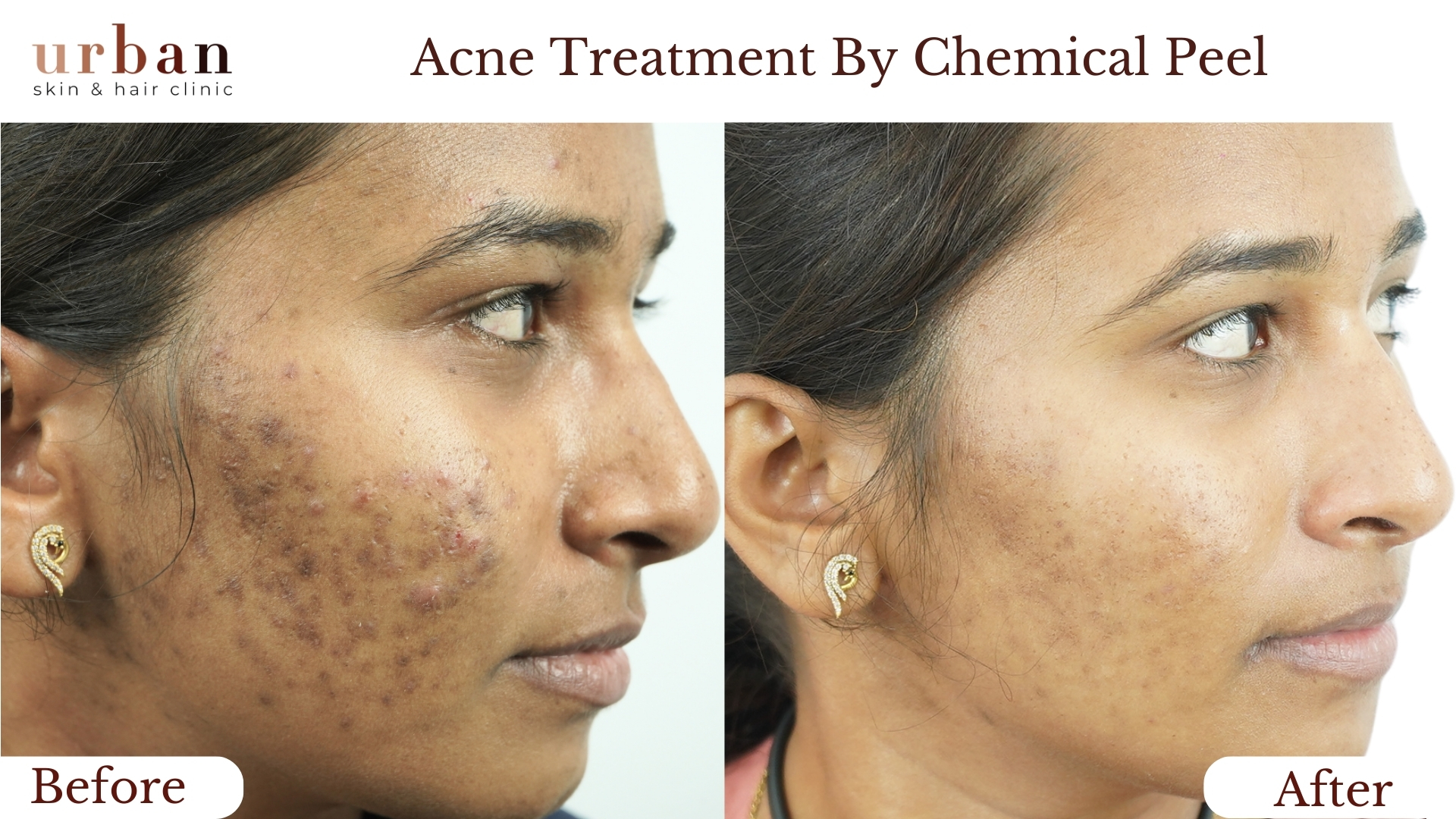
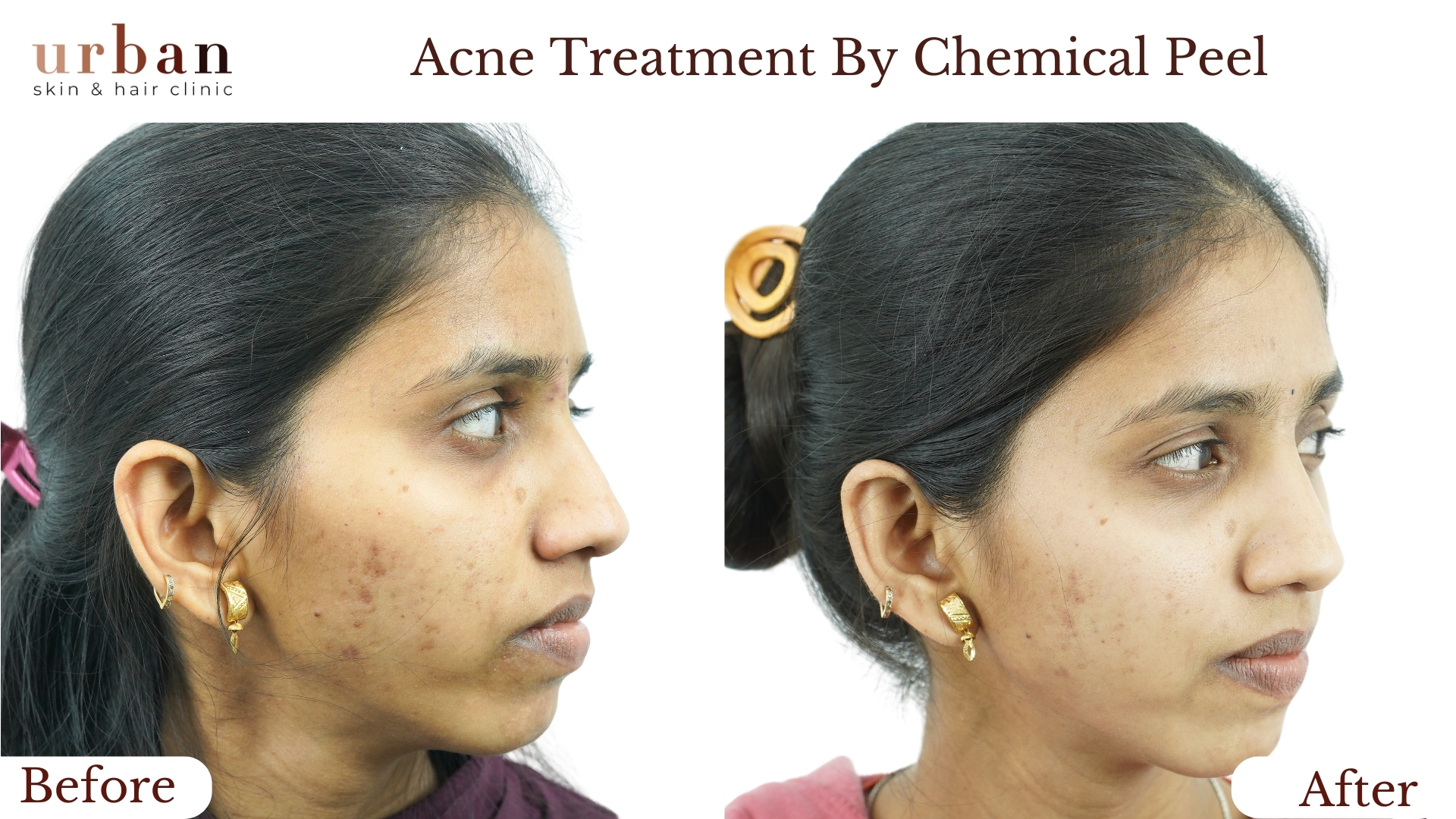
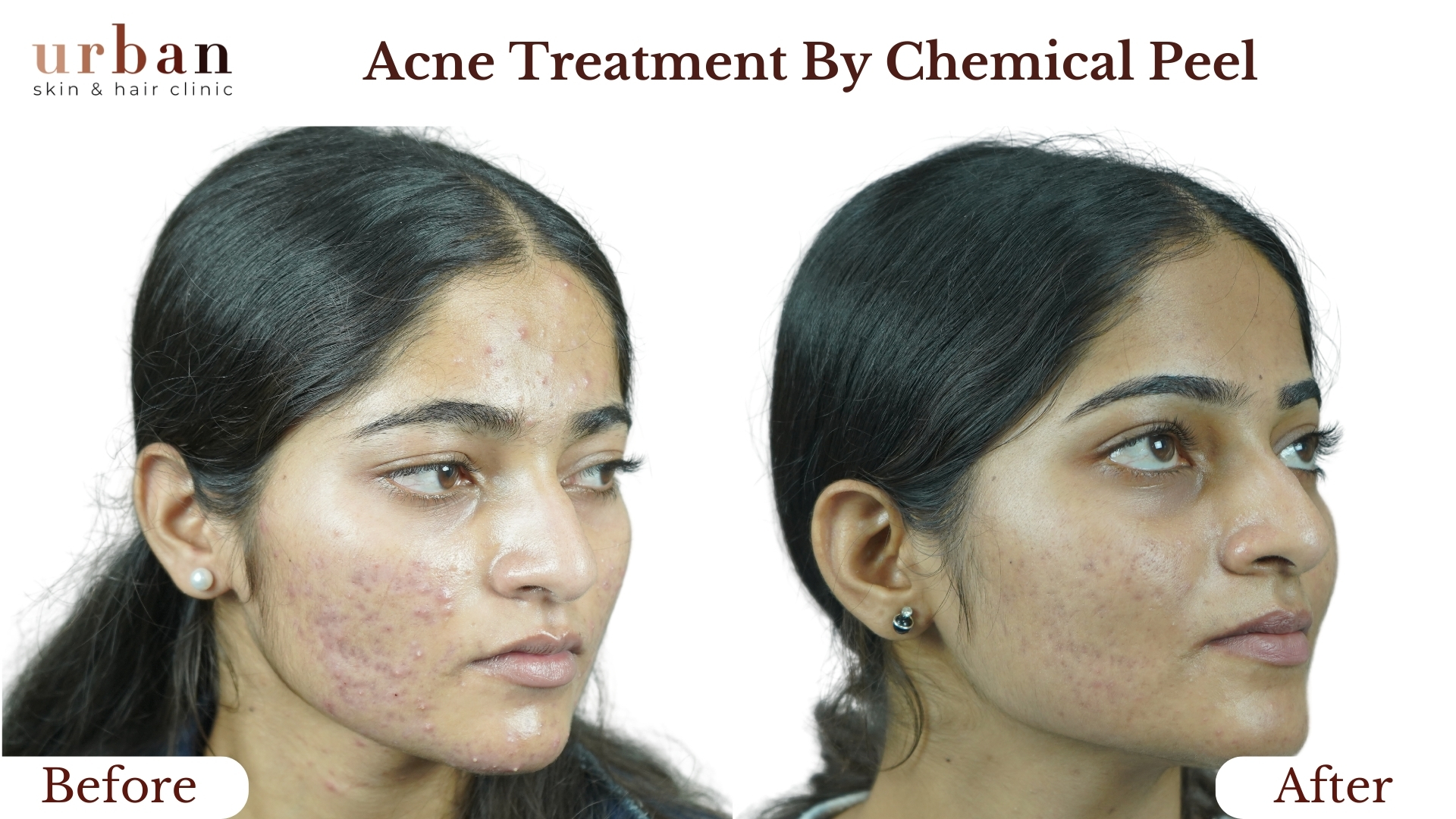
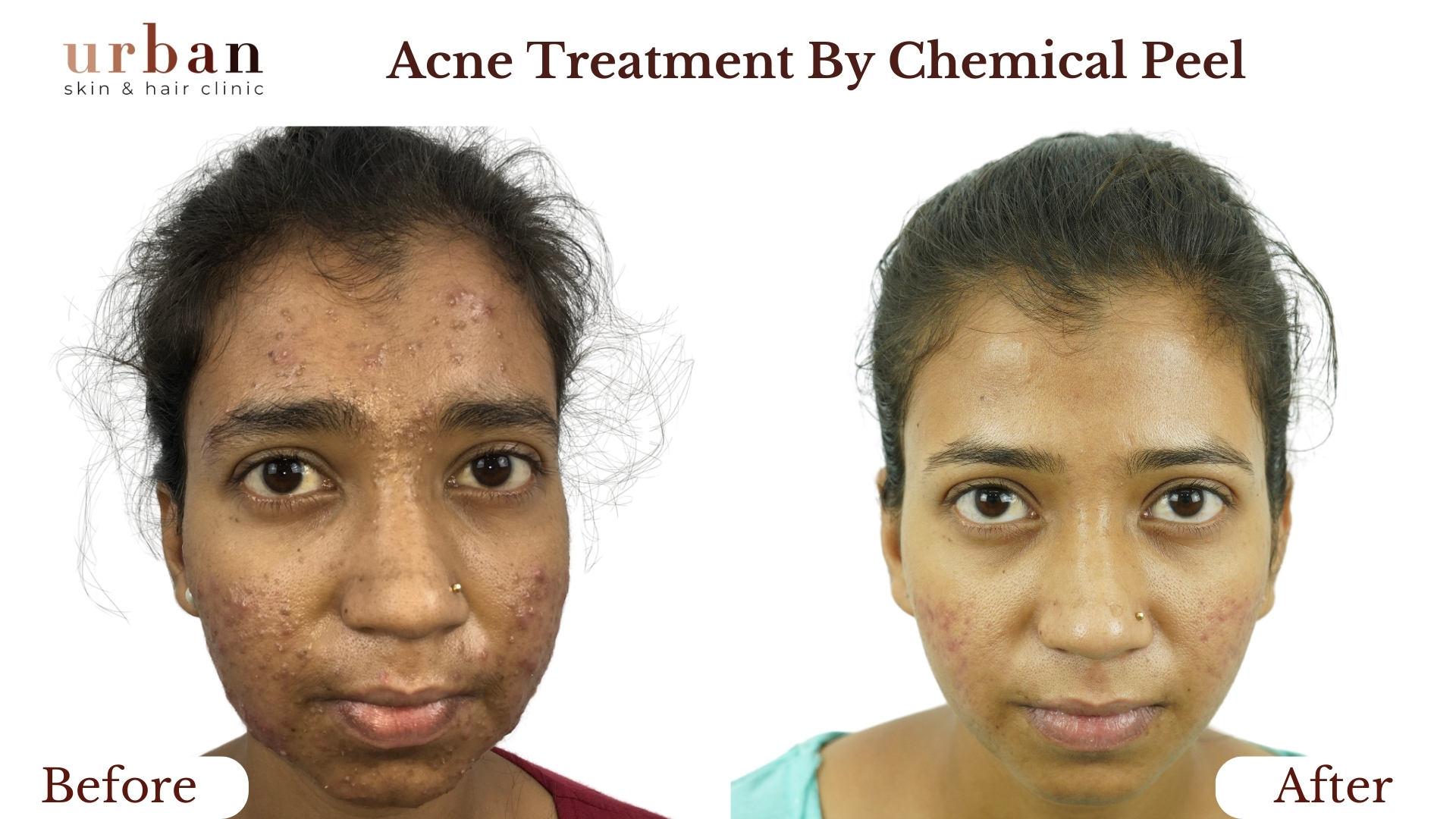
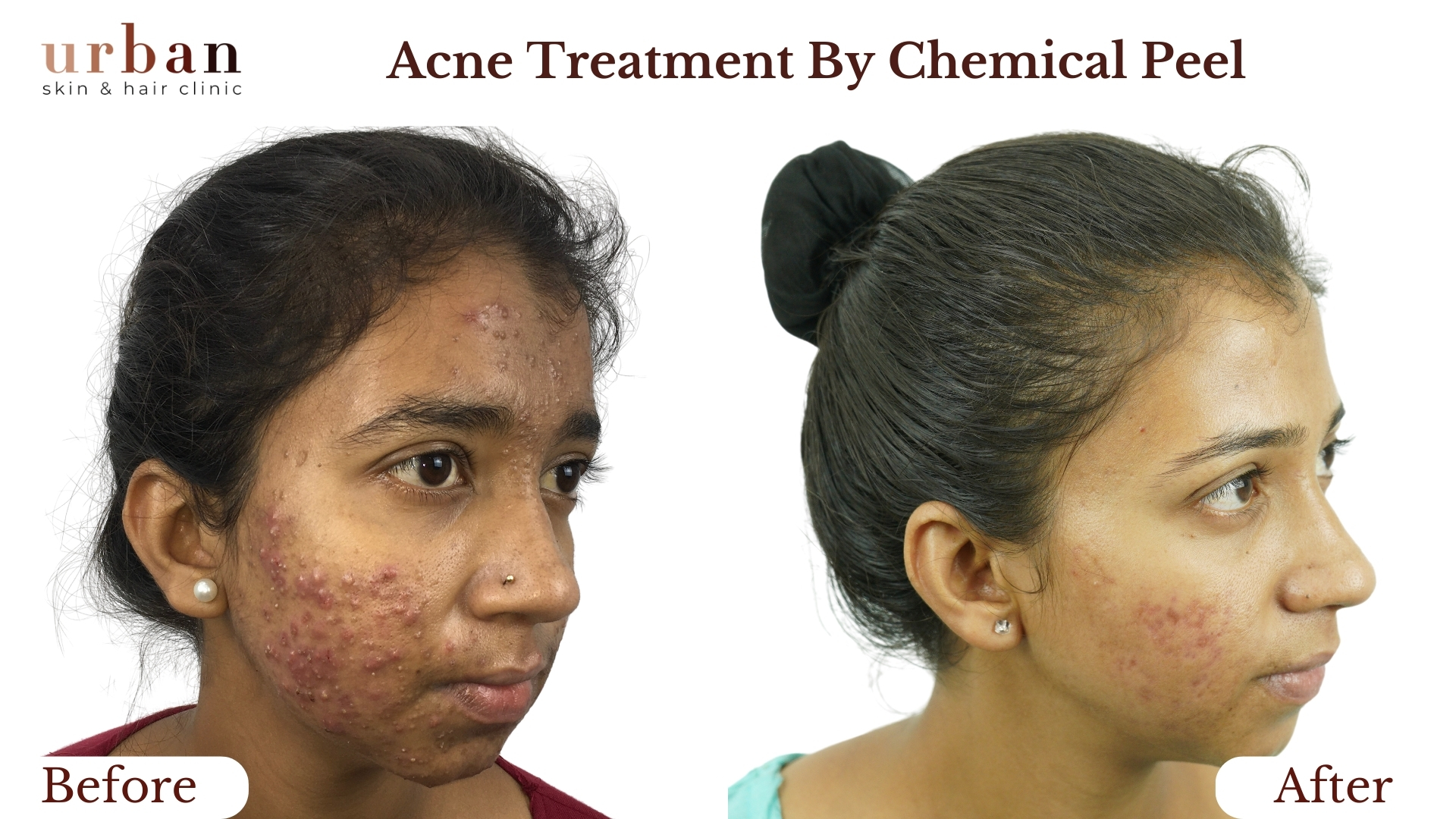
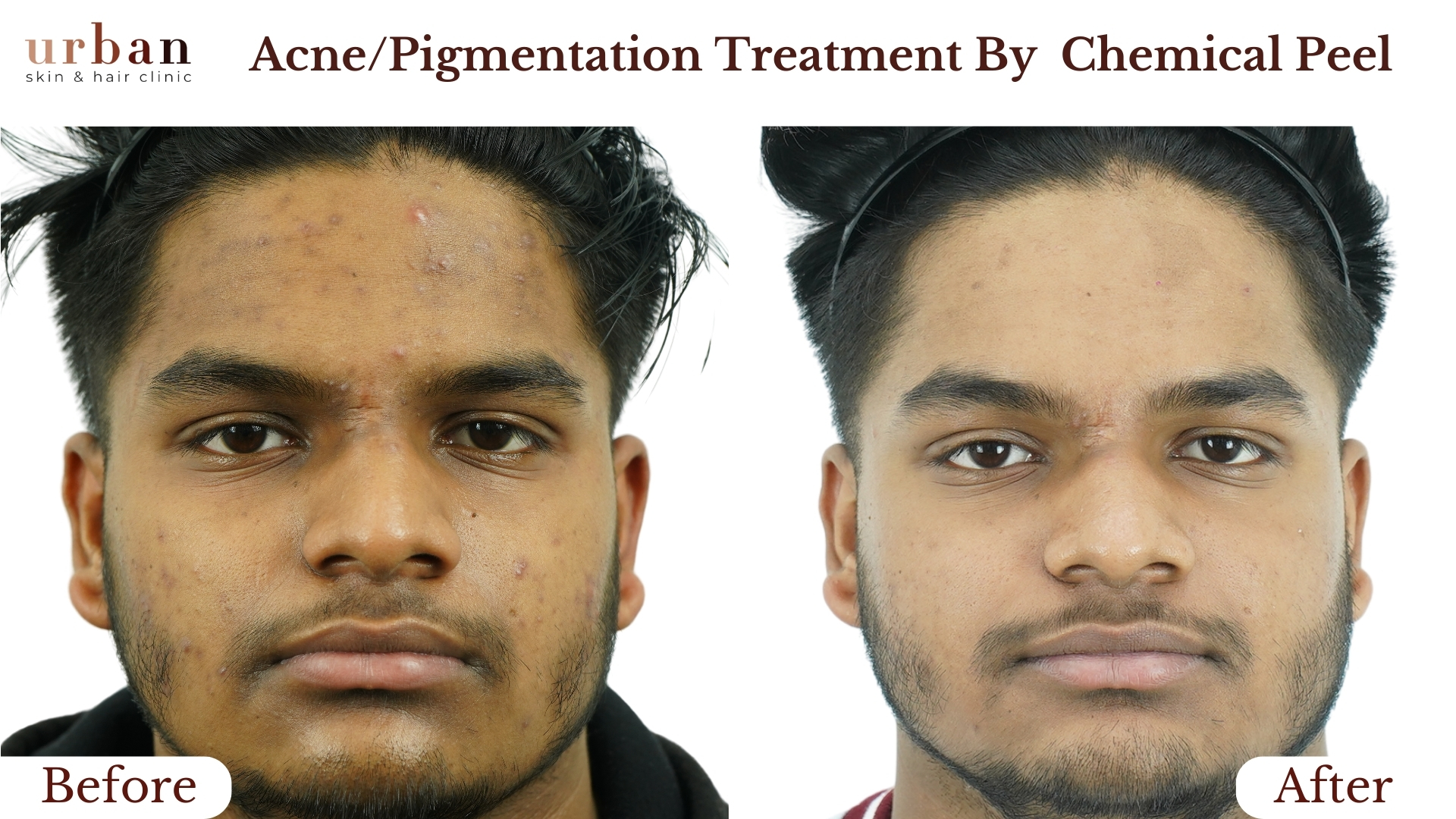
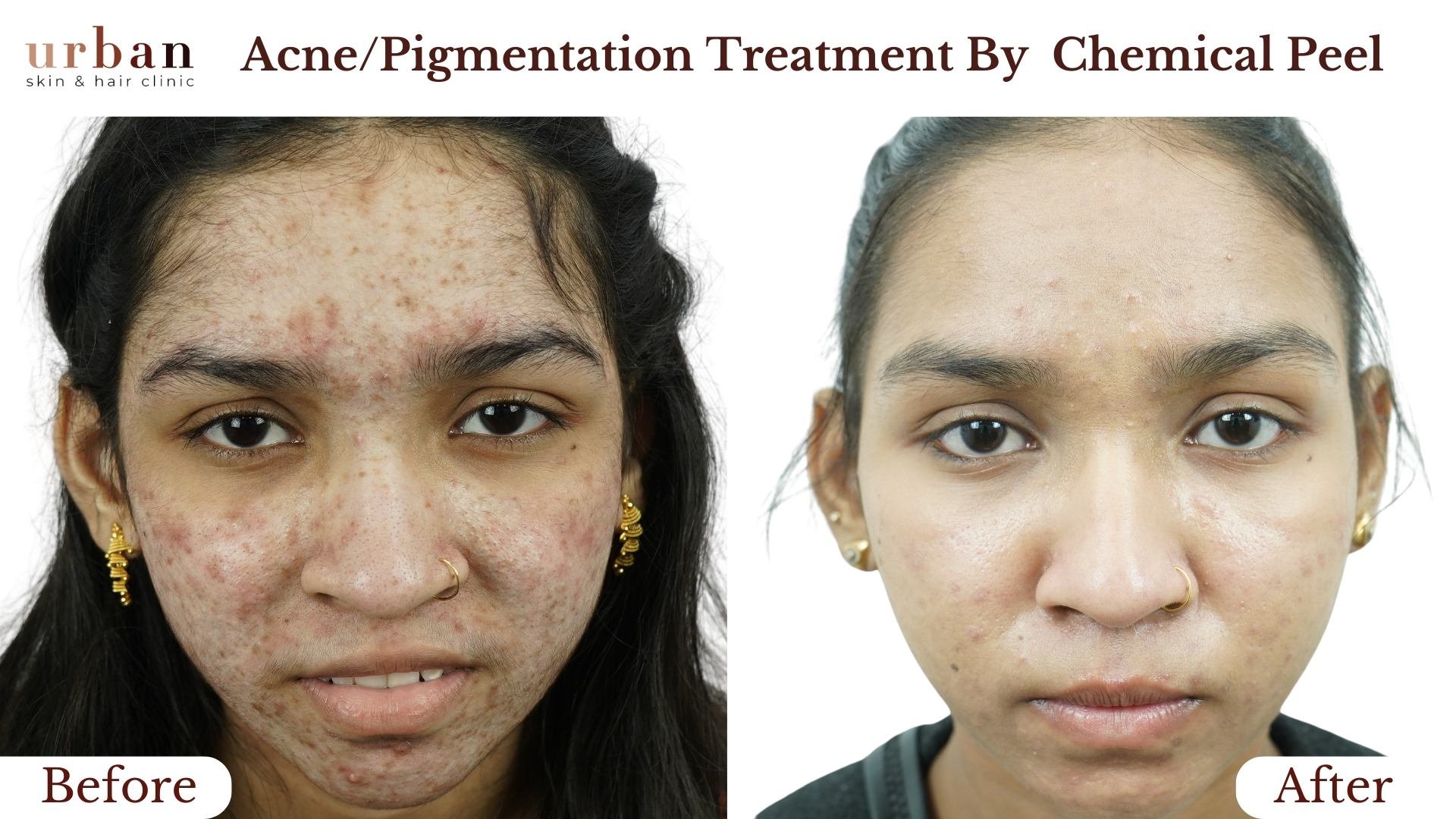

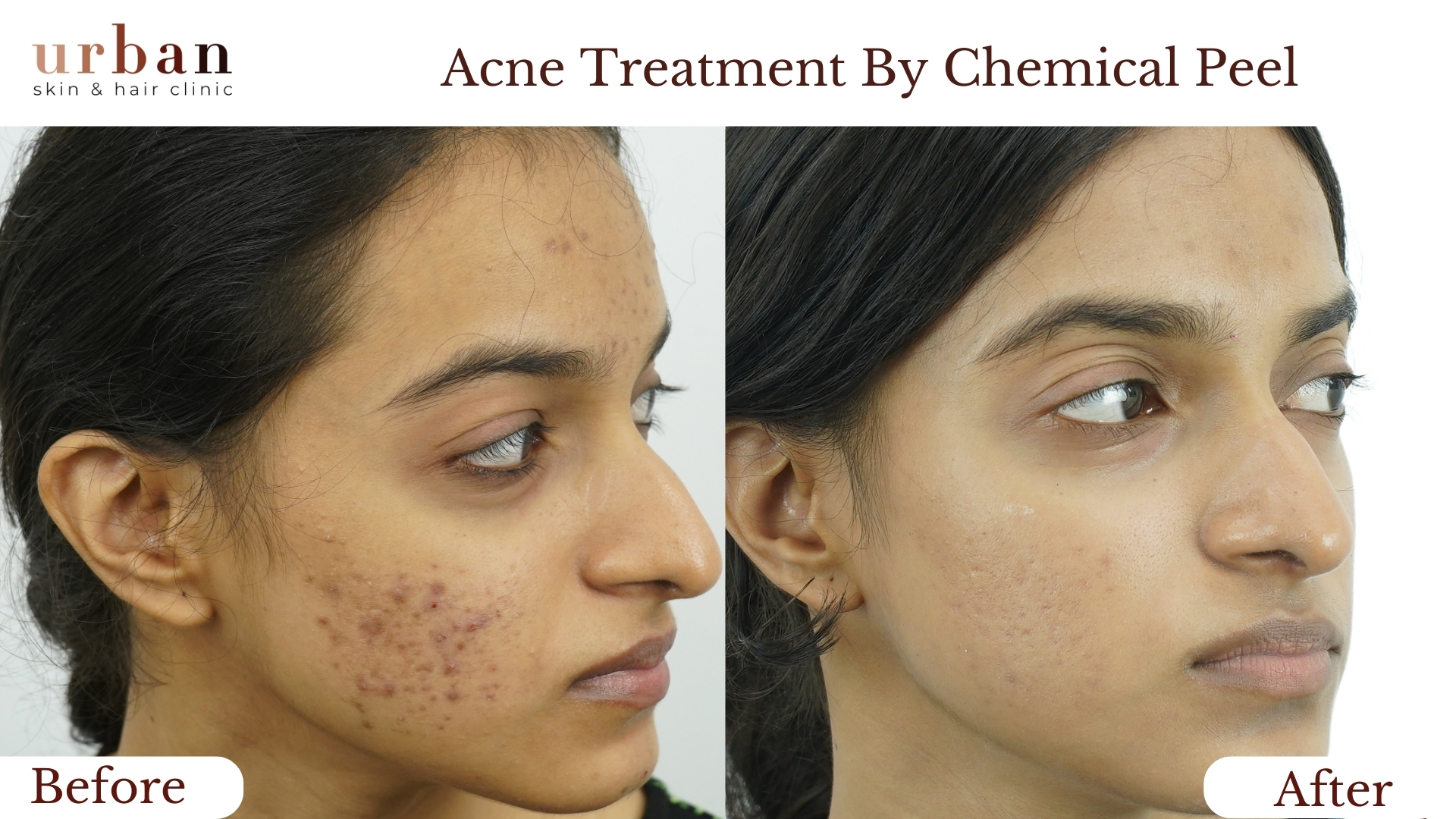
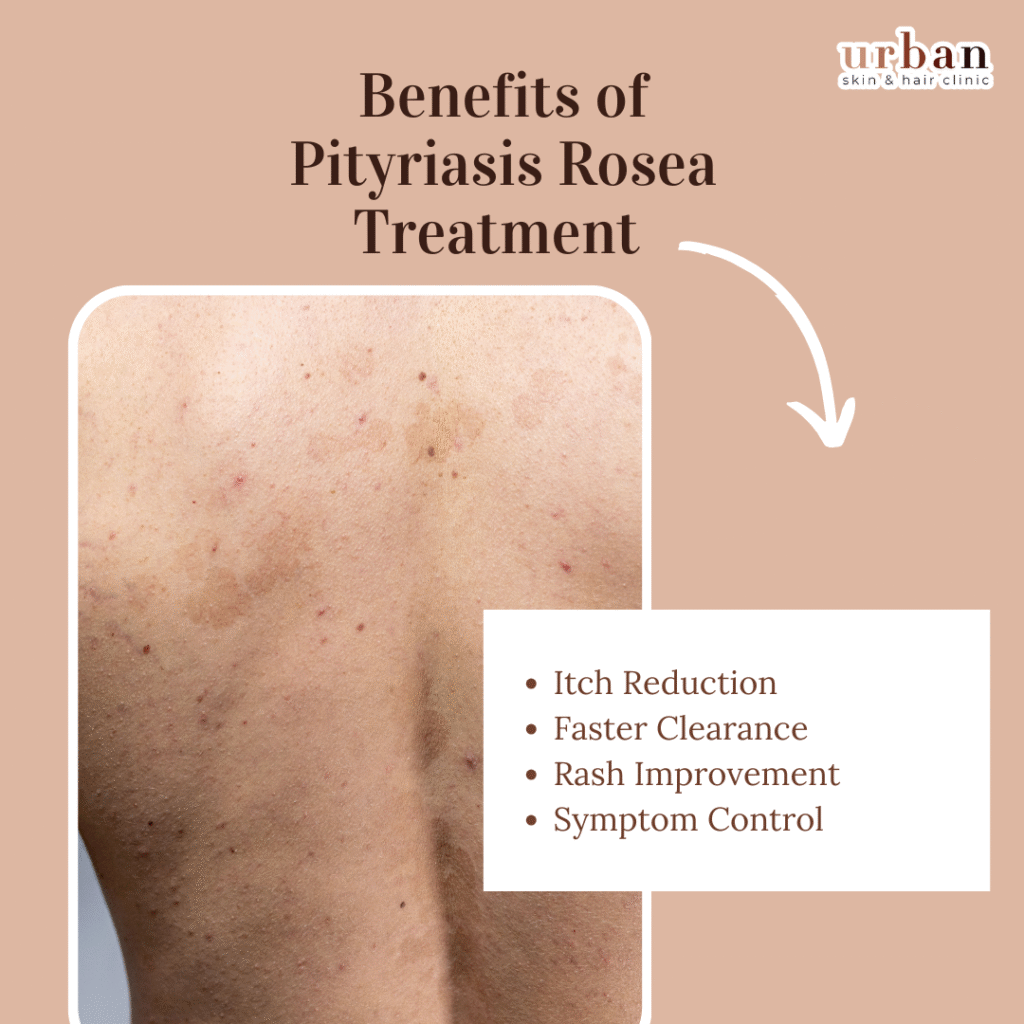
Benefits of Pityriasis Rosea Treatment
Pityriasis rosea treatment accelerates rash resolution and relieves symptoms in this self-limiting viral rash affecting young adults.
Itch Reduction
Oral antihistamines like cetirizine or topical corticosteroids decrease pruritus intensity by 50-70% within days, improving sleep and comfort.
Faster Clearance
Acyclovir (400-800 mg five times daily for 7 days) shortens duration from 6-12 weeks to 1-4 weeks, with practitioner-rated excellent improvement in moderate-quality trials.
Rash Improvement
Erythromycin or narrowband UVB phototherapy reduces lesion severity and scaling more effectively than placebo, based on low-to-moderate evidence.
Symptom Control
Moisturizers and emollients soothe dry skin, preventing secondary irritation during the 2-12 week natural course.
Popular Treatments for Pityriasis Rosea
How To Prevent Pityriasis Rosea?
Pityriasis rosea has no proven prevention strategy due to its likely viral etiology from HHV-6/7 reactivation, which cannot be fully avoided.
Skin Protection
Apply broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen and cover rash areas to prevent UV-induced worsening or hyperpigmentation during active episodes.
Irritant Avoidance
Use fragrance-free moisturizers, mild cleansers, and loose cotton clothing to minimize friction, dryness, and flare exacerbation.
Immune Support
Maintain balanced diet, regular exercise, stress reduction, and adequate sleep to potentially lower reactivation risk from immune fluctuations.
Hygiene Practices
Practice frequent handwashing and avoid close contact with active cases, though person-to-person transmission evidence remains weak.
Consult a Specialist Today
Many of the techniques for preventing pimples may also be used to cure them. Eating well, avoiding stress, and not popping pimples may help manage zits and reduce their length. If your acne continues despite your best efforts, you may need prescription acne treatment. Consult your dermatologist if you’re uncertain about treatment.
FAQ's
Likely triggered by reactivation of human herpesviruses 6 or 7 (HHV-6/7), often after respiratory infections or stress, though exact etiology remains unproven.
No, it’s not transmitted person-to-person despite viral links; close contact doesn’t spread it reliably.
Typically 6-12 weeks total, starting with a herald patch then smaller lesions; resolves without scarring in most cases.
Mild itching affects 50% of cases, worsening with heat or sweat; rarely painful or accompanied by flu-like symptoms.
Recurrence is rare post-resolution; darker skin may show temporary hyperpigmentation, but no permanent scars.