
Introduction
Alopecia Areata is a distressing condition that causes sudden, round patches of hair loss on the scalp and other areas of the body. At Urban Skin and Hair Clinic, Pune, we offer effective Alopecia Areata treatments to help you manage and treat Alopecia Areata, regrow lost hair, and restore your confidence. Our specialized therapies focus on stimulating hair regrowth and reducing the risk of recurrence.
What is Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, leading to hair loss in small, round patches. The condition can affect any part of the body, but it’s most commonly seen on the scalp and face. The severity varies: some experience only a few patches of hair loss, while others may suffer from complete scalp hair loss (Alopecia Totalis) or even total body hair loss (Alopecia Universalis).
Causes of Alopecia Areata
The exact cause of Alopecia Areata is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Autoimmune Response: The immune system targets hair follicles as though they are foreign invaders, leading to hair loss.
- Genetics: A family history of autoimmune diseases or Alopecia Areata increases the risk.
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress is believed to trigger or worsen hair loss in some cases.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like thyroid disease can increase susceptibility to Alopecia Areata.
- Infections or Viral Illnesses: Certain viral infections have been linked to autoimmune responses that cause hair loss.
- Environmental Factors: Pollutants and toxins may trigger flare-ups in those genetically predisposed.

Treatment Benefits
- Stimulates Hair Regrowth: Aims to activate dormant follicles and regenerate hair growth.
- Reduces Inflammation: Calms the immune response and prevents further damage to follicles.
- Strengthens Hair and Roots: Promotes the growth of thicker, stronger hair strands.
- Prevents Future Hair Loss: Helps stabilize hair regrowth and reduces the risk of recurrence.
- Non-Surgical Options: Safe, non-invasive treatments with minimal downtime.
- Suitable for All Ages and Severity Levels: From patchy hair loss to more extensive cases.
- Improves Scalp Health: Enhances overall scalp nourishment for healthier hair.
Before-After Results Alopecia Areata
Patients typically notice the regrowth of fine hair in the affected areas within 3–6 months of treatment. The density and thickness of the regrown hair improve with ongoing sessions, and many patients experience long-term hair restoration with proper care. Our dermatologists track progress through before-and-after photos to document hair restoration.
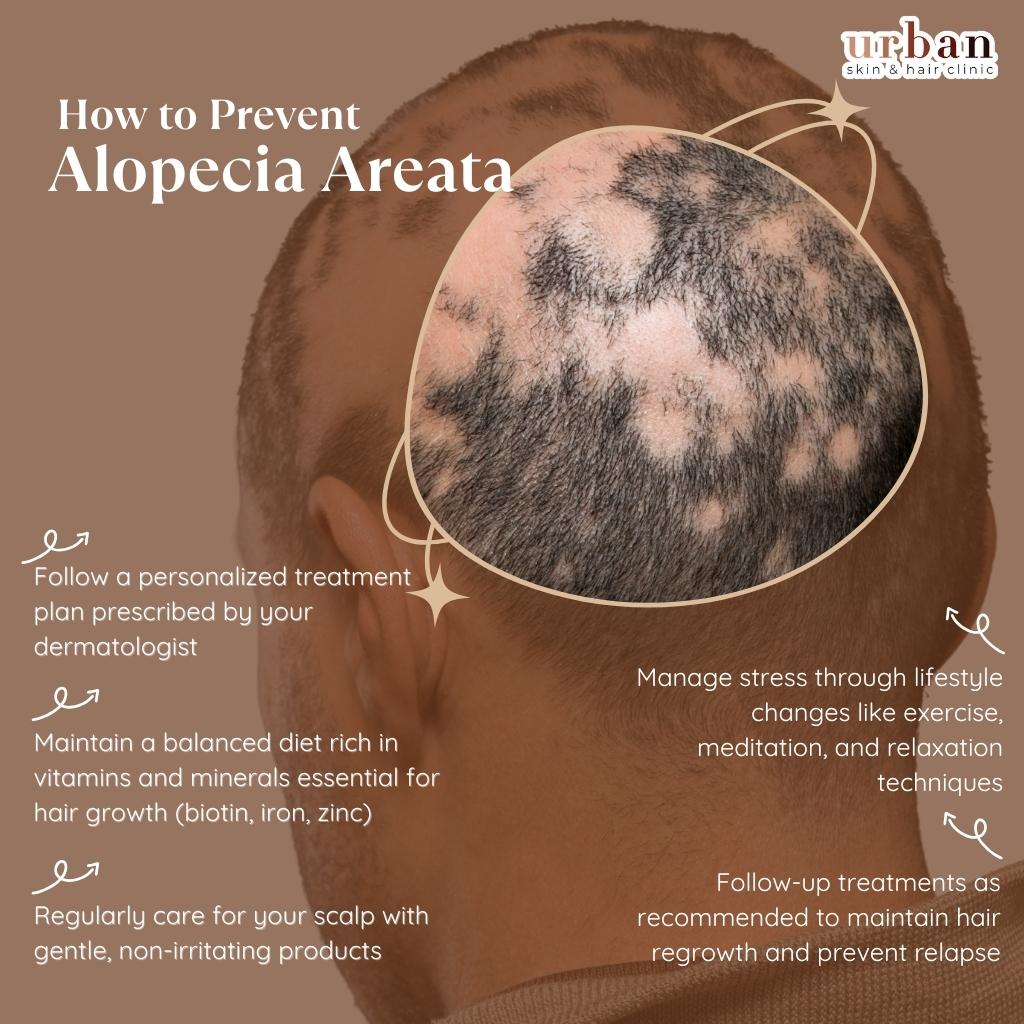
How to Prevent Alopecia Areata Recurrence
- Follow a personalized treatment plan prescribed by your dermatologist
- Manage stress through lifestyle changes like exercise, meditation, and relaxation techniques
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals essential for hair growth (biotin, iron, zinc)
- Regularly care for your scalp with gentle, non-irritating products
- Avoid harsh chemical treatments, heat styling, and tight hairstyles
- Follow-up treatments as recommended to maintain hair regrowth and prevent relapse
Treatment Options at Urban Skin and Hair Clinic
At Urban Skin and Hair Clinic, we offer a variety of treatments designed to manage and treat Alopecia Areata effectively:
- Steroid Injections: Administered directly into the affected areas to reduce inflammation and promote hair regrowth.
- Topical Steroid Creams: Applied to patches of hair loss to encourage follicular activity.
- PRP Therapy (Platelet-Rich Plasma): Stimulates hair follicles and promotes healing of the scalp.
- Micro needling: Creates micro-injuries on the scalp to encourage hair regrowth by enhancing nutrient absorption.
- Mesotherapy: Delivers essential nutrients directly into the scalp to strengthen hair follicles.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Stimulates hair follicles and improves blood circulation in the scalp.
- Oral Medications: Prescription options for autoimmune response regulation, such as corticosteroids or immune system modulators.
Each treatment is tailored to the patient’s needs, taking into account the severity of the condition and the patient’s health history.

Meet Our Expert Dermatologist
Dr. Kiran Chotaliya, M.D. Dermatology, is an expert in autoimmune hair loss treatments, including Alopecia Areata. With a compassionate approach and extensive clinical experience, Dr. Kiran will guide you through every step of the treatment process to ensure the best possible outcome.
Before treatment precaution
- Consult a dermatologist or trichologist to diagnose the condition and determine the best treatment plan.
- Keep a record of any family history of alopecia areata or autoimmune disorders.
- Avoid hair treatments such as coloring, perming, or straightening during the active phase of the condition.
- Protect your hair from harsh chemicals and excessive heat styling.
- Maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle to support overall hair health.
- Consider using topical products like minoxidil, corticosteroids, or anthralin under medical supervision.
After treatment precaution
- Follow up with your doctor to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
- Avoid any triggers that may have caused the alopecia areata, such as stress or certain medications.
- Continue to protect your hair from damage by avoiding harsh chemicals and excessive heat styling.
- Use gentle shampoos and conditioners designed for sensitive scalps.
- Incorporate hair-healthy vitamins and supplements into your diet, such as biotin, vitamin D, and iron.
- Be patient – regrowth can take time and may not be fully restored even with treatment.
What is the Average Cost of Alopecia Areata Treatment in India?
The average cost of Alopecia Areata treatment in India can vary depending on several factors, such as the severity of the condition, the location of the clinic or medical center, and the experience of the trichologist.
The cost of oils and lotion used for the treatment can start from INR 500. However, this is only a small part of the overall cost of treatment.
Treatment and tests can be expensive and vary widely depending on the clinic or medical center you choose. Choosing a clinic with a good reputation and a trichologist with experience in treating Alopecia Areata is always advisable.
Meet Our Expert Dermatologist
Dr. Kiran Chotaliya, M.D. Dermatology, is an expert in autoimmune hair loss treatments, including Alopecia Areata. With a compassionate approach and extensive clinical experience, Dr. Kiran will guide you through every step of the treatment process to ensure the best possible outcome.
Alopecia Areata Treatment FAQ
While there is no permanent cure, Alopecia Areata can be effectively managed, and hair regrowth is possible with the right treatments.
Hair regrowth typically begins in 3–6 months, with ongoing treatments recommended to ensure lasting results.
Yes, when administered by a qualified dermatologist, steroid injections are safe and effective for Alopecia Areata.
Yes, it can cause hair loss on the scalp, face (eyebrows, eyelashes), and even the body (Alopecia Universalis). Treatment will be adjusted based on the severity and area affected.
Why Urban Skin and Hair Clinic

TEAM OF CERTIFIED DERMATOLOGISTS

US-FDA APPROVED EQUIPMENTS

HIGHLY STANDARDISED PROTOCOLS

1 LAKH + HAPPY CLIENTS
Alopecia Areata Treatment Results Before & After

Problem; alopecia areata
Procedure: mesotherapy
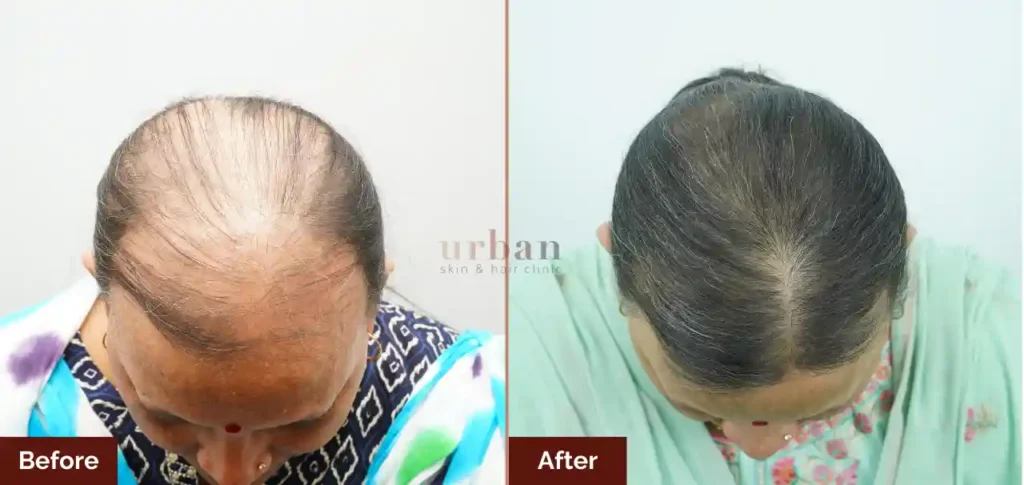
Problem; alopecia areata
Procedure: mesotherapy
Why Urban Skin and Hair Clinic

TEAM OF CERTIFIED DERMATOLOGISTS

US-FDA APPROVED EQUIPMENTS

HIGHLY STANDARDISED PROTOCOLS




