Strong, Healthy & Beautiful Hair with Hair Loss Treatment
Female hair loss is a common concern that affects women across all age groups, often leading to thinning, reduced volume, and a drop in confidence. At Urban Skin and Hair Clinic, our advanced female hair loss treatments are designed to address the root causes—whether hormonal changes, stress, genetics, nutritional deficiencies, or underlying scalp conditions. We focus on reducing hair fall, improving hair density, and restoring natural volume with safe, science-backed solutions. With expert dermatologists and personalised treatment plans tailored to every hair type, we help women achieve stronger, fuller, and healthier hair while boosting confidence and long-term hair wellness.
Symptoms and Causes
Symptoms of Women Hair Loss
Hair loss in women can appear in different ways and may develop gradually or suddenly. Common symptoms include:
Thinning hair on the crown or top of the head, often widening the part line.
Sudden hair shedding that becomes noticeable while combing, washing, or on pillows and clothes.
Patchy or circular bald spots on the scalp.
Weakened or brittle hair strands that break easily.
Receding hairline (less common but possible in women).
Itchy, scaly, or irritated scalp, sometimes linked with underlying conditions.


Causes of Women Hair Loss
Hair loss in women can result from multiple internal and external factors. The most common causes include:
Hormonal Changes – Pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, thyroid issues, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can disrupt hair growth.
Genetics – Family history of female pattern baldness can increase the risk.
Stress – Emotional or physical stress may lead to sudden hair shedding (telogen effluvium).
Nutritional Deficiencies – Lack of iron, vitamin D, protein, or other essential nutrients weakens hair.
Medical Conditions – Autoimmune diseases, scalp infections, or chronic illnesses may trigger hair loss.
Hairstyles & Treatments – Tight hairstyles, heat styling, chemical dyes, or harsh products can damage and thin hair.
Medications – Drugs for cancer, depression, blood pressure, or birth control may have hair loss as a side effect.

Types of Women Hair Loss
Hair loss in women can appear in different patterns and forms. The common types include:
Female Pattern Hair Loss (Androgenetic Alopecia) – The most common type, leading to gradual thinning on the crown or widening of the hair part.
Telogen Effluvium – Sudden hair shedding caused by stress, illness, childbirth, or hormonal changes.
Alopecia Areata – An autoimmune condition that results in patchy bald spots on the scalp or other body areas.
Traction Alopecia – Hair loss caused by tight hairstyles like braids, ponytails, or extensions that pull on the roots.
Cicatricial Alopecia (Scarring Alopecia) – A rare type where inflammation damages hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss.
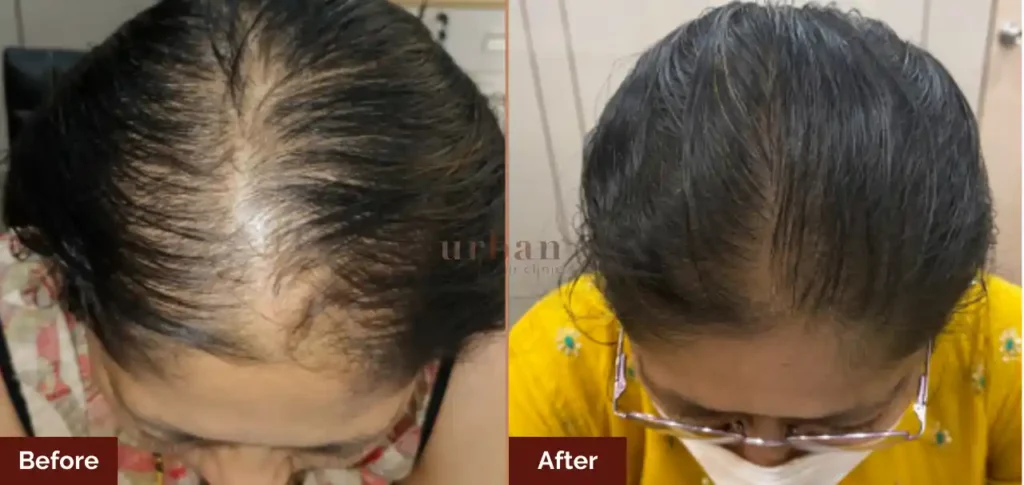
Results Before & After
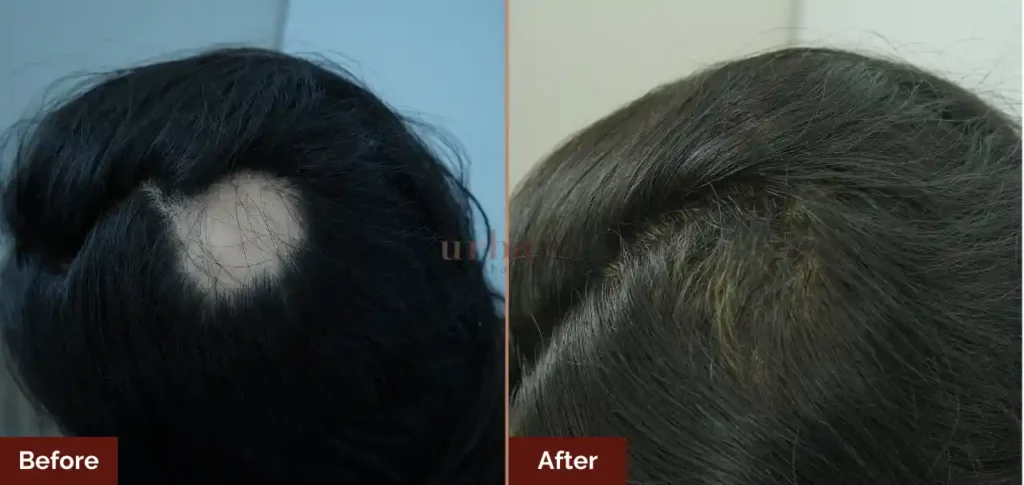

Benefits of Women Hair Loss Treatment
Expert treatments at Urban Skin Hair Clinic (USHC) address female pattern hair loss, hormonal imbalances, or stress-related thinning effectively.
Promotes Regrowth: Minoxidil and PRP stimulate follicles for thicker, fuller hair in 3-6 months.
Halts Progression: Spironolactone blocks DHT hormones, slowing diffuse thinning common post-menopause.
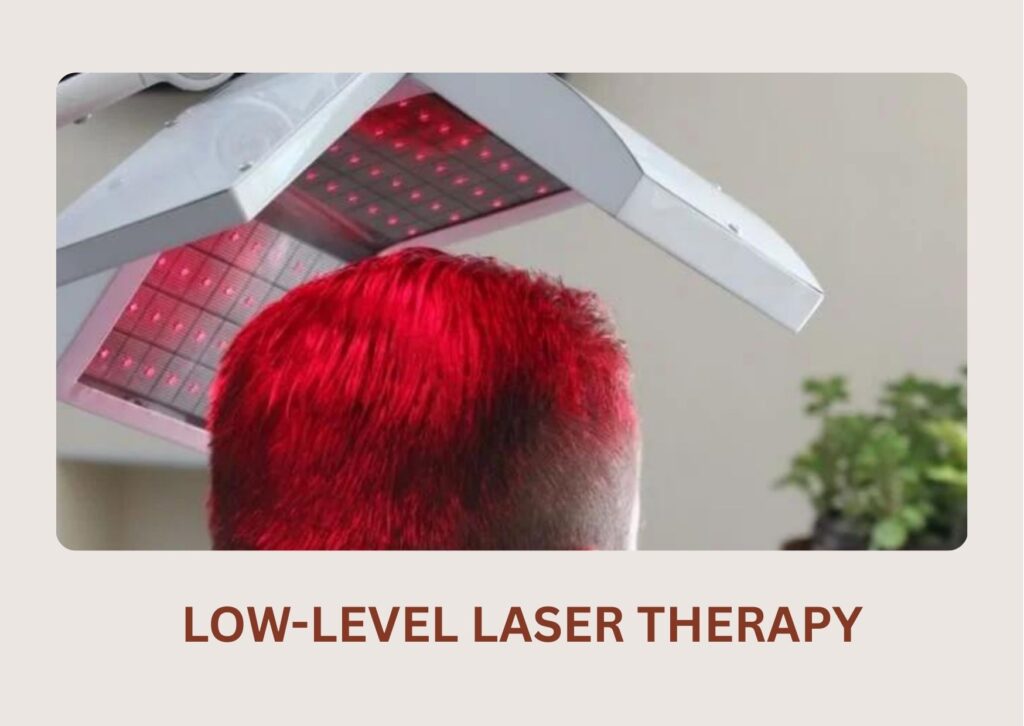
Increases Density: Low-level laser therapy boosts circulation for visible volume without surgery.
Restores Confidence: Natural-looking results reduce emotional distress from widening parts.
Sustains Health: Supplements and topicals maintain gains, preventing further shedding long-term.

Popular Treatments for Hair Loss
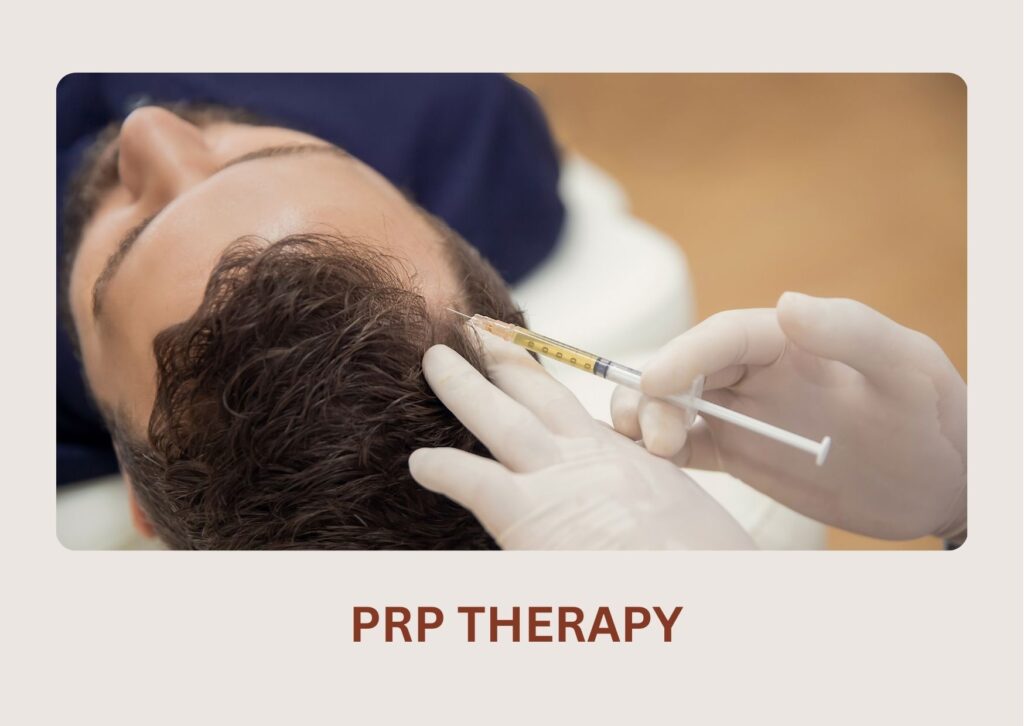
A highly effective treatment where your own growth-factor-rich plasma is injected into the scalp to strengthen follicles, reduce hair fall, and boost regrowth.
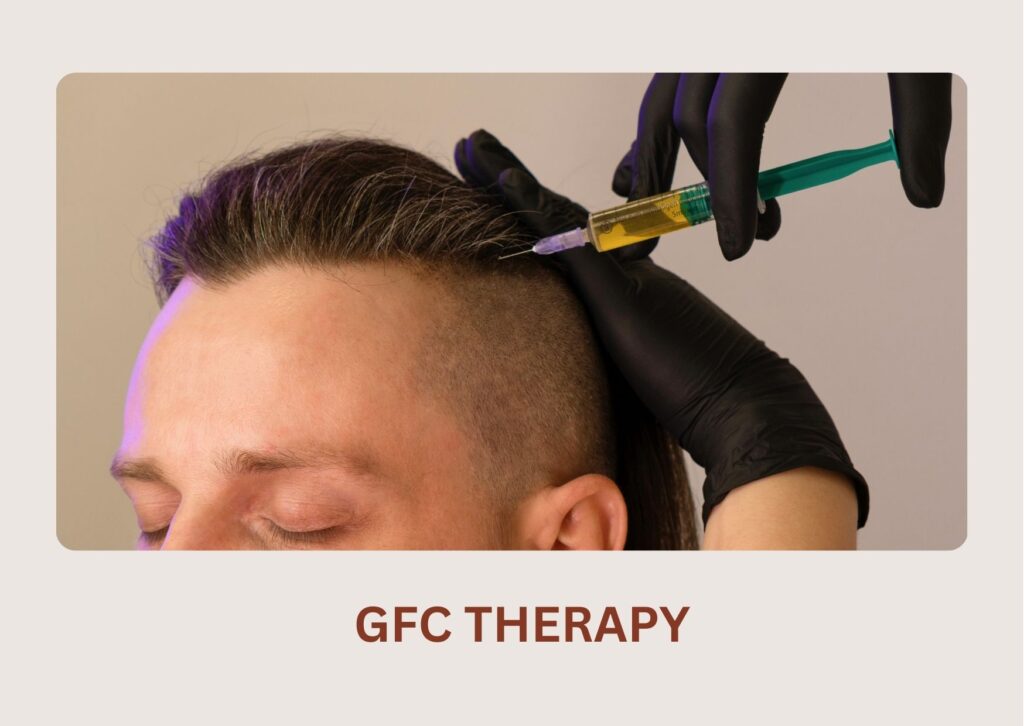
Advanced version of PRP that offers higher growth factor concentration for faster and more noticeable results.
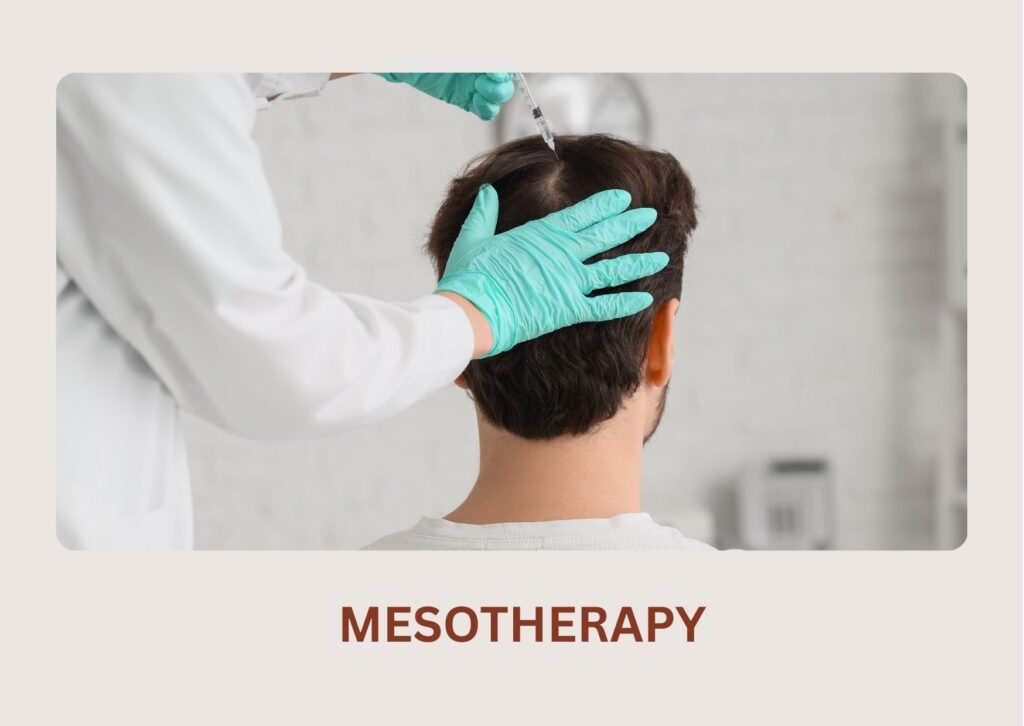
A nutrient-rich cocktail of vitamins, peptides, and growth boosters is delivered into the scalp to improve hair density and reduce thinning.
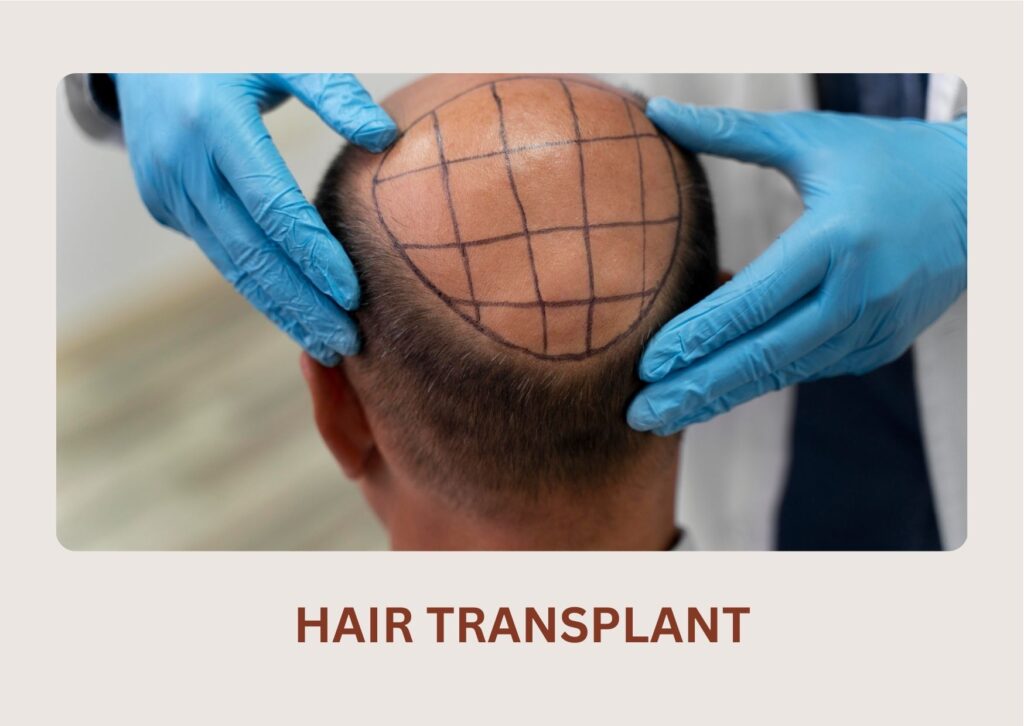
A permanent solution where healthy follicles from the donor area are transplanted to bald or thinning areas for natural, long-lasting results.
Fine needles create microchannels on the scalp to enhance absorption of growth serums and activate collagen production.
How To Prevent Women Hair Loss?
Prevent female hair loss by addressing hormonal shifts, nutritional gaps, and stress that trigger diffuse thinning or telogen effluvium.
Eat a nutrient-dense diet rich in iron, biotin, zinc, and protein from eggs, spinach, nuts, and lean meats to fuel follicle health.
Massage scalp daily for 4-5 minutes with gentle oils like coconut or rosemary to improve circulation and reduce tension.
Avoid tight hairstyles, heat tools, and chemical treatments; use wide-tooth combs and silk pillowcases to minimize breakage.
Manage stress with yoga, meditation, or 7-9 hours sleep nightly, as cortisol disrupts growth cycles.
Consult at Urban Skin Hair Clinic (USHC) for early screening of thyroid, PCOS, or deficiencies via blood tests.
Consult a Specialist Today
Many of the techniques for preventing pimples may also be used to cure them. Eating well, avoiding stress, and not popping pimples may help manage zits and reduce their length. If your acne continues despite your best efforts, you may need prescription acne treatment. Consult your dermatologist if you’re uncertain about treatment.
FAQ's
Hormonal changes, genetics, stress, nutritional deficiencies, and certain medical conditions are the most common causes of hair loss in women.
Yes, in many cases. Hair loss caused by stress, diet, or medical conditions can be reversed with proper treatment, while genetic hair loss can be slowed and managed with medical therapies.
Options include minoxidil, PRP therapy, nutritional supplements, laser therapy, and hair transplants for advanced cases.
Yes, high stress can trigger temporary hair shedding (telogen effluvium), but hair usually regrows once stress is managed.
If you notice sudden shedding, bald patches, or thinning that worsens over time, consult a dermatologist for diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Female Hair Loss
Genetic:
Androgenetic alopecia is female pattern baldness or hair loss caused by genetics. It’s the leading cause of hair loss in women and generally begins between the ages of 12 to 40 years old.
Menopause
Menopause is a natural biological process that all women experience at some point in their lives. Hair loss during menopause is the result of a hormonal imbalance. It’s related to a lowered production of estrogen and progesterone. These hormones help hair grow faster and stay on the head for longer periods of time. When the levels of estrogen and progesterone drop, hair grows more slowly and becomes much thinner. A decrease in these hormones also triggers an increase in the production of androgens, or a group of male hormones. Androgens shrink hair follicles, resulting in hair loss on the head.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS):
Your body makes more male hormones, or androgen, than it should. This can cause extra hair to sprout on your face and body while the hair on your head thins out.
Alopecia Areata
The culprit is your own immune system, which attacks healthy hair follicles by mistake. In most cases, the damage isn’t permanent. The missing locks should grow back in 6 months to a year.
Childbirth
You might notice your hair seems fuller during pregnancy. That’s because high hormone levels keep resting hairs from falling out. But after the baby comes, things go back to normal and those strands will fall out quickly. You could lose a lot of hair at once. It could take up to 2 years for your locks to return to normal.
The Pill
The hormones that suppress ovulation could cause your hair to thin. It’s more likely if you have a family history of hair loss. It might happen when you stop taking the pill. Other drugs linked to hair loss include blood thinners and medicines that treat high blood pressure, heart disease, arthritis, and depression.
Crash Diets
If you drop 15 pounds or more, you might also shed some hair. Don’t worry too much — it’ll return when you’re back on a healthy diet.
Tight Hairstyles
Wearing cornrows or tight ponytails can irritate your scalp and cause hair to fall out. The same goes for using tight rollers.Be aware that long-term use of these styles can scar your scalp and lead to permanent hair loss.
Thyroid Problems
If this butterfly-shaped gland at the front of your neck, makes too much or too little thyroid hormone, your hair growth cycle might take a hit.
Ringworm
When the ringworm fungus affects your scalp, it triggers a distinct hair loss pattern — itchy, round bald patches. They might look scaly and red.
Extreme Stress
High-level physical or emotional stress can cause you to suddenly shed huge amounts of hair. e.g.Serious illness or major surgery,Trauma involving blood loss, Severe emotional distress.
Symptoms of Female Hair Loss
- Gradual thinning of hair on top of head
- Sudden loosening of hair
- Patchy bald spots on scalp
Classification of Female Pattern Hair Loss
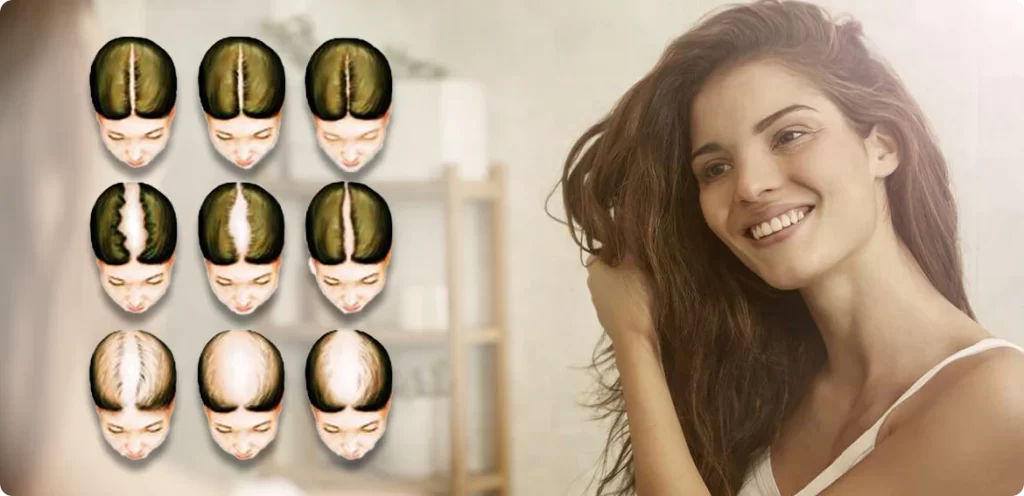

How to Prevent Female Hair Loss?
- Avoid hairstyles that pull on the hair
- Avoid high-heat hair styling tools
- Don’t chemically treat or bleach your hair
- Use a shampoo that’s mild and suited for your hair
- Use a soft brush made from natural fibers
Treatment Options
Minoxidil, also known as Rogaine, is an over-the-counter (OTC) medication that can be used for men or women with alopecia areata or androgenic alopecia. FDA approved drugs come in foam or liquid form and are spread on the scalp each day. It may cause more hair loss at first, and new growth may be shorter and thinner than before. You may also need to use it for 6 months or more to prevent further loss and promote regrowth.
Possible side effects include scalp irritation, hair growth on other parts of the face or hands that come in contact with the medication, tachycardia (rapid heart rate).
Foods rich in vitamin A can help hair regrowth e.g.sweet potatoes, carrots, pumpkins, spinach. Consuming whole grains, almonds, fish, and meat rich in vitamin B can help to get healthy hair.
Vitamin C rich foods can help to create a protein known as collagen — an important part of hair structure.e.g., strawberries, peppers, guavas, and citrus fruits. Iron and zinc supplements also play a role in the development of healthy hair.
FAQ for Female Hair Loss
Hair loss commonly referred to as alopecia or baldness, is the loss of hair on one’s head or body. At the very least, the head is usually engaged. Hair loss can range in intensity from a tiny patch to the full body. In most cases, there is no inflammation or scarring. Some people experience psychological anguish as a result of hair loss.
Common kinds include male or female hair loss patterns, alopecia areata, and hair dilution called telogen effluvium. The reason for hair loss by male pattern baldness is a mixture of heredity and male hormones, certain causes of the hair loss in females; autoimmune causes alopecia areata, and generally physically or mentally stressful effects of telogen effluvium. After pregnancy, telogen effluvium is fairly prevalent.
One or more of the following reasons are commonly linked to hair loss:
- History of the family (heredity)
An inherited disease that occurs with aging is the most prevalent cause of hair loss. Androgenic alopecia, often known as male-pattern baldness or female-pattern baldness, is a disorder that affects both men and women. In men, it manifests as a receding hairline and bald patches, whereas in women, it manifests as thinning hair around the crown of the head.
- Hormonal and medicinal changes
Hormonal changes caused by pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, and thyroid disorders are just a few of the diseases that can cause permanent or temporary hair loss. Alopecia areata, an immune system ailment that causes patchy hair loss, scalp infections like ringworm, and trichotillomania, a hair-pulling disease, are examples of medical diseases.
- Radiation treatment
You may lose all (or most) of your hair in a few weeks after commencing treatment if you are receiving chemotherapy or getting radiation treatment on your head or neck.
- Age
Hair loss is common as individuals become older because hair growth slows. Hair follicles eventually cease producing hair, causing the hair on our scalp to diminish. Hair begins to lose its color as well. The hairline of a woman begins to recede with time.
- Hair Cosmetics and hairstyles
Excessive hairstyling or hairstyles that pull your hair tight, such as pigtails or cornrows, can lead to traction alopecia, a kind of hair loss. The hot-oil hair treatments and irreversible hair loss can also be triggered. Hair loss might be permanent if scarring develops.
PRP Hair Loss Treatment costs are estimated to be roughly INR 10,000 to 25,000 for 3 sessions in India.
Hair transplantation is a permanent process, which is why it is regarded as the most efficient way to restore your hair. Our surgeons utilize your healthy hair follicles to fill up thinning or balding regions during surgery. These hairs are considered permanent because they are resistant to the hormone that causes hair loss, dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The transplanted hairs will continue to grow even if the non-transplanted hairs surrounding them continue to miniaturize and fall out since they are DHT resistant.
Whether you have decided to use FUT or FUE differs in recovery time. You should expect your surgical sites to cure in two or three weeks and to restart regular activities within a comparable time for FUT treatments. In FUE you will be able to recover your sites in one to two weeks and then you will be able to restart regularly.
Hair loss can be caused by a variety of circumstances, including:
- A mother’s or father’s side of the family has a history of baldness
- Age
- The significant weight reduction
- Diabetes and lupus are two examples of medical diseases.
- There’s a lot of pressure on
- Nutritional deficiencies
Alopecia, or hair loss, can be diagnosed by several different types of doctors. Patients with thinning, losing, or balding hair are frequently seen by the professions listed below.
- Trichologists
They are professionals who have studied trichology, or the health of the hair and scalp. However, not all trichologists are licensed, physicians. For successful hair loss treatments, patients should pick a hair loss clinic to guarantee correct diagnosis and therapy and/or licensed medical professionals.
- Dermatologists
They are certified medical specialists that specialize in skin, nail, and hair care. Dermatologists that are Board Certified in Dermatology are the ablest to determine the cause of hair loss and propose an appropriate therapy. A dermatologist can diagnose and treat more than 3,000 conditions. These conditions include hair loss, Acne pigmentation, eczema, psoriasis, and skin cancer, among many others.
If you or your kid is experiencing persistent hair loss and would like to seek treatment, see your doctor. If you have a receding hairline (facial fibrosing alopecia), talk to your doctor about getting treatment as soon as possible to avoid irreversible baldness.
When combing or washing your or your child’s hair, talk to your doctor if you detect abrupt or uneven hair loss or greater than typical hair loss. Sudden hair loss might be an indication of a medical problem that needs to be addressed.
Androgenetic alopecia is a kind of alopecia that affects men. Is it a characteristic that is influenced by androgens? The terminal hair follicle becomes vulnerable to dihydrotestosterone, which causes the anagen phase to be shortened and terminal hair to be miniaturized. Male androgenetic alopecia is mostly passed down via the generations. In men, family investigations demonstrate that twins have a high probability of concordance and that sons with bald dads are at a higher risk. Furthermore, androgen receptor genes and chromosomal variants are linked to the development of androgenetic alopecia in men.
Androgenic areata is a kind of alopecia that affects women also. Hair loss may run in the family, and there appears to be a significant hereditary propensity. Although the majority of women with alopecia have normal levels of androgens in their blood, there is a group of women with alopecia who have concomitant hyperandrogenism, such as that caused by Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome.
Informative Resources:
Before you start blaming yourself for what you think you did to trigger your hair loss, have a look at this list of busted hair loss myths we’ve compiled.
Hair loss can be caused by wearing hats too regularly
This is not true. The notion is that the scalp needs air to breathe and that hats can suffocate this. This is not the case. The bloodstream, not the surrounding air, provides the oxygen your hair follicles require for development.
Wear a hat that’s not going to make your hair collapse! Hats may be particularly useful to disguise thinning hair and bald places over the head, hence why we combine hair loss with them. However, using one doesn’t accelerate hair loss or in any way hinder growth.
Baldness affects just the elderly
This is a wrong statement. You may notice the first indications of hair loss in your twenties if you have a family history of hair loss. While the majority of men begin to encounter male pattern baldness in their forties and fifties, up to a fifth of men begin the process before they turn 21.
However, this does not guarantee that you will see it immediately away. Until half the hair is gone most of the hair loss is not evident.
Every hair loss is continuous
It’s wrong. The common cause of male hair loss, male shallowness of the pattern is an irreversible hereditary disorder. But other reasons, like stress, hormonal changes, eating disorders, or disease can also cause hair loss. Women may experience a hair loss after birth that rectifies about six months after birth.
Hair loss due to something other than pattern baldness is usually only transitory.
Why Urban Skin and Hair Clinic

TEAM OF CERTIFIED DERMATOLOGISTS

US-FDA APPROVED EQUIPMENTS

HIGHLY STANDARDISED PROTOCOLS