Strong, Healthy & Beautiful Hair Premature Graying Treatment
Premature graying, also known as premature hair whitening, refers to the early onset of gray or white hair before the age of 30.
While gray hair is a natural part of aging, premature graying occurs prematurely and may have underlying reasons beyond chronological age.
Symptoms and Causes
Signs & Symptoms of Premature Graying
While genetics play a significant role in premature graying, several other factors can contribute to the condition:
- Genetic Predisposition: If premature graying runs in your family, there’s a higher likelihood of experiencing it yourself.
- Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt melanin production and accelerate the graying process.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of essential vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin B12 and catalase, can lead to premature graying.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions like thyroid disorders and vitiligo have been linked to premature graying.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and an unhealthy diet can contribute to premature graying.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, toxins, and harmful chemicals may hasten the graying process.


What are the Causes of Premature Graying?
Premature graying occurs when hair loses melanin before age 30 in Asians/Indians, driven by genetics and lifestyle factors depleting melanocyte stem cells.
Genetics: Family history strongly predisposes early graying, as inherited traits control melanin production timing.
Oxidative Stress: Free radicals from pollution, UV rays, or smoking damage melanocytes, accelerating pigment loss.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Low vitamin B12, iron, copper, zinc, or folate impairs melanin synthesis in hair follicles.
Stress: Chronic stress elevates norepinephrine, depleting pigment-producing cells via sympathetic overactivation.
Medical Conditions: Thyroid disorders, vitiligo, pernicious anemia, or autoimmune issues disrupt melanogenesis.

What are the Types of Premature Graying?
Premature graying can be categorized into two main types:
- Premature Canities: This type of premature graying is genetically determined and often runs in families. It is a result of the groladual loss of pigment-producing cells called melanocytes, leading to the loss of hair color.
- Reactive Premature Graying: This type is caused by external factors and may be triggered by various underlying health conditions, lifestyle choices, or environmental factors.
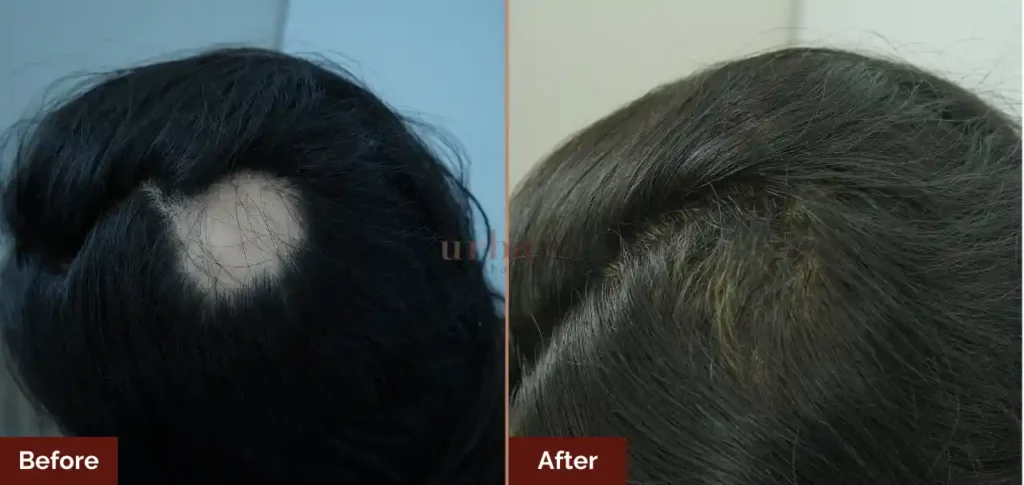
Results Before & After
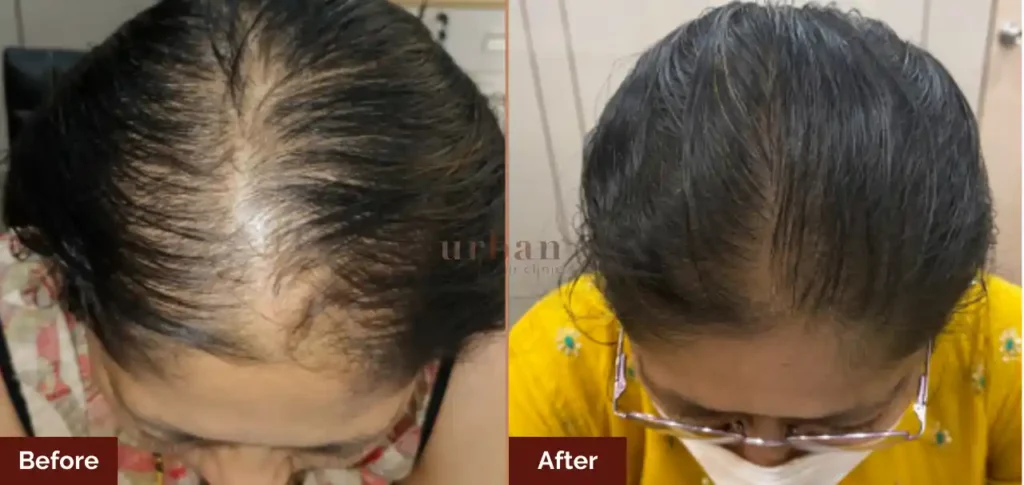

Benefits of Premature Graying Treatment
Targeted treatments at Urban Skin Hair Clinic (USHC) address melanin depletion from oxidative stress or deficiencies, potentially reversing early graying.
Restores Pigmentation: Topical peptides like Greyverse stimulate melanogenesis, achieving >90% color return in months.
Reduces Oxidative Damage: Antioxidants and supplements protect melanocytes, slowing further graying progression.
Improves Hair Health: Biotin and calcium pantothenate strengthen follicles alongside repigmentation.
Boosts Confidence: Natural dark hair recovery enhances appearance without dyes.
Long-Term Reversal: PRP and microneedling promote sustained melanocyte activity and follicle vitality.

Popular Treatments for Premature Graying
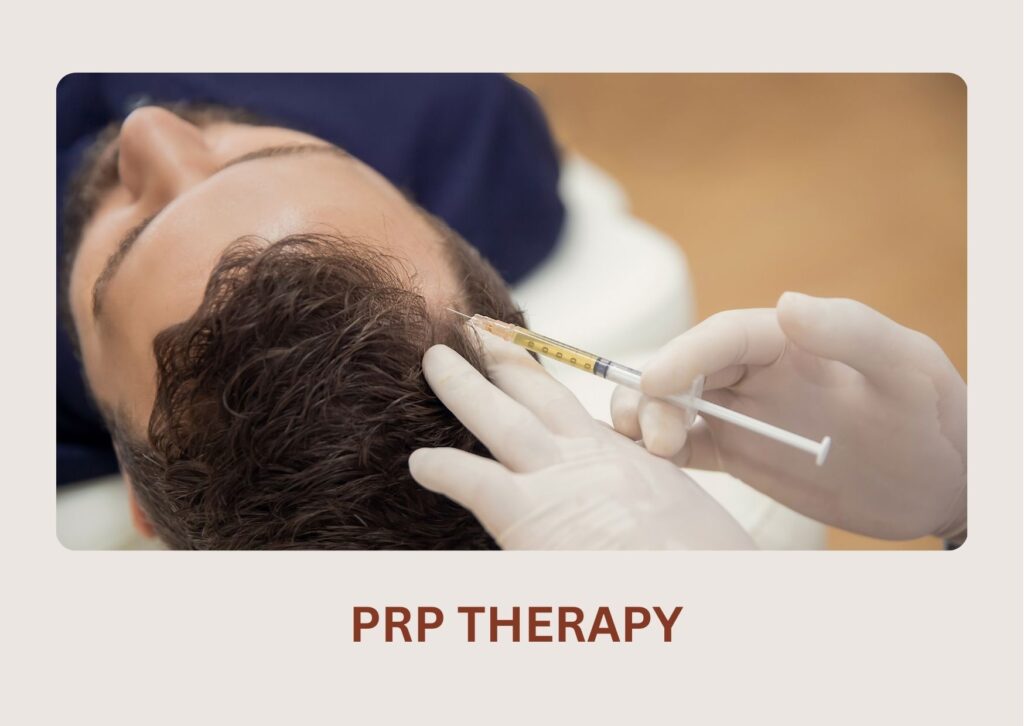
A highly effective treatment where your own growth-factor-rich plasma is injected into the scalp to strengthen follicles, reduce hair fall, and boost regrowth.
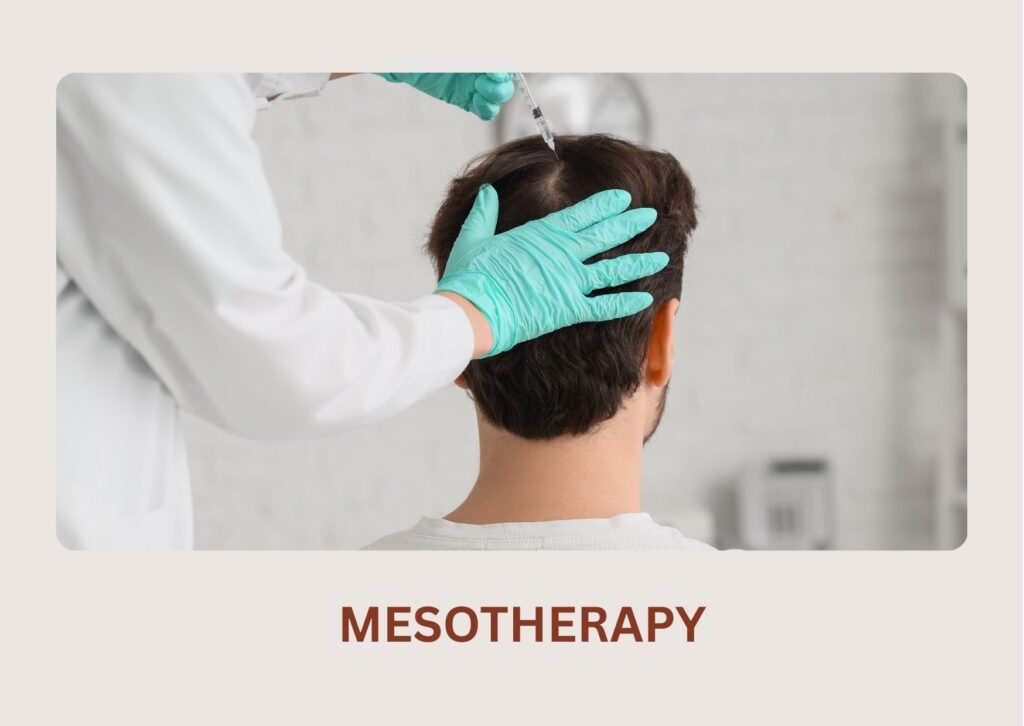
A nutrient-rich cocktail of vitamins, peptides, and growth boosters is delivered into the scalp to improve hair density and reduce thinning.
How To Prevent Premature Graying?
Prevent premature graying by combating oxidative stress, nutritional gaps, and lifestyle triggers that deplete hair melanin before age 30.
Consume antioxidant-rich foods like berries, amla, nuts, and greens daily, plus B12, copper, iron, and zinc from eggs, spinach, and lentils.
Quit smoking and limit alcohol, as they accelerate free radical damage to melanocytes.
Manage stress through yoga, meditation, and 7-9 hours sleep to lower norepinephrine levels harming pigment cells.
Protect hair from sun/pollution with hats, scarves, and mild, chemical-free products; avoid excessive heat styling.
Supplement deficiencies after blood tests (B-vitamins, minerals) and massage scalp weekly with curry leaf or coconut oil.
Consult a Specialist Today
Many of the techniques for preventing pimples may also be used to cure them. Eating well, avoiding stress, and not popping pimples may help manage zits and reduce their length. If your acne continues despite your best efforts, you may need prescription acne treatment. Consult your dermatologist if you’re uncertain about treatment.
FAQ's
Premature graying, or canities, occurs when hair loses melanin before age 20 in Caucasians or 30 in Asians/Indians, unlike normal aging after 40.
Reversal is possible in cases tied to deficiencies or medical issues like B12 shortage or thyroid problems, but genetics-driven graying resists full reversal.
Chronic stress contributes by raising norepinephrine, depleting melanocytes, though genetics dominate; manage via meditation or yoga.
Rarely signals issues like vitiligo, anemia, or thyroid disorders; consult a doctor for blood tests if sudden or patchy.
Yes, B-vitamins, copper, iron, and antioxidants from amla or nuts support melanin; test for deficiencies first.