
What is Mollascum?
Molluscum contagiosum is a common and contagious skin infection caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). It is characterized by the formation of small, raised, and painless bumps on the skin’s surface. These bumps typically have a central indentation and may appear flesh-colored, pink, or white. Molluscum contagiosum is highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact or by sharing personal items.
Seeking professional medical evaluation at Urban Skin & Hair Clinic is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of molluscum contagiosum.
Causes of Mollascum
Molluscum contagiosum presents with distinct signs and symptoms, characterized by the appearance of small, raised bumps on the skin. These symptoms can help identify the condition and distinguish it from other skin conditions. Here are the common signs and symptoms of molluscum contagiosum:
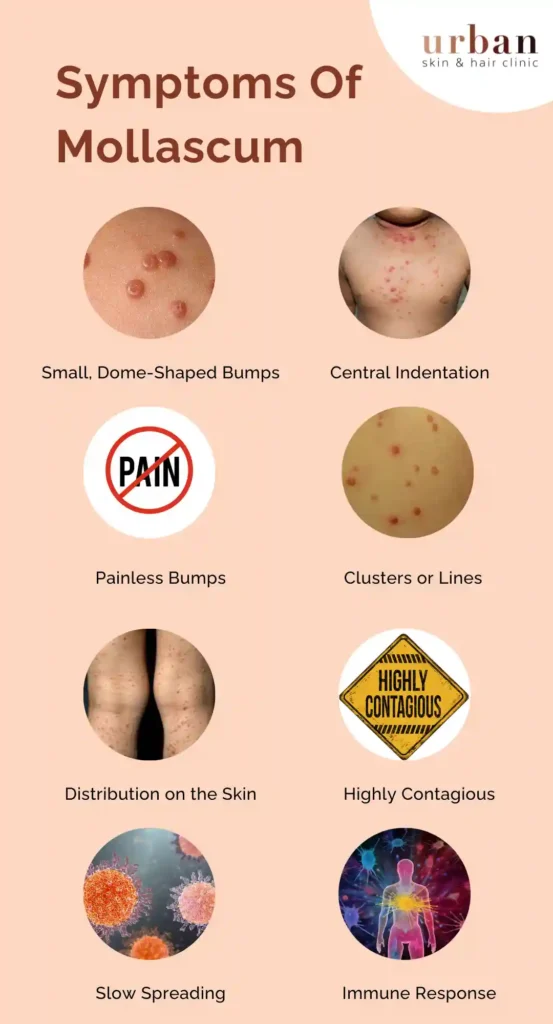
Signs & Symptoms of Mollascum
Molluscum contagiosum presents with distinct signs and symptoms, characterized by the appearance of small, raised bumps on the skin. These symptoms can help identify the condition and distinguish it from other skin conditions. Here are the common signs and symptoms of molluscum contagiosum:
- Small, Dome-Shaped Bumps: The hallmark symptom of molluscum contagiosum is the presence of small, smooth, and dome-shaped bumps on the skin. These bumps are usually flesh-colored, pink, or white and can vary in size from a pinhead to a small pea.
- Central Indentation: Each molluscum bump typically has a central indentation or dimple, resembling a small bellybutton.
- Painless Bumps: Molluscum contagiosum bumps are usually painless, although they can be slightly itchy or tender in some cases.
- Clusters or Lines: The bumps may appear individually or in clusters on the skin. In some cases, they may form linear patterns, especially in areas where the skin has been scratched or irritated.
- Distribution on the Skin: Molluscum contagiosum bumps can occur anywhere on the body but are commonly found on areas with thin and moist skin, such as the face, neck, armpits, arms, and hands in children. In adults, the bumps may be more prevalent in the genital area, lower abdomen, inner thighs, and buttocks, especially in cases of sexual transmission.
- Highly Contagious: Molluscum contagiosum is highly contagious and can be spread through direct skin-to-skin contact or by sharing personal items such as towels or clothing. Scratching or rubbing the bumps can also facilitate the spread of the virus to other areas of the skin.
- Slow Spreading and Self-Resolving: The condition is usually self-limiting and may resolve on its own over several months to years. In some cases, it may take up to 18 months for the bumps to disappear completely.
- Immune Response: Molluscum contagiosum is more commonly seen in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as young children, people with HIV/AIDS, or those undergoing immunosuppressive therapy.
Treatment for Mollascum
Molluscum contagiosum is a self-limiting condition that typically resolves on its own over time without specific treatment. However, treatment may be recommended to manage symptoms, prevent the spread of the virus to others, and accelerate the healing process. It’s essential to consult with a dermatologist or medical professional at Urban Skin & Hair Clinic for personalized treatment options. Here are the common approaches to treating molluscum contagiosum:
In many cases, especially in children and individuals with a healthy immune system, molluscum contagiosum may resolve without intervention. The condition typically clears up on its own within several months to years. If the bumps are not bothersome or causing discomfort, a “watch and wait” approach may be suggested.
Curettage is a procedure where the dermatologist uses a small, sharp instrument called a curette to scrape off the molluscum bumps from the skin’s surface. Local anesthesia may be applied before the procedure to minimize discomfort.
Cryotherapy involves freezing the molluscum bumps with liquid nitrogen to destroy the affected tissue. This procedure is relatively quick and may cause mild discomfort during the freezing process.
Various topical treatments, such as creams or ointments containing salicylic acid or tretinoin, may be prescribed to help speed up the resolution of molluscum contagiosum. These treatments work by promoting the shedding of the affected skin cells.
Cantharidin is a substance derived from blister beetles and is sometimes used to treat molluscum contagiosum. The dermatologist applies the solution to the bumps, causing a blister to form. The blister and the underlying molluscum tissue are then removed.
In some cases, laser therapy may be considered to treat molluscum contagiosum. Laser treatment can target and destroy the bumps while minimizing damage to the surrounding skin.
It’s important to note that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to treating molluscum contagiosum, and the most suitable treatment may vary based on factors such as the individual’s age, the number and location of the bumps, and the overall health status. Seeking professional medical evaluation at Urban Skin & Hair Clinic can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan and ensure the best possible outcome for managing molluscum contagiosum effectively.


