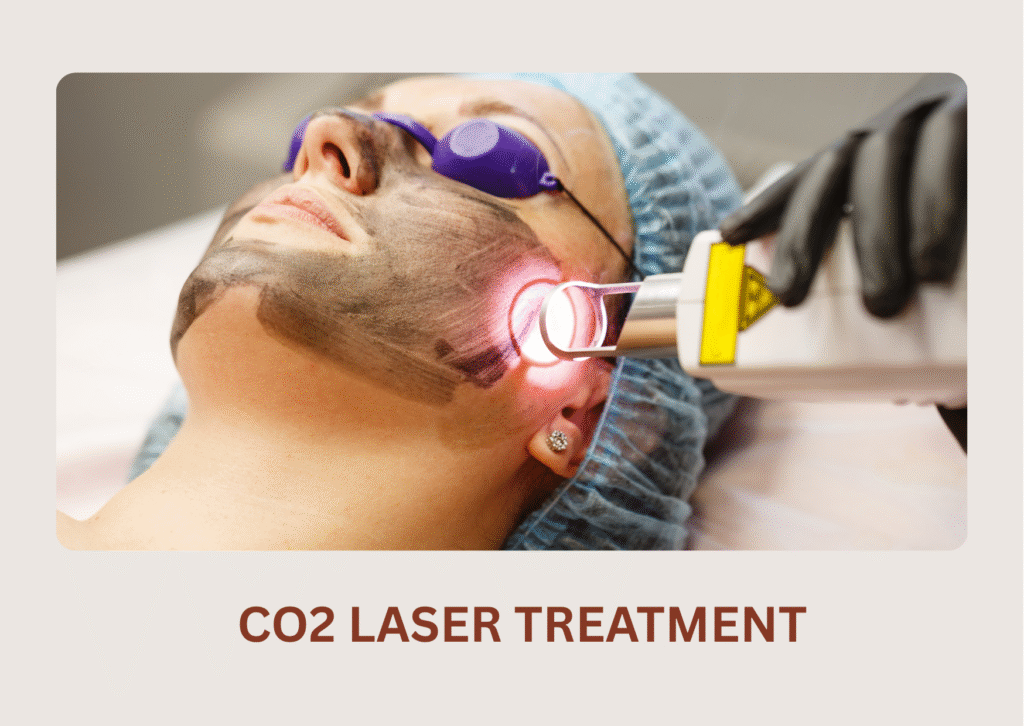
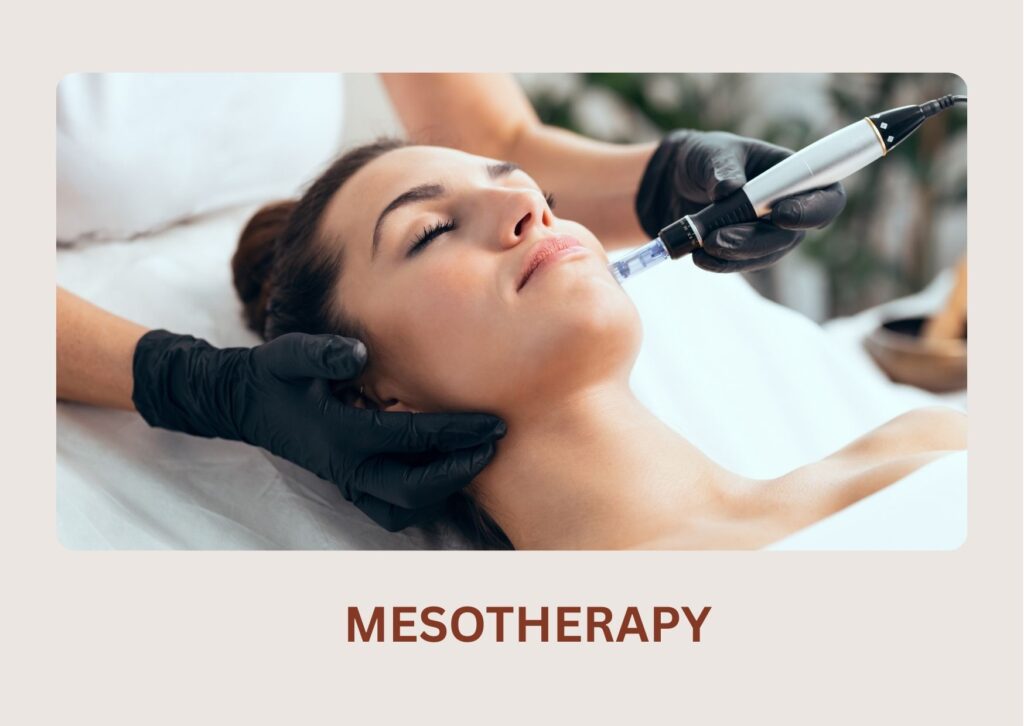
Clear, Even-Toned & Radiant Skin with Melasma Treatment
Melasma is a common pigmentation concern that causes dark patches on the face, often triggered by sun exposure, hormones, and skin sensitivity. At Urban Skin and Hair Clinic, our advanced melasma treatment solutions are designed to lighten pigmentation, control melanin production, and restore natural skin clarity. Using a combination of medical peels, lasers, topical therapies, and personalised skincare routines, we target the root cause of melasma for long-lasting improvement. With expert dermatologists and customised treatment plans, we help you achieve brighter, clearer, and more even-toned skin safely and effectively.
Symptoms and Causes
Symptoms of Melasma
The primary symptom of melasma is the appearance of dark, irregular patches or hyperpigmentation on the skin. These patches are typically brown or gray-brown in color and may have irregular borders. Here are some key symptoms of melasma:
Dark patches: Melasma presents as patches of darker skin coloration, commonly on the face. The patches are usually symmetrical, meaning they appear on both sides of the face, and they can vary in size and shape.
Facial involvement: Melasma predominantly affects the face, particularly the cheeks, forehead, chin, and upper lip. However, it can also occur on other sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the neck and forearms.
Sun-exposed areas: The patches of melasma tend to develop on areas of the skin that are regularly exposed to the sun.
Cosmetic concern: While melasma does not cause any physical discomfort or pain, it can be a source of cosmetic concern. The noticeable dark patches on the face can affect a person’s self-esteem and quality of life.

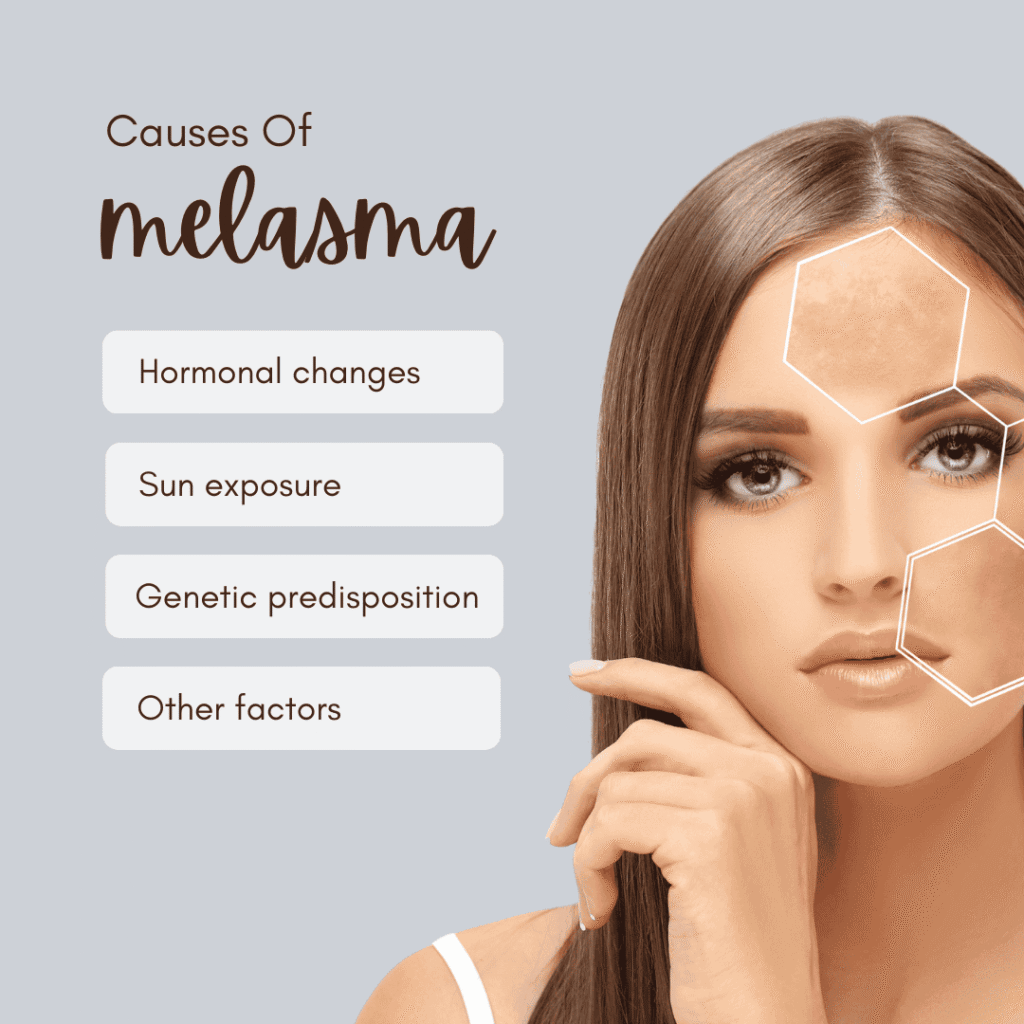
Causes of melasma
Melasma is believed to be caused by a combination of factors, including exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, hormonal changes, and genetic predisposition. Exposure to sunlight and other sources of UV radiation, such as visible light and heat, can trigger the development of melasma. Genetic factors may also influence the development of melasma.
Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations and imbalances play a significant role in melasma.
Sun exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a major trigger for melasma.
Genetic predisposition: There appears to be a genetic component to melasma, as it tends to run in families.
Other factors: Other factors that may contribute to the development of melasma include certain medications (such as antiepileptics and photosensitizing drugs), cosmetics or skincare products that irritate the skin, and heat exposure.

What are the types of melasma?
Melasma can be categorized into three main types based on the depth of pigmentation within the skin:
Epidermal Melasma: This type of melasma involves excess pigmentation in the epidermis, the topmost layer of the skin. This type of melasma has a well-defined border and a dark brown color. They tend to darken with sun exposure and can often improve with treatment.
Dermal Melasma: Dermal melasma occurs when excess pigmentation is located in the deeper layers of the skin, specifically the dermis. The patches appear bluish-gray in color and have less defined borders compared to epidermal melasma. Dermal melasma is more challenging to treat and may require more aggressive treatment approaches.
Mixed Melasma: As the name suggests, this type of melasma is a mixture of both epidermal and dermal melasma, where there is excess pigmentation in both the epidermis and dermis. Mixed melasma shows characteristics of both the above types, with a light to dark brown color and an indistinct border.
Treatment Options
Dermatologists diagnose melasma through a combination of medical history and visual examination. They evaluate the characteristic appearance of the skin, looking for dark, irregular patches or hyperpigmentation. A Wood’s lamp examination may be used to assess the depth of pigmentation. In rare cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. Consulting a dermatologist is important for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Melasma Treatment Results Before & After

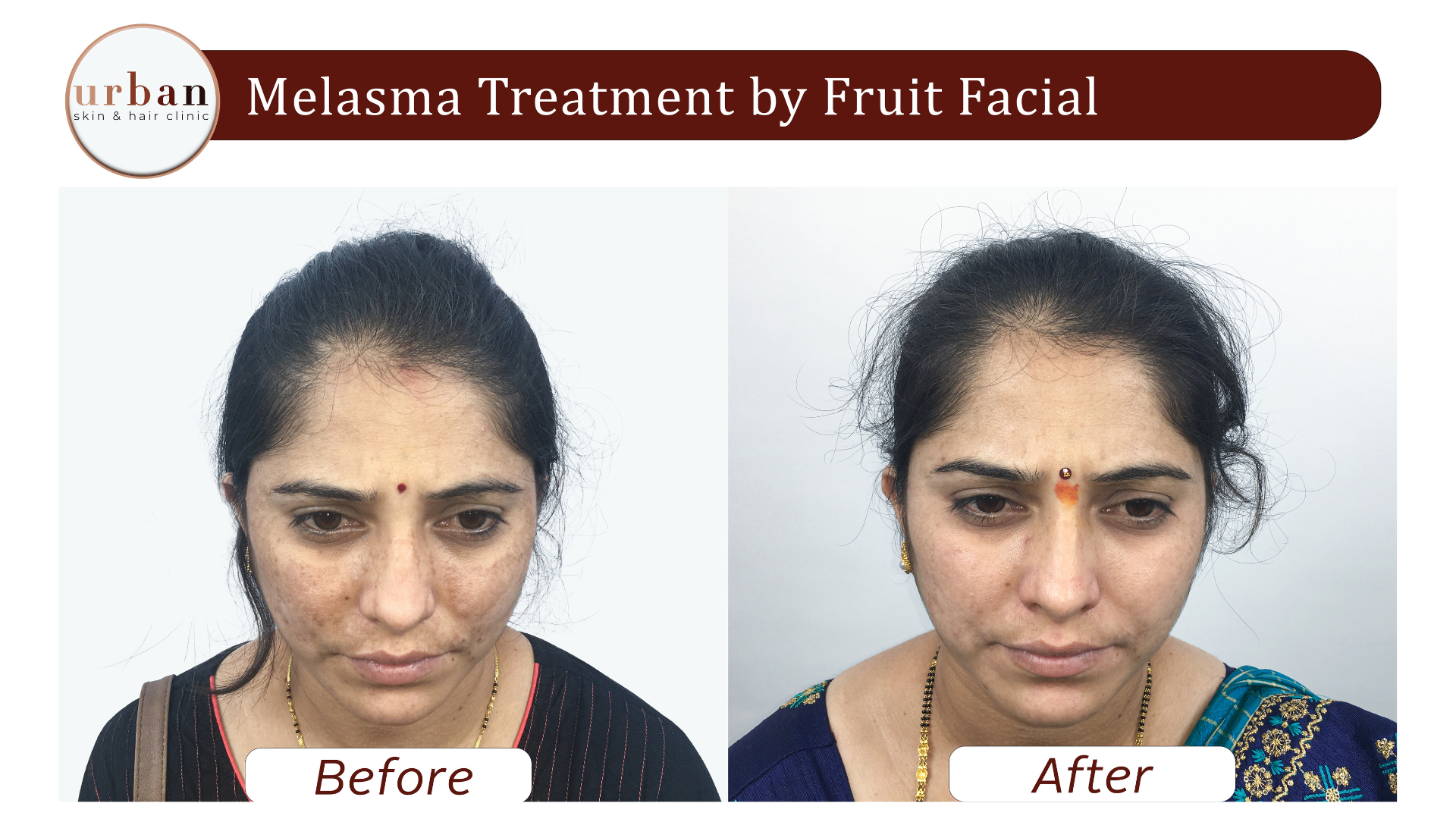
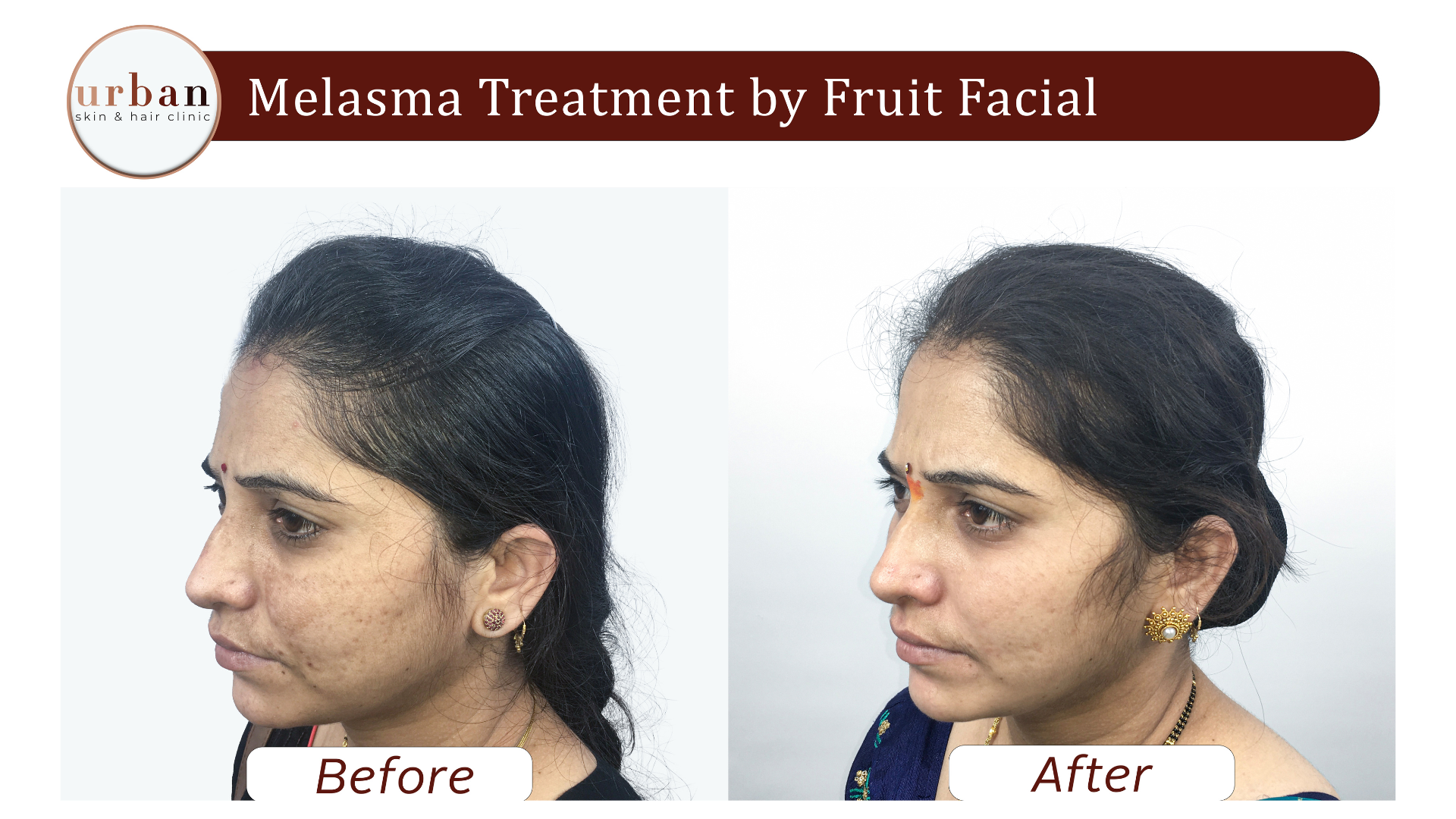
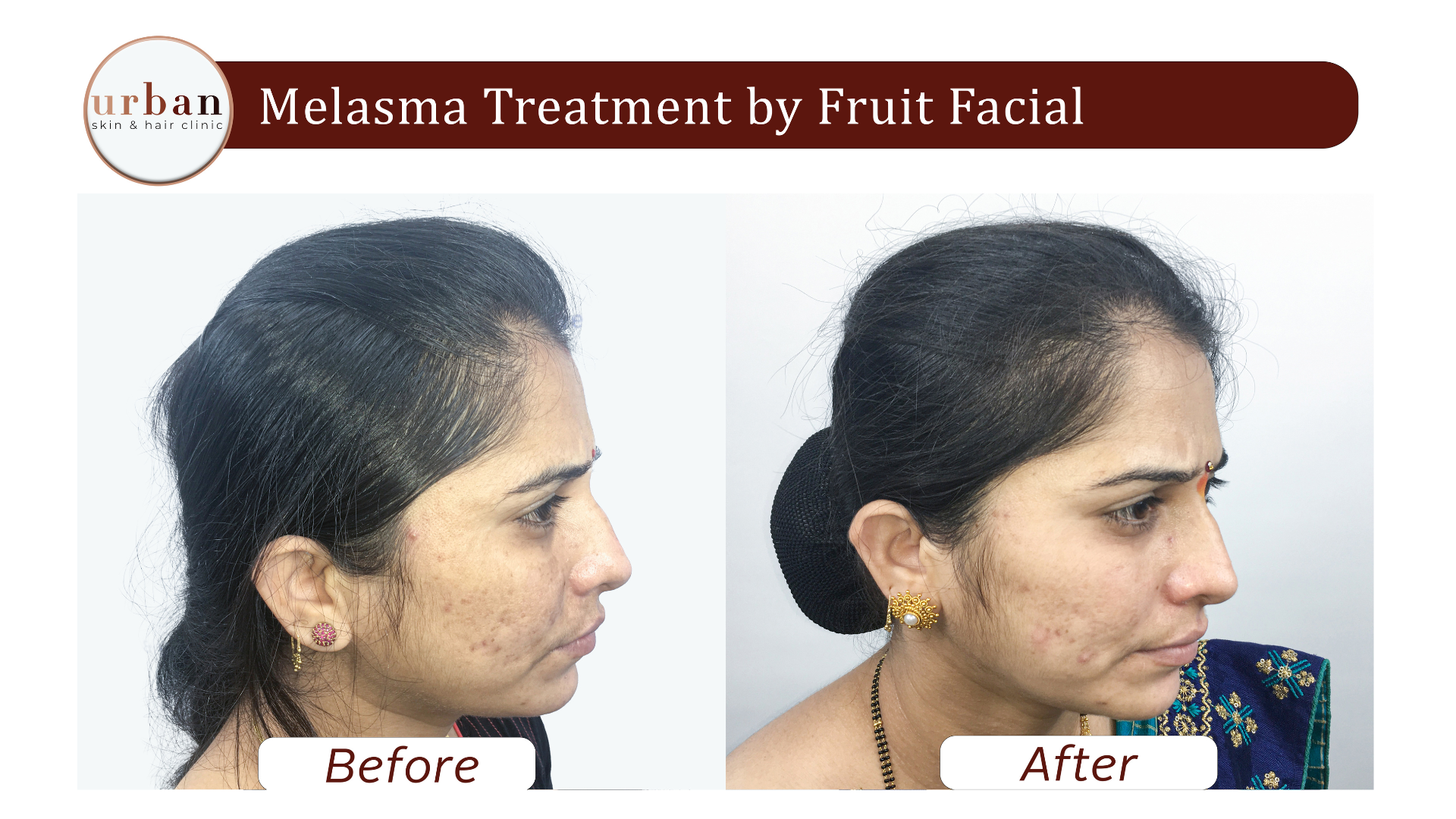
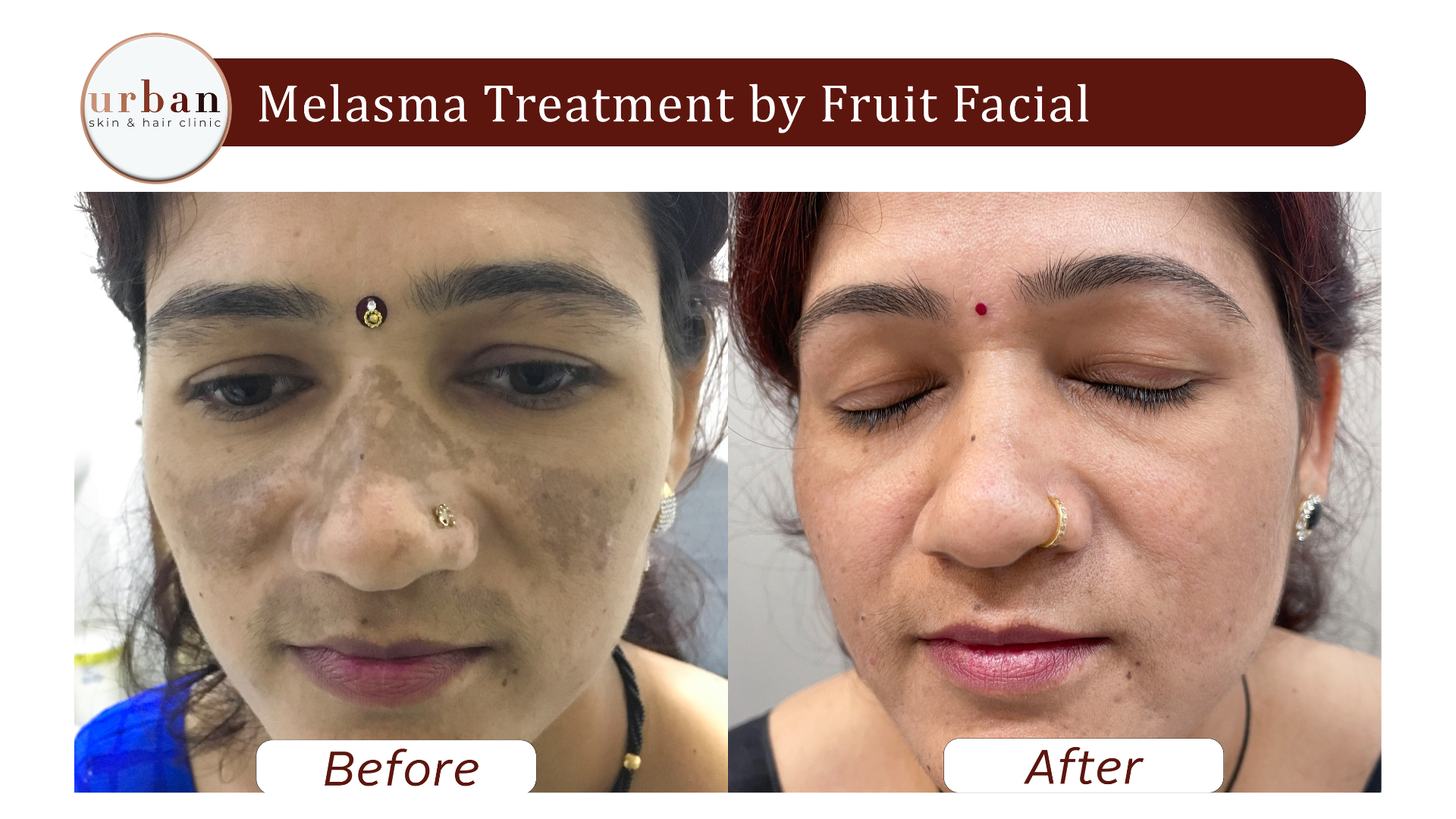
Benefits of Melasma Treatment
Experience the transformative benefits of expert melasma treatment at Urban Skin Hair Clinic (USHC):
Even Skin Tone: Fade stubborn brown-gray patches on cheeks, forehead, and upper lip for uniform complexion.
Reduced Pigmentation: Inhibit melanin overproduction with topicals like hydroquinone or triple combinations for visible lightening.
Smoother Texture: Improve skin clarity and radiance, minimizing blotchiness from hormonal or sun-induced changes.
Boosted Confidence: Restore balanced facial skin to enhance self-esteem and daily comfort.
Long-Term Maintenance: Prevent recurrence with sunscreens and oral tranexamic acid for sustained results.
Popular Treatments for Melasma
How To Prevent Melasma?
Follow these dermatologist-recommended strategies to prevent melasma by minimizing UV exposure, heat triggers, and hormonal fluctuations that darken patches:
Apply broad-spectrum tinted sunscreen (SPF 50+ with iron oxides) daily, reapplying every 2 hours outdoors or after sweating, even on cloudy days.
Limit peak sun hours (10 AM-4 PM), wear wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and protective clothing to block UVA, UVB, and visible light.
Use gentle, antioxidant-rich skincare with niacinamide, vitamin C, or azelaic acid to inhibit melanin without irritation.
Avoid hormonal triggers like certain birth controls; manage stress and heat exposure through diet, exercise, and cool environments.
Maintain consistency year-round, as prevention outperforms treatment for this recurrent condition.
For personalized plans at Urban Skin Hair Clinic (USHC), consult experts early to safeguard your even skin tone.
Consult a Specialist Today
Many of the techniques for preventing pimples may also be used to cure them. Eating well, avoiding stress, and not popping pimples may help manage zits and reduce their length. If your acne continues despite your best efforts, you may need prescription acne treatment. Consult your dermatologist if you’re uncertain about treatment.
FAQ's
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes dark, brown, or gray patches, usually on the face. It’s often triggered by sun exposure, hormones, or genetics.
Melasma is mainly caused by overproduction of melanin due to sun exposure, pregnancy, birth control pills, thyroid issues, or certain medications.
Melasma is not always permanent. With proper treatment, sun protection, and lifestyle care, the patches can fade, but they may return with triggers.
Treatments include topical creams (like hydroquinone), chemical peels, laser therapy, microneedling, and strict sun protection. A dermatologist can recommend the best plan.
Yes. Using sunscreen daily, avoiding long sun exposure, wearing hats, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help prevent melasma from worsening or recurring.
Symptoms of Melasma?
The primary symptom of melasma is the appearance of dark, irregular patches or hyperpigmentation on the skin. These patches are typically brown or gray-brown in color and may have irregular borders. Here are some key symptoms of melasma:
Dark patches: Melasma presents as patches of darker skin coloration, commonly on the face. The patches are usually symmetrical, meaning they appear on both sides of the face, and they can vary in size and shape.
Facial involvement: Melasma predominantly affects the face, particularly the cheeks, forehead, chin, and upper lip. However, it can also occur on other sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the neck and forearms.
Sun-exposed areas: The patches of melasma tend to develop on areas of the skin that are regularly exposed to the sun.
Irregular borders: The borders of the patches are often irregular or poorly defined, giving them a blotchy or mottled appearance.
Cosmetic concern: While melasma does not cause any physical discomfort or pain, it can be a source of cosmetic concern. The noticeable dark patches on the face can affect a person’s self-esteem and quality of life.
Additionally, melasma is not usually accompanied by any physical symptoms, such as itching, irritation, or pain.

Where does Melasma Develop on the Body?
Melasma primarily develops on the face, particularly in sun-exposed areas. The most common areas affected by melasma include:
Cheeks: Melasma patches can appear on the cheeks, often on the upper cheekbones or along the cheek area.
Forehead: The forehead is another common site for melasma patches. They can occur across the forehead or concentrated in specific areas.
Upper lip: Melasma can affect the upper lip, resulting in dark patches or a “mustache-like” appearance.
Chin: Some individuals may develop melasma patches on the chin or around the mouth area.
Occasionally, melasma can also appear on the jawline, neck, arms, or other parts of the body that are exposed to sunlight. In addition to these facial areas, melasma can also occur on other sun-exposed parts of the body, although it is less common. It is important to note that melasma patches are typically symmetrical, meaning they appear on both sides of the face or body. The patches can range in color from light brown to dark brown or grayish brown, and they may have an indistinct border.
Are there complications/side effects of the medications
Melasma can be identified through a visual examination by a dermatologist, who will closely inspect the affected areas, typically the face, and neck. Melasma can be identified through a visual examination of the skin by a dermatologist or healthcare professional. Here are some key aspects that help in identifying melasma:
Dark, irregular patches: Melasma is characterized by the presence of dark, irregular patches or hyperpigmentation on the skin. These patches are typically brown or gray-brown in color.
Symmetrical distribution: Melasma often appears symmetrically on both sides of the face. The patches usually occur in similar locations and have a mirrored pattern.
Commonly affected areas: Melasma commonly affects sun-exposed areas of the face, including the cheeks, forehead, chin, and upper lip. However, it can also occur in other parts of the body, although less frequently.
Border characteristics: The borders of melasma patches may be irregular or poorly defined. The patches often have a blotchy or mottled appearance.
During the evaluation, the healthcare professional may use additional tools or techniques to aid in the identification and assessment of melasma, such as:
- Wood’s lamp examination: Wood’s lamp emits ultraviolet light that helps to determine the depth of the pigmentation in the layers of the skin. This examination can help distinguish between different types of melasma, such as epidermal, dermal, or mixed.
- Skin biopsy: In rare cases where the diagnosis is uncertain, a skin biopsy may be performed. A small sample of skin is taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of melasma and rule out other skin conditions.
Dermal melasma has a light brown or bluish color with a blurry border, while epidermal melasma appears dark brown and has a well-defined border. Mixed melasma, which is the most common type, presents as a combination of bluish and brown patches.
What causes melasma?
Melasma is believed to be caused by a combination of factors, including exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, hormonal changes, and genetic predisposition. Exposure to sunlight and other sources of UV radiation, such as visible light and heat, can trigger the development of melasma. Genetic factors may also influence the development of melasma. A family history of melasma increases the likelihood of developing the condition. However, more research is needed to fully understand the genetic aspects of melasma.
Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations and imbalances play a significant role in melasma. The condition is commonly associated with hormonal changes during pregnancy, which is why it is often referred to as “the mask of pregnancy.” Hormonal contraceptive use, such as birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy, can also trigger melasma. In some cases, melasma may improve after pregnancy or discontinuation of hormonal contraceptives.
Sun exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a major trigger for melasma. Sun exposure stimulates the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Melasma patches tend to darken when exposed to sunlight, and unprotected sun exposure can worsen the condition. Individuals with melasma should take precautions to protect their skin from the sun, such as using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade.
Genetic predisposition: There appears to be a genetic component to melasma, as it tends to run in families. If you have a family history of melasma, you may be more susceptible to developing the condition.
Other factors: Other factors that may contribute to the development of melasma include certain medications (such as antiepileptics and photosensitizing drugs), cosmetics or skincare products that irritate the skin, and heat exposure.

Is there a cure for melasma?
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, there is no cure for melasma. However, various treatments are available to manage the condition and improve the appearance of the skin. The goal of melasma treatment is to reduce the amount of pigment that your body produces and even out your skin tone.
Here are some common treatment approaches for melasma
These include creams, gels, or lotions that are applied directly to the skin. Commonly used topical agents for melasma include hydroquinone, retinoids, corticosteroids, and azelaic acid. These substances help to lighten the skin and reduce the production of melanin. Topical treatments are often the first-line approach and may be used alone or in combination.
Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to the skin, which causes exfoliation and the removal of the top layers of skin. This can help to lighten melasma patches and promote skin renewal. Different types of chemical peels, such as alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peels, may be used based on the individual’s needs and the severity of melasma.
This procedure uses a device to gently exfoliate the skin, removing the outer layer and promoting skin rejuvenation. Microdermabrasion can help to improve the appearance of melasma by reducing pigmentation and encouraging new, healthier skin growth.
Laser treatments, such as fractional laser resurfacing or Q-switched Nd: YAG laser, can be effective in targeting and lightening melasma patches. These treatments work by delivering laser energy to the affected areas, breaking down the excess pigmentation, and stimulating collagen production.
IPL uses broad-spectrum light to target pigmented areas of the skin. It can help to lighten melasma patches and improve overall skin tone and texture.
Dermatologists diagnose melasma through a combination of medical history and visual examination. They evaluate the characteristic appearance of the skin, looking for dark, irregular patches or hyperpigmentation. A Wood’s lamp examination may be used to assess the depth of pigmentation. In rare cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. Consulting a dermatologist is important for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
In some cases, dermatologists may also recommend additional tests or examinations to rule out other conditions and evaluate any underlying factors associated with melasma. For instance, they might conduct thyroid checks as there seems to be an association between thyroid disease and melasma.
Are there complications/side effects of the medications
While using topical medications for melasma, such as hydroquinone or retinoids, there is a possibility of experiencing side effects or complications. Some individuals may notice skin irritation, including redness, itching, or peeling in the treated areas. This is typically mild and temporary and can be managed by adjusting the application frequency or using moisturizers. In rare cases, changes in skin pigmentation may occur, with some areas becoming darker (hyperpigmentation) or lighter (hypopigmentation). It’s important to closely monitor the skin’s response and inform your dermatologist if any significant changes occur. Additionally, certain medications can increase photosensitivity, making the skin more prone to sunburn. It’s crucial to apply sunscreen and protect your skin from excessive sun exposure. While uncommon, allergic reactions can happen, presenting as severe itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention. To ensure the safe and effective use of medications, it’s essential to consult with a dermatologist, follow their recommendations, and communicate any concerns or side effects that arise.