
What Is Eczema
Eczema, also known as dermatitis, is a common skin condition characterized by inflammation, redness, itching, and the development of rashes on the skin. It can affect people of all ages but most commonly begins in childhood. Eczema is not contagious. The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with eczema often have a hypersensitive immune system, which reacts to certain triggers, leading to inflammation and skin irritation.
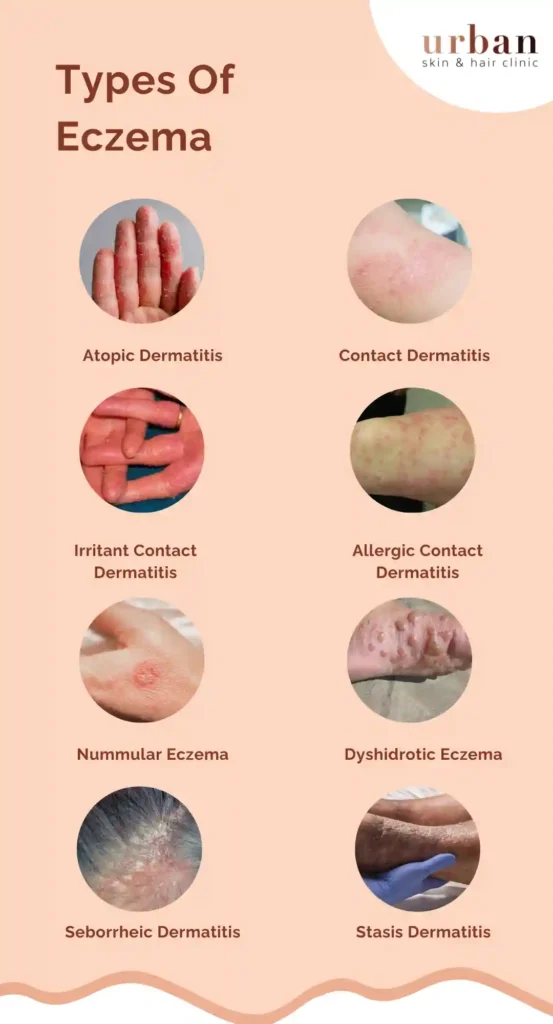
What Are The Types Of Eczema?
- Atopic Dermatitis: This is the most prevalent form of eczema, often occurring in individuals with a family history of allergies, asthma, or atopic conditions. It typically begins in childhood and is characterized by itchy, dry, and inflamed skin. Atopic dermatitis commonly affects the face, hands, feet, and skin folds.
- Contact Dermatitis: This type of eczema occurs when the skin comes into contact with irritants or allergens. There are two subtypes of contact dermatitis.
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis: Caused by contact with substances like chemicals, detergents, solvents, or prolonged exposure to water.
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis: Caused by an allergic reaction to specific substances such as metals (e.g., nickel), latex, certain cosmetics, fragrances, or plants like poison ivy or poison oak.
- Nummular Eczema: Also known as discoid eczema, coin-shaped patches of irritated skin characterize this form of eczema. It often occurs in adults and is associated with dry skin and a tendency to develop after skin injuries.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: This type of eczema primarily affects the hands and feet, leading to the formation of tiny, itchy blisters on the palms, fingers, soles, or toes. The blisters may be accompanied by redness, swelling, and flaking skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: This eczema affects areas rich in oil glands, such as the scalp, face (particularly the eyebrows, eyelids, and sides of the nose), and upper chest. It is characterized by red, scaly patches that may be itchy or uncomfortable. Seborrheic dermatitis can also occur in infants (known as cradle cap) and is often associated with dandruff.
- Stasis Dermatitis: Also referred to as gravitational dermatitis, this type of eczema typically affects the lower legs in individuals with poor circulation or venous insufficiency. It results from fluid buildup in the legs, leading to swollen, itchy, and discolored skin.
What Causes Eczema?
The exact causes of eczema are not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Here are some potential causes and contributing factors:
- Genetic Predisposition: Eczema often runs in families, suggesting a genetic component. Certain gene variations can affect the skin’s barrier function, immune response, and ability to retain moisture, making individuals more susceptible to eczema.
- Abnormal Immune Response: People with eczema tend to have an overactive immune system that reacts to certain triggers, leading to inflammation and skin irritation. This immune dysregulation can contribute to the development and persistence of eczema symptoms.
- Skin Barrier Dysfunction: The outermost layer of the skin, known as the epidermal barrier, helps retain moisture and protect against irritants and allergens. The skin barrier may be compromised in individuals with eczema, allowing moisture loss and increased susceptibility to irritants and allergens.
- Environmental Factors: Various environmental factors can trigger or exacerbate eczema symptoms, including.
- Irritants: Substances like soaps, detergents, shampoos, perfumes, certain fabrics, and chemicals can irritate the skin and trigger eczema flare-ups.
- Allergens: Some people with eczema may be sensitive or allergic to specific allergens, such as pollen, pet dander, mold, dust mites, certain foods, or airborne irritants like smoke or pollution.
- Climate and weather: Dry, cold weather with low humidity can lead to dry skin, while hot weather or excessive sweating can cause sweating and irritation.
- Microorganisms: Certain bacteria, viruses, or fungi on the skin can contribute to eczema symptoms or infections.

What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Eczema?
- Itchy Skin: Itching is one of the hallmark symptoms of eczema. The affected skin often feels intensely itchy, and scratching can provide temporary relief but may worsen the condition.
- Dry, Sensitive Skin: Eczema-prone skin tends to be dry, sensitive, and easily irritated. The skin may feel rough, scaly, or flaky and appear red or inflamed.
- Red Or Inflamed Patches: Eczema commonly causes redness and inflammation in the affected skin areas. These patches may vary in size and can occur anywhere on the body, depending on the type of eczema.
- Rash Or Blisters: In some forms of eczema, such as atopic dermatitis or dyshidrotic eczema, small, fluid-filled blisters may develop. When scratched, these blisters can be itchy and may lead to oozing or crusting.
- Thickened, leathery Skin: With prolonged or repeated scratching and inflammation, the affected skin can become thickened, rough, and leathery in texture. This is known as lichenification and commonly occurs in chronic eczema cases.
- Flare-Ups And Remission: Eczema tends to have periods of flare-ups and remission. During flare-ups, symptoms worsen and may become more severe, while the symptoms improve or disappear during remission.
- Skin Discoloration: In some cases, eczema can lead to changes in skin pigmentation, causing the affected areas to appear lighter or darker than the surrounding skin.
- Secondary Infections: Due to the compromised skin barrier and excessive scratching, eczema-affected skin can be prone to bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. These infections may cause additional symptoms like oozing, crusting, pus-filled bumps, or increased pain and tenderness.


