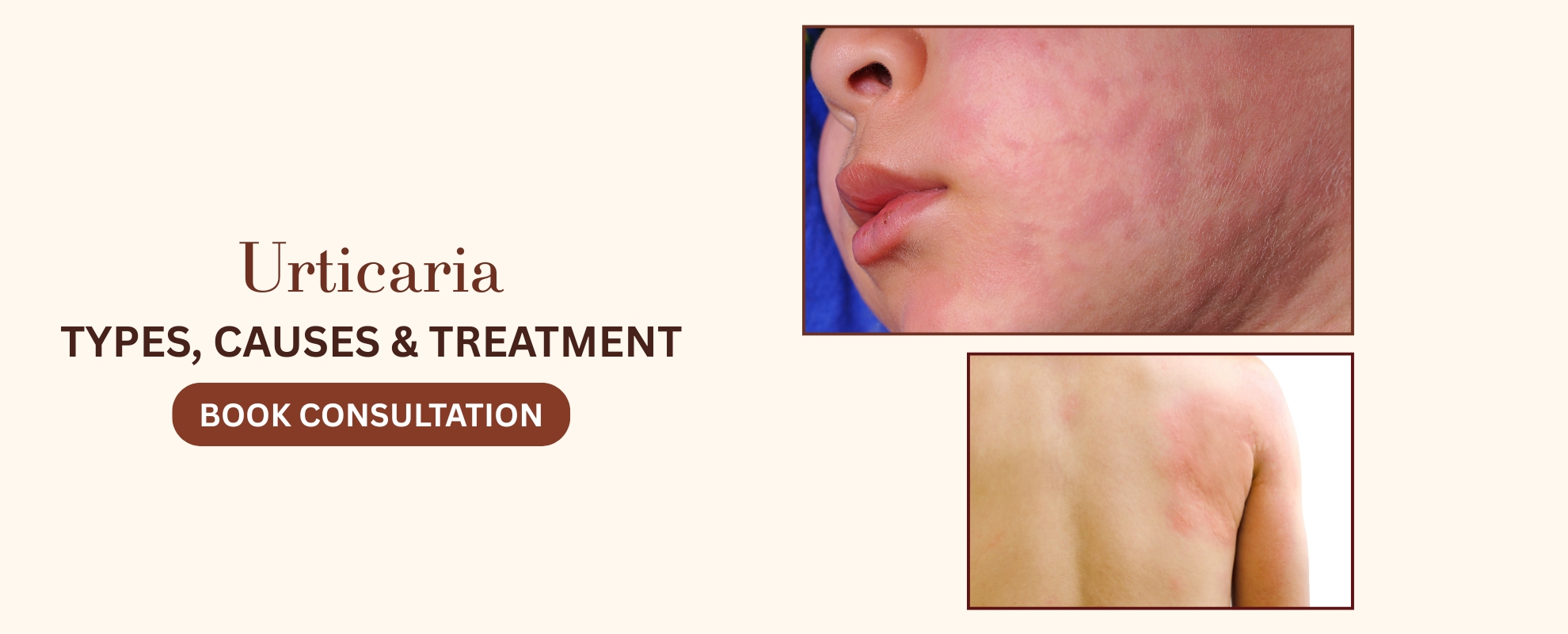
Clear, Healthy & Confident Skin with Urticaria Treatment
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by the sudden appearance of raised, itchy, and often red or pale welts or bumps on the skin. These welts, or wheals, can vary in size and shape, ranging from small dots to larger patches.
Urticaria can occur anywhere on the body and may change in location and size over time.
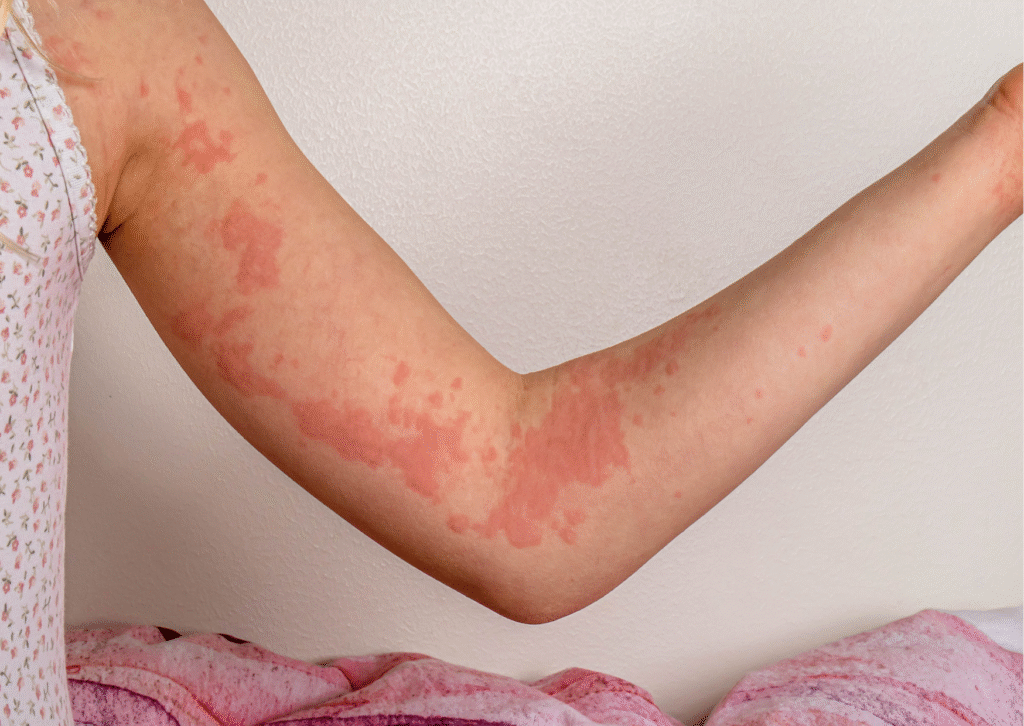
Symptoms and Causes
Signs & Symptoms Of Urticaria
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by raised, itchy, and often red welts or bumps on the skin. The symptoms of urticaria can vary in appearance, duration, and severity. Here are the key symptoms associated with urticaria:
- Raised Welts Or Bumps: The primary symptom of urticaria is the presence of raised, swollen areas on the skin. These welts or bumps are usually round or oval-shaped and can vary in size from small dots to larger patches. They may appear pale or red, and their borders may be well-defined or irregular.
- Itching: Urticaria typically accompanies intense itching or a burning sensation in the affected areas. The itching can range from mild to severe and may significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
- Rapid Onset And Resolution: Urticaria often appears suddenly and may resolve within a few hours or persist for several days before fading away. The welts or bumps can change in size, shape, and location over time.
- Skin Redness: The affected areas of the skin may appear red or flushed, especially around the raised welts or bumps.
- Swelling: In some cases, urticaria may cause swelling, also known as angioedema, in deeper layers of the skin. Angioedema commonly affects the lips, eyelids, face, hands, feet, or genitalia and can sometimes cause pain or a tingling sensation.
- Triggers: Urticaria can be triggered by various factors, including allergic reactions to certain foods, medications, insect bites, pollen, or latex. Other triggers may include physical factors such as pressure, heat, cold, exercise, or sunlight. In some cases, urticaria may occur without an identifiable trigger, referred to as idiopathic urticaria.

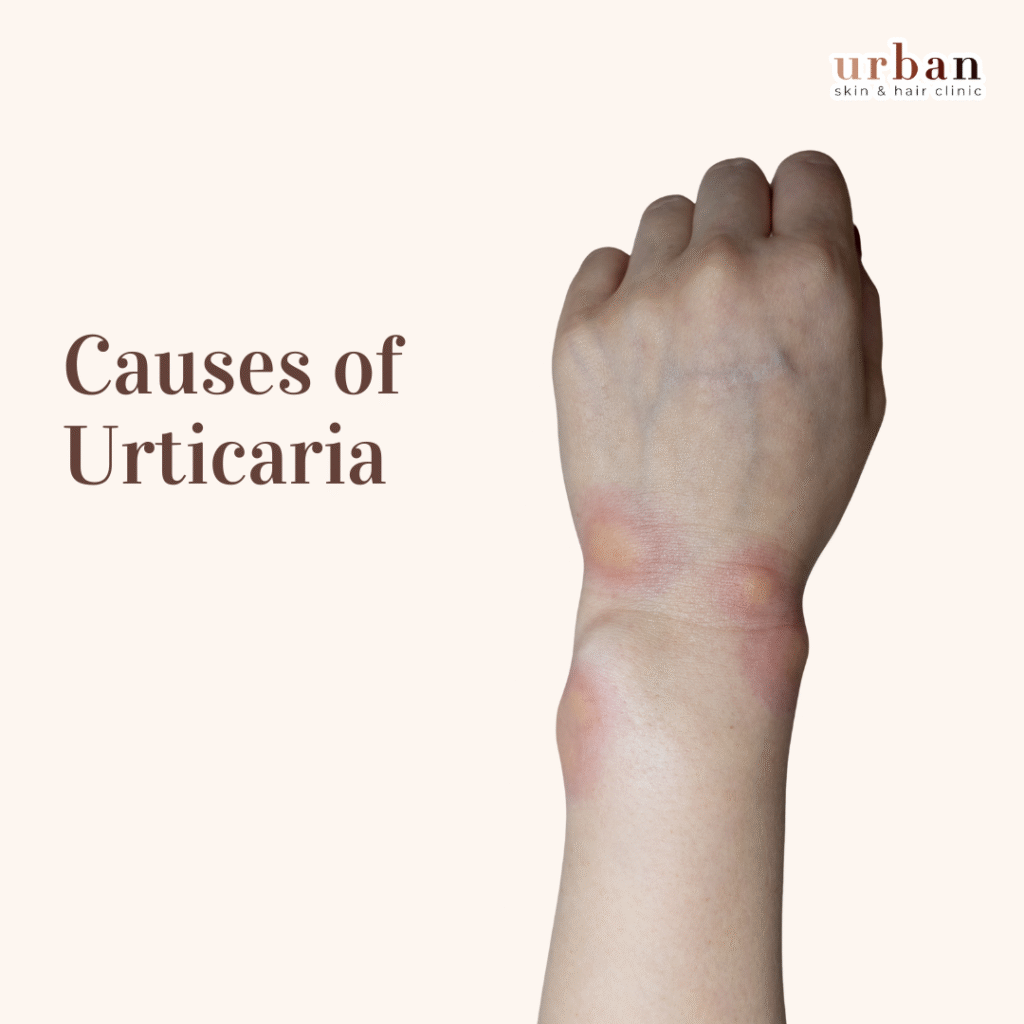
What are the Causes Of Hives/Urticaria?
Urticaria, or hives, can be caused by various factors, including.
- Allergic Reactions: Allergies to certain substances can trigger urticaria. (such as antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Physical Triggers: Urticaria can be induced by physical factors such as pressure on the skin
- Infections: Certain infections can cause urticaria or trigger its onset. These may include viral infections like the common cold, influenza, hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis, and bacterial infections.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Some autoimmune conditions, such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or thyroid disorders, can be associated with chronic urticaria.
- Stress or Emotional Triggers: Emotional stress, anxiety, or heightened emotional states can sometimes trigger or worsen urticaria.
- Unknown causes: In some cases, the exact cause of urticaria remains unknown and is referred to as idiopathic urticaria.

What are the Types Of Urticaria
- Acute Urticaria: is the most common form of urticaria and typically lasts less than six weeks. It can be triggered by various factors such as allergic reactions to certain foods, medications, insect bites or stings, infections, and exposure to certain chemicals.
- Chronic Urticaria: Chronic urticaria lasts for more than six weeks and can persist for months or even years. The exact cause of chronic urticaria is often unknown, but it may be related to autoimmune reactions, thyroid disorders, or other underlying health conditions.
- Physical Urticaria: This type of urticaria is triggered by physical stimuli such as pressure, cold, heat, sunlight, exercise, or vibration. Examples include dermatographism (hives that appear after scratching the skin), cold urticaria (hives triggered by exposure to cold temperatures), and cholinergic urticaria (hives induced by sweating or an increase in body temperature).
- Dermatographic Urticaria: Also known as dermatographism, this condition is characterized by hives that appear after firmly stroking or scratching the skin. The hives typically develop within a few minutes at the site of the skin stimulation.
- Aquagenic Urticaria: This rare form of urticaria is triggered by contact with water, regardless of its temperature. Hives usually develop within a few minutes after exposure to water, and symptoms can range from mild itching to severe allergic reactions.
- Solar Urticaria: Solar urticaria is a type of physical urticaria triggered by exposure to sunlight or other types of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. It results in the rapid onset of hives and can be associated with symptoms such as itching, burning, and swelling.
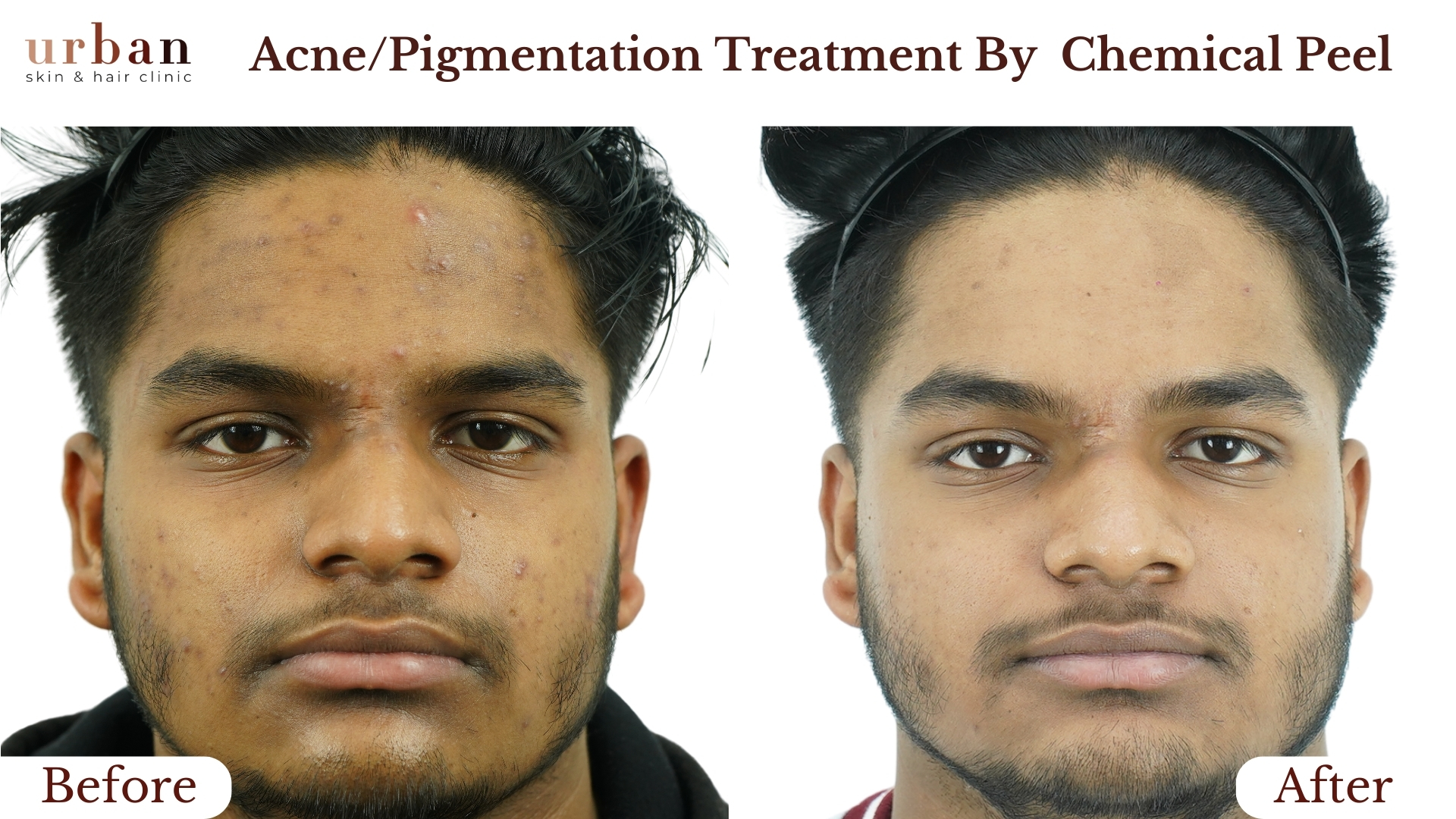
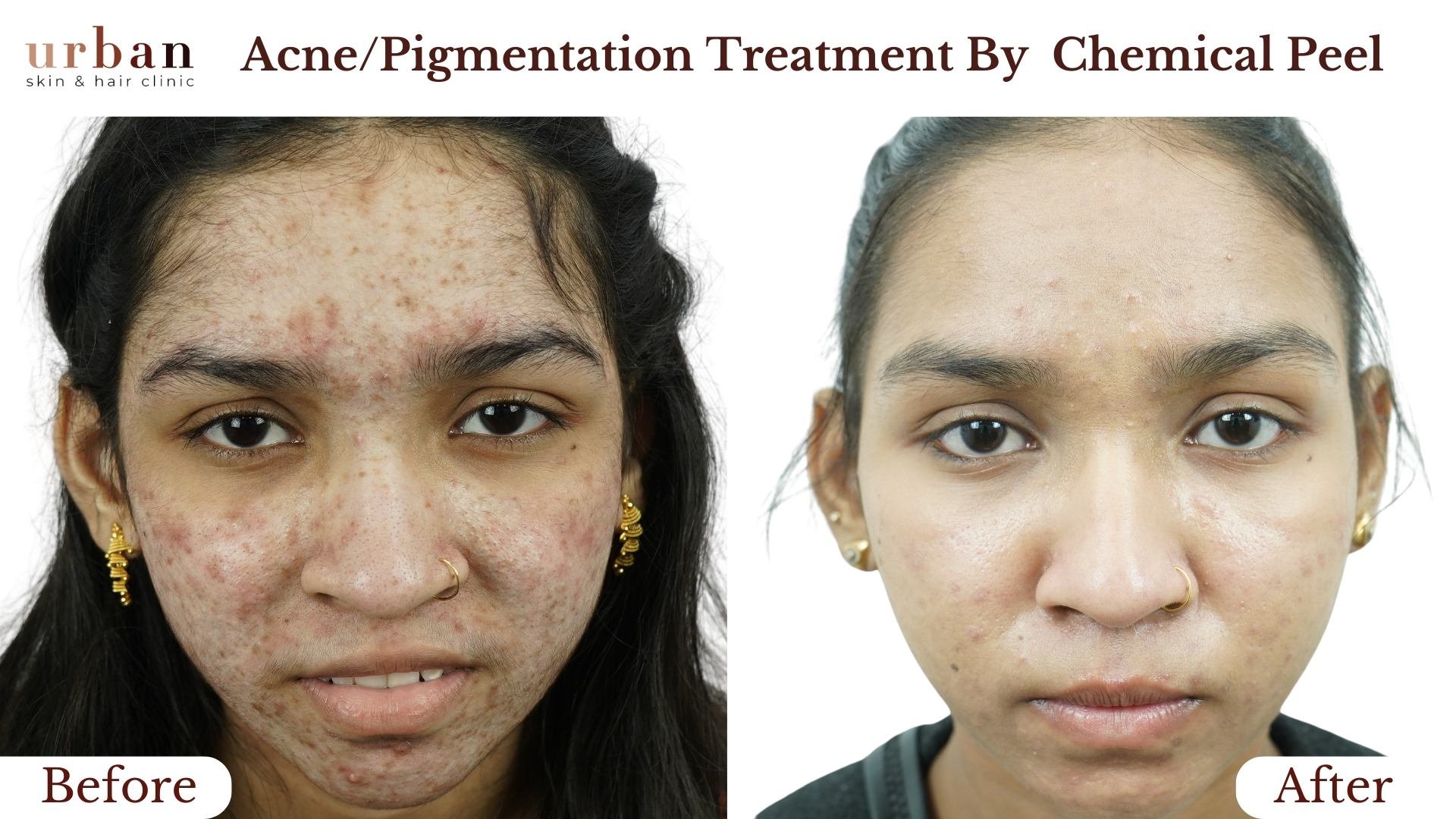
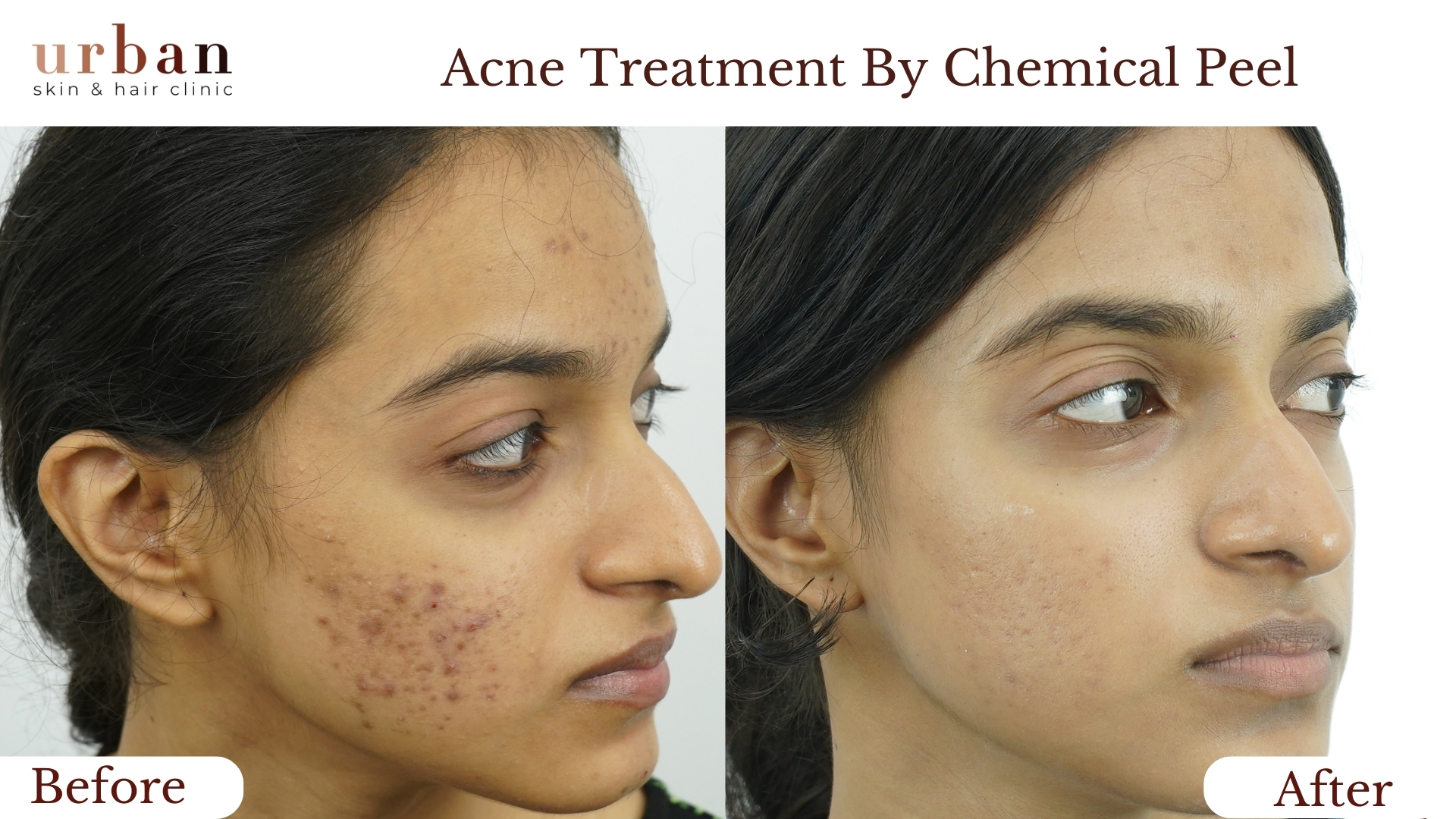
Urticaria Treatment Results Before & After


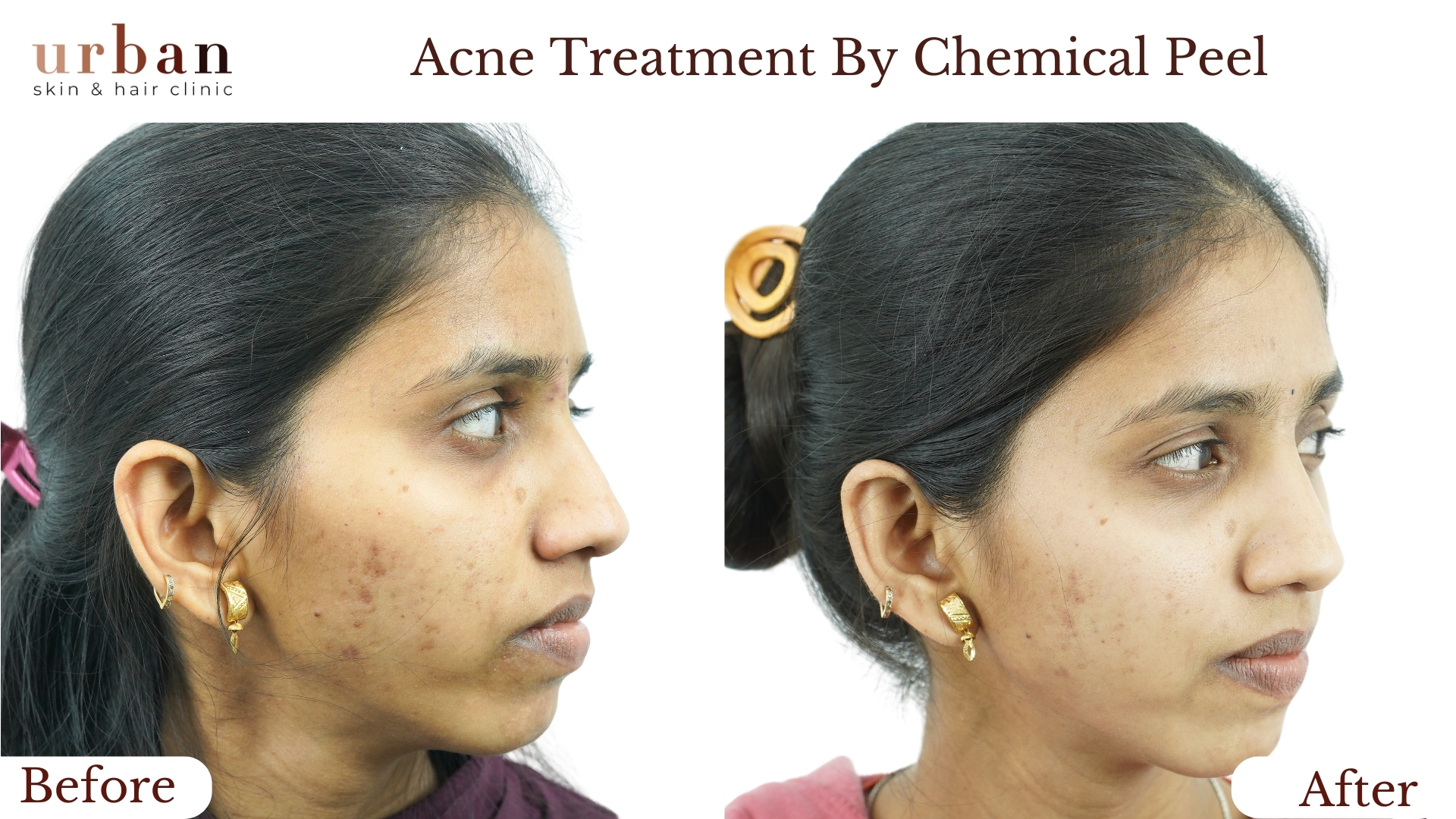
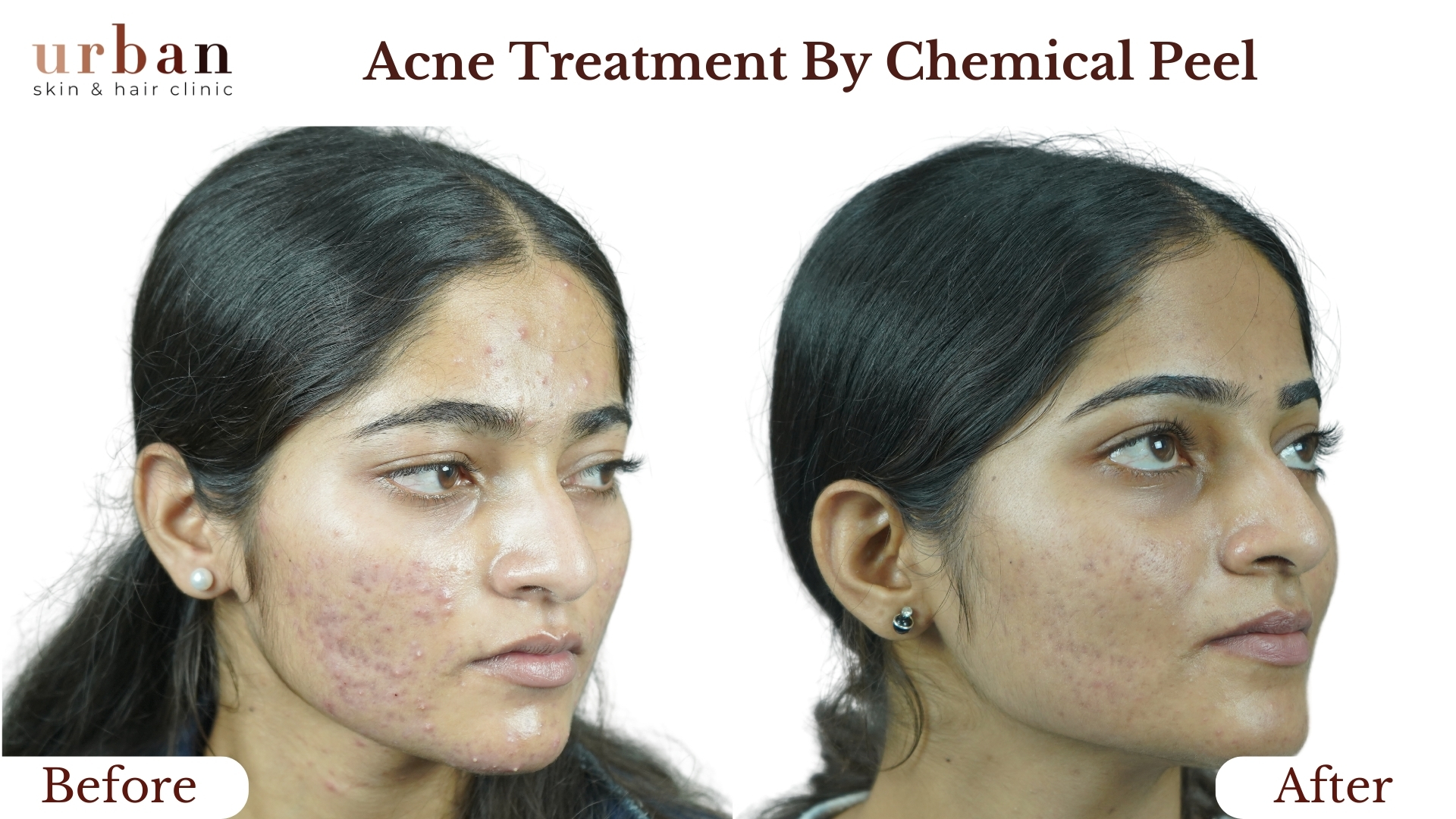
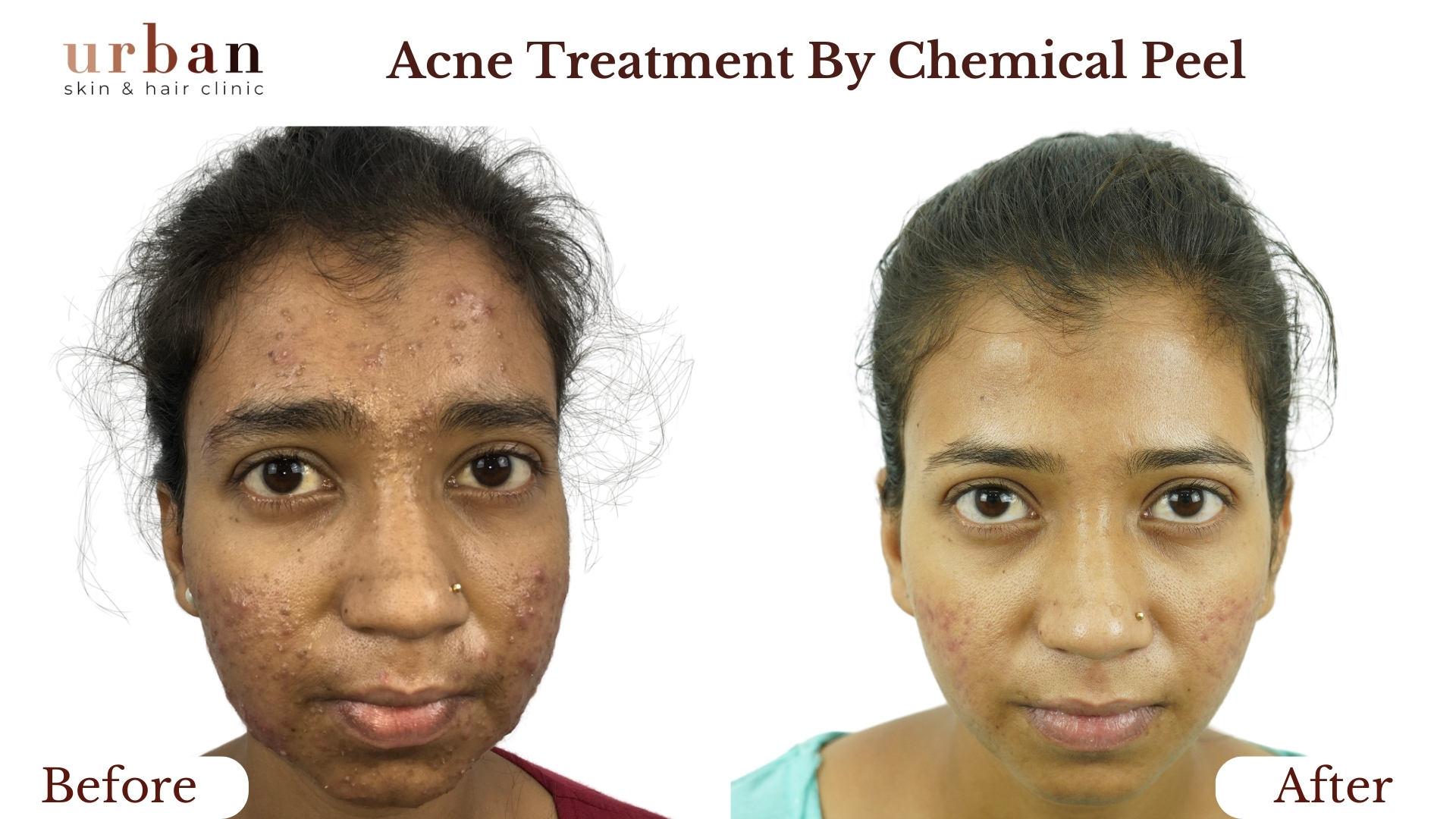
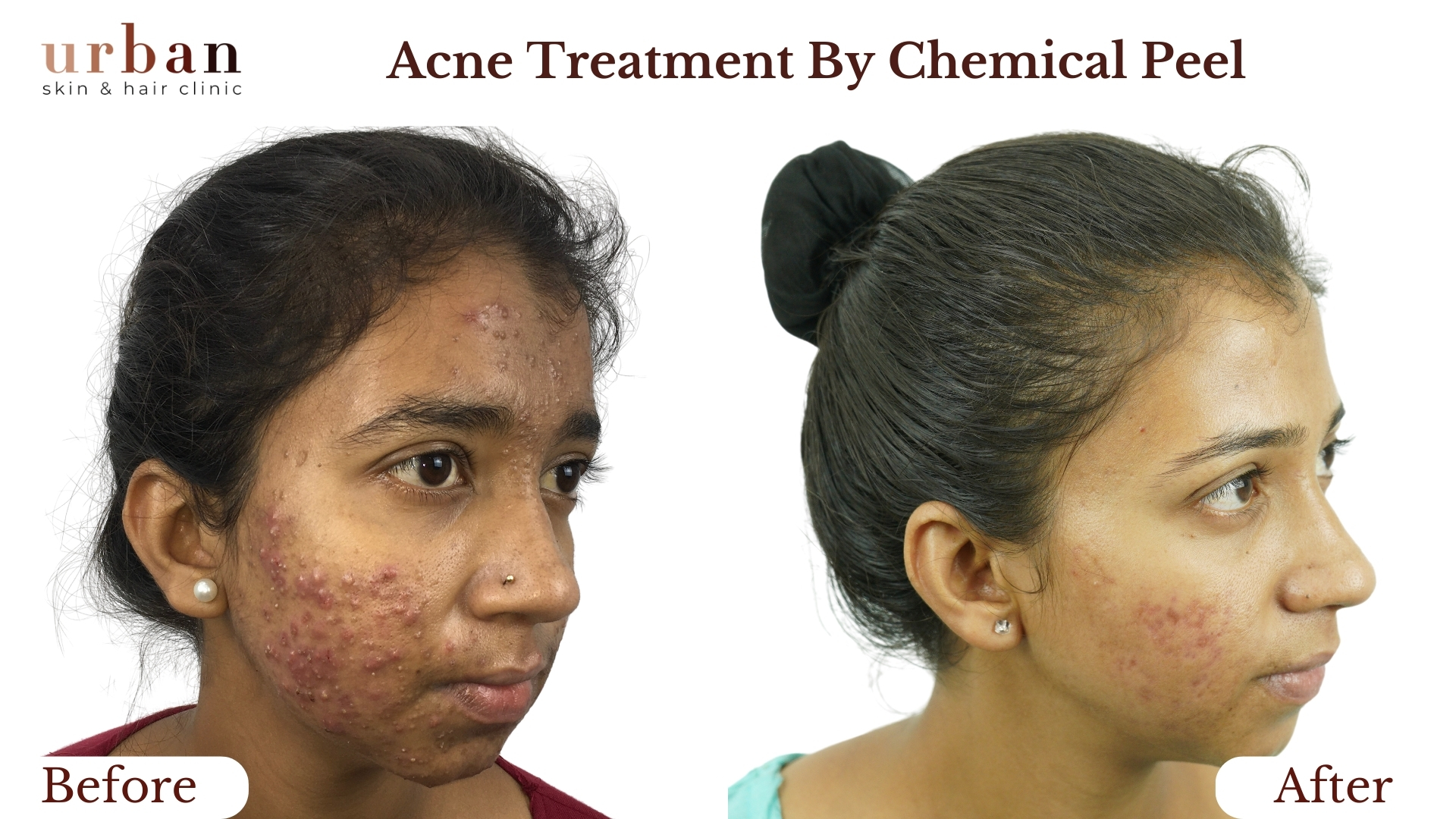

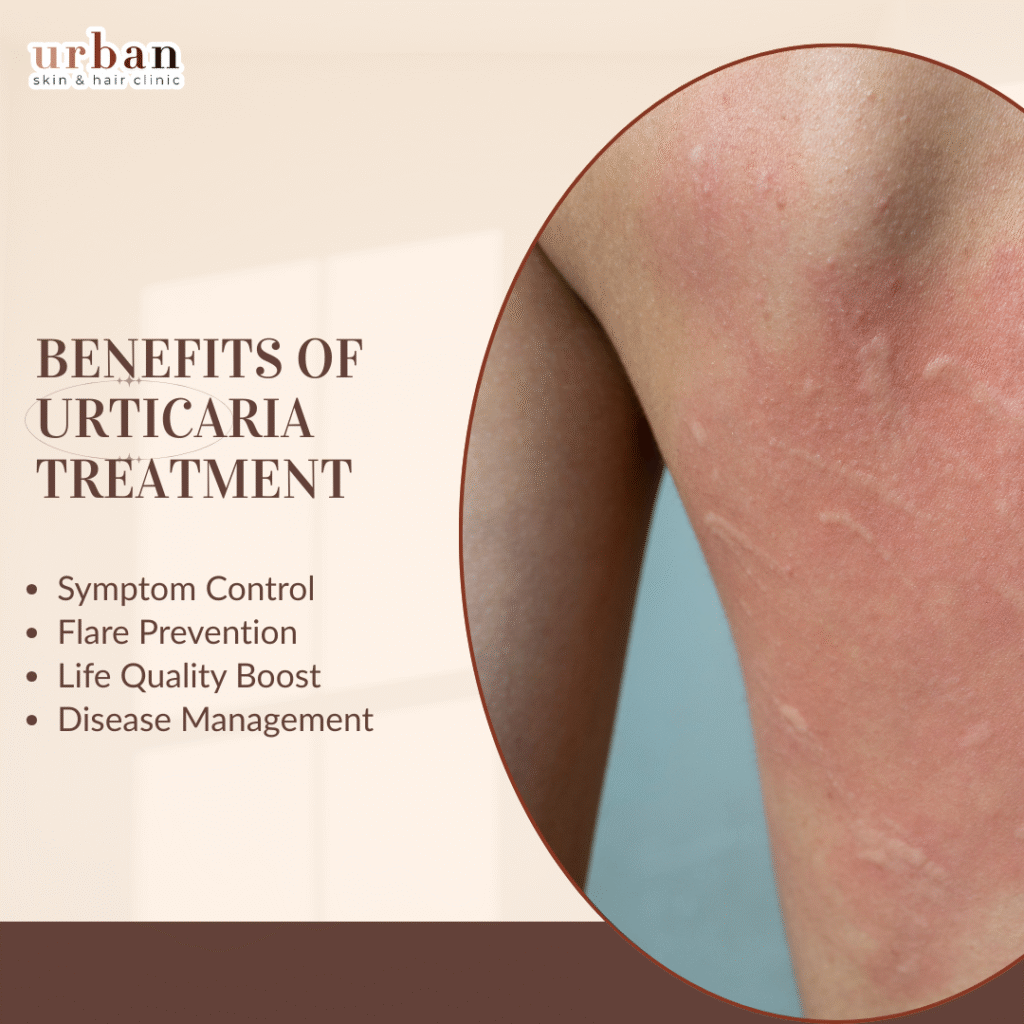
Benefits of Urticaria Treatment
Urticaria treatment provides rapid relief from itchy hives and swelling, improving daily comfort and quality of life.
Symptom Control
Antihistamines like cetirizine or fexofenadine reduce wheals and pruritus in 70-90% of cases within hours by blocking histamine release.
Flare Prevention
Second-generation H1 blockers at updose achieve complete control in 50% of chronic cases, minimizing recurrence over months.
Life Quality Boost
Cuts Dermatology Life Quality Index scores dramatically (from 18 to <2), easing sleep disruption and emotional distress.
Disease Management
Omalizumab or cyclosporine controls refractory urticaria in 60-80%, offering sustained remission without steroids.
Popular Treatments for Urticaria
How To Prevent Urticaria?
Urticaria prevention involves identifying and avoiding personal triggers like allergens, pressure, or temperature extremes to minimize hive outbreaks.
Avoid Known Triggers
Track symptoms in a diary to spot culprits (foods like shellfish, NSAIDs, pollen); eliminate them promptly for 80% flare reduction.
Wear Loose Clothing
Opt for breathable, non-tight fabrics to prevent dermographism or pressure hives from friction on skin folds.
Temperature Control
Stay cool with fans/AC, avoid hot showers/spicy foods for cholinergic urticaria; cover skin in cold/AC environments.
Stress Management
Practice relaxation like meditation, as anxiety worsens histamine release; combine with daily antihistamines preemptively.
Consult a Specialist Today
Many of the techniques for preventing pimples may also be used to cure them. Eating well, avoiding stress, and not popping pimples may help manage zits and reduce their length. If your acne continues despite your best efforts, you may need prescription acne treatment. Consult your dermatologist if you’re uncertain about treatment.
FAQ's
Urticaria results from allergic reactions (foods, drugs), physical stimuli (pressure, cold), infections, or idiopathic factors in chronic cases lasting over 6 weeks.
No, hives spread via immune responses, not person-to-person; they appear suddenly as red wheals that blanch under pressure.
Acute urticaria resolves in hours to 6 weeks; chronic persists >6 weeks, often daily, with 50% resolving in 1 year
Yes, emotional stress worsens cholinergic urticaria through heat/sweat; relaxation techniques help alongside antihistamines.
Seek care for swelling in throat/mouth, breathing difficulty, or dizziness indicating anaphylaxis requiring epinephrine.