
WHAT IS SKIN TAN?
Skin tan refers to the process in which the skin becomes darker in color due to exposure to the sun. When the skin is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun, the body produces melanin, a pigment that gives color to the skin . Melanin acts as a natural defence mechanism to protect the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation . As a result, the skin becomes darker, or tanned, as a means of sun protection.
Getting a suntan usually occurs when someone spends time outdoors and their skin is exposed to the sun’s rays. It can result in a pleasant brown color of the skin and is often associated with spending time at the beach or in sunny locations.
It’s important to note that excessive sun exposure can damage the skin and increase the risk of skin cancer. It is recommended to practice safe sun habits, such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak sun hours.
Type of TAN ?
There are different types of tan based on how the skin gets tanned. Here are a few common types:
Natural Tan: This is the most common type of tan that occurs when the skin is exposed to sunlight. Natural tanning happens when the skin produces melanin as a response to UV radiation from the sun. It developed gradually over time by spending short periods in the sun or using a gradual self-tanning product. A base tan is often sought before going on a vacation or spending extended time outdoors to provide some initial protection against sunburn.
Artificial Tan: An artificial tan refers to a tan that is achieved through the use of artificial methods instead of natural sunlight. This can include self-tanning lotions, sprays, or creams that contain DHA (dihydroxyacetone). DHA interacts with the dead skin cells on the surface of the skin and temporarily darkens them, creating the appearance of a tan. Tanning beds or sun lamps that emit UV radiation can also be used to obtain an artificial tan.
Sunburn Tan: Sunburn is a type of tan that occurs when the skin is overexposed to UV radiation. A sunburn tan occurs when the skin gets burned from excessive sun exposure. Sunburned skin becomes red, inflamed, and painful. Over time, sunburn may fade into a tan, but it’s important to note that sunburn is harmful to the skin and can increase the risk of skin damage and skin cancer.
It’s important to remember that prolonged exposure to the sun without proper protection or excessive use of tanning beds can increase the risk of skin damage and other health issues. Always practise safe sun habits and use sunscreen when spending time outdoors.
Types And Classification Of Acne

What is Sunburn ?
unburn is a condition characterised by inflammation and redness of the skin that occurs due to overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, typically from the sun. It is a result of direct DNA damage caused by UV radiation, triggering an inflammatory response in the skin tissue. When the skin is exposed to excessive UV radiation, the body’s defence mechanism is activated, leading to an increase in blood flow to the affected area. This causes the skin to become red, sensitive, and painful to the touch. Sunburn usually appears within a few hours of sun exposure and may take several days to fade.
The severity of sunburn can vary depending on factors such as the intensity of the UV radiation, duration of exposure, and individual skin type. Mild sunburn may cause redness, discomfort, and slight peeling, while more severe cases can result in blistering, swelling, and intense pain.
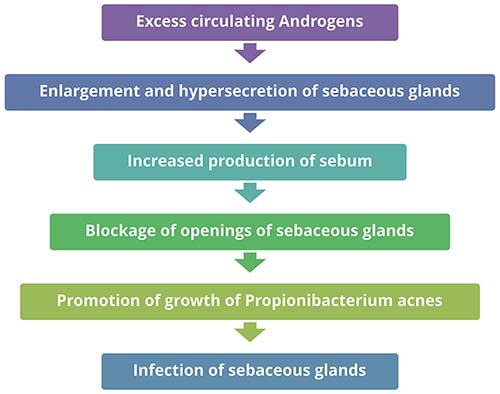
Common Causes Of Acne Vulgaris
Why does tanning happen?
Tanning occurs as a result of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The body’s natural response to UV radiation is to produce more melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color and helps protect it from further damage. Melanin absorbs UV radiation and interacts with skin cells to create a tan appearance.
The amount of melanin produced in response to UV radiation is influenced by an individual’s skin color, genetics, and history of sun exposure. People with fair skin tend to produce less melanin and burn more easily, while people with darker skin produce more melanin and tend to tan more easily
How do you know if you have a tan?
Change in Skin Color: Tanning occurs when the skin produces more melanin, a pigment that darkens the skin. If you have a tan, you may notice a darker shade or a bronze/brownish color on your skin.
Sun-Exposed Areas: Tanning usually occurs in areas of the body that are exposed to the sun. If you’ve spent time outdoors or in a tanning bed without proper protection, the exposed areas such as the face, arms, legs, or shoulders are more likely to develop a tan.
Contrast with Untanned Skin: If you have a tan, you may notice a noticeable contrast between your tanned skin and areas that haven’t been exposed to the sun. For example, your tanned arms may appear darker than your covered torso.
Gradual Development: Tans usually develop gradually over time. If you’ve been spending time in the sun or using tanning methods, you might notice a gradual darkening of your skin tone.
When to Consult a Doctor for Sun Tan?
Severe Sunburn: If your sun exposure has resulted in a severe sunburn rather than just a tan, with symptoms such as blistering, intense pain, swelling, or fever, it’s important to consult a doctor. Severe sunburns can be a sign of sun poisoning, which may require medical treatment.
Unusual Skin Changes: If you notice any unusual changes in your skin, such as new moles, growths, or spots that are irregular in shape, have uneven borders, change in color, or bleed easily, it’s essential to have them evaluated by a healthcare professional. These could be signs of skin damage or potentially indicate skin cancer.
Allergic Reactions: In some cases, individuals may develop an allergic reaction to sun exposure, known as photosensitivity. If you experience symptoms like a rash, hives, itching, or swelling after being in the sun, it’s recommended to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Persistent or Worsening Skin Issues: If you have pre-existing skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, or rosacea, and notice that sun exposure is aggravating your symptoms or causing flare-ups, it’s advisable to consult a dermatologist for guidance on managing your condition effectively.


