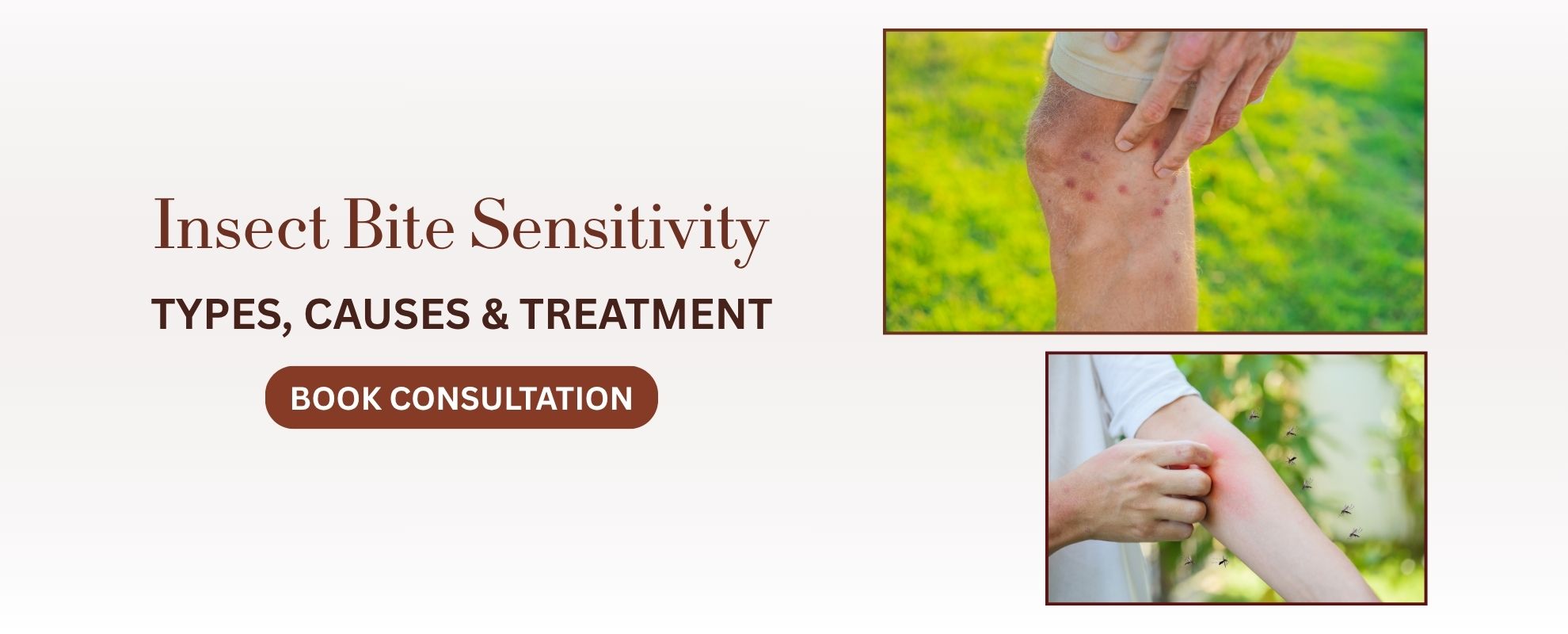
Clear, Healthy & Confident Skin with Insect Bite Sensitivity Treatment
As of my last update in September 2021, “Insect Bite Sensitivity” is not a specific medical term or condition. It seems to be a phrase used to describe an individual’s heightened reaction or sensitivity to insect bites. People can react differently to insect bites based on their immune response and individual factors.
Some individuals may experience mild reactions, such as redness, itching, and swelling, while others might have more severe reactions, including extensive swelling, blistering, and even systemic symptoms like fever or difficulty breathing. In extreme cases, some individuals may experience anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction.

Symptoms and Causes
signs & Symptoms Of Insect Bite Sensitivity
The symptoms of insect bite sensitivity can vary depending on the individual’s immune response and the type of insect involved. Here are some common symptoms that people may experience if they are sensitive or allergic to insect bites:
- Localized skin reactions: The most common symptom of insect bite sensitivity is a localized skin reaction at the site of the bite.
- Pain or tenderness: Some individuals may experience pain or tenderness at the site of the bite, especially if it’s a larger or more severe reaction.
- Hives: Insect bite sensitivity can lead to the development of hives (urticaria) in some people. Hives are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can appear around the bite site or in other areas of the body.
- Blistering: In more severe reactions, the skin around the bite may form blisters, which can be painful and may take longer to heal.
- Large local reactions: Some people may develop a larger area of swelling and redness around the bite, extending beyond the immediate site of the bite.
- Anaphylaxis: In severe cases, anaphylaxis may occur, which is a life-threatening allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms of anaphylaxis can include a severe drop in blood pressure, difficulty breathing, loss of consciousness, and shock.
- Skeeter Syndrome: This term is often used to describe an exaggerated allergic reaction to mosquito bites. People with skeeter syndrome may experience very pronounced swelling, redness, and itching at the site of the mosquito bite.
It’s important to remember that individual reactions can vary, and some people may not have any noticeable reaction to insect bites.

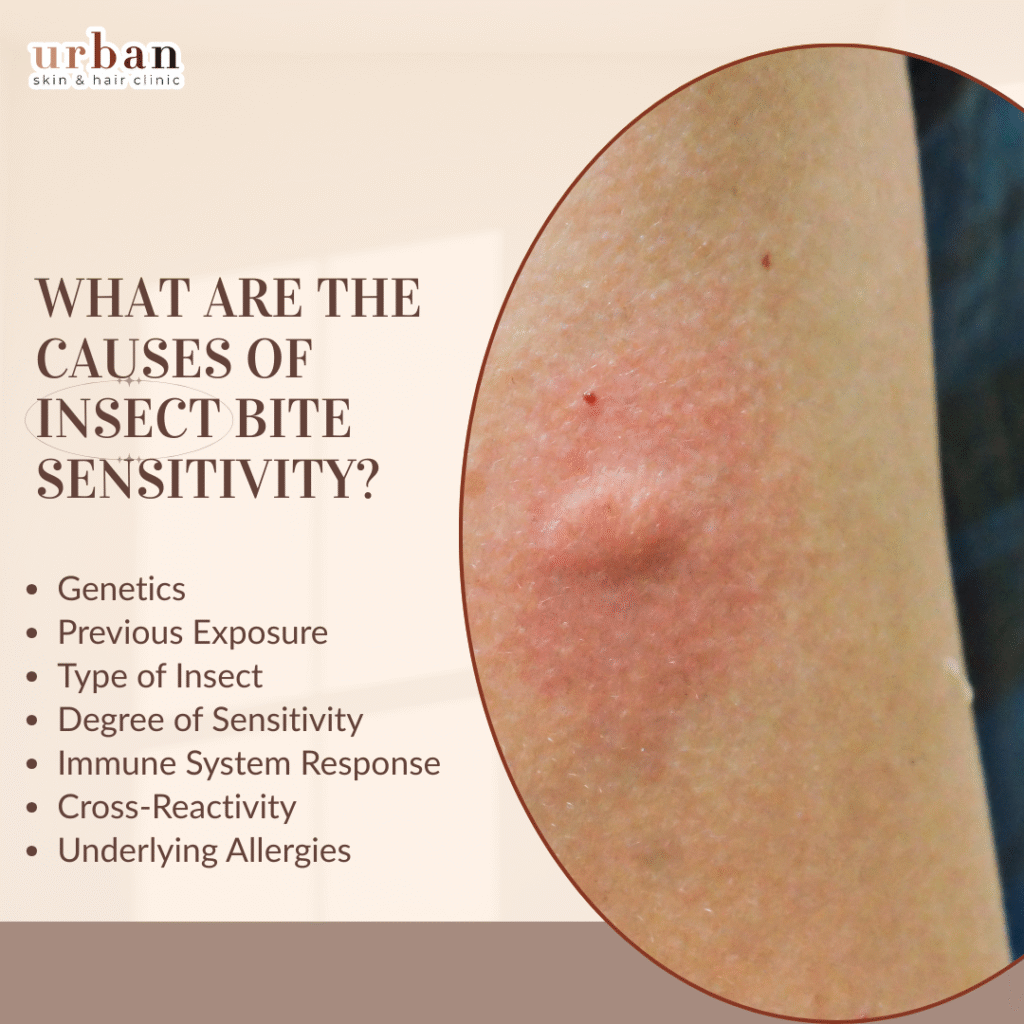
What are the Causes of Insect Bite Sensitivity?
Insect bite sensitivity or allergic reactions to insect bites occur when the immune system overreacts to the proteins or components present in the saliva or venom of the biting insect.
- Genetics: Allergies and sensitivities, including those to insect bites, can have a genetic component. If there is a family history of insect bite allergies.
- Previous Exposure: Repeated exposure to insect bites can sensitize the immune system and lead to increased sensitivity over time.
- Type of Insect: Different insects inject varying components with their bites or stings, which can trigger different immune responses.
- Degree of Sensitivity: The extent of sensitivity can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience only mild local reactions.
- Immune System Response: The way an individual’s immune system reacts to the components of the insect’s saliva or venom plays a crucial role in determining the severity of the reaction.
- Cross-Reactivity: In some cases, individuals who are sensitive to one type of insect bite may also react to bites from related insects due to cross-reactivity.
- Underlying Allergies: People with existing allergies, such as pollen or certain food allergies, may have an increased risk of developing insect bite sensitivity.
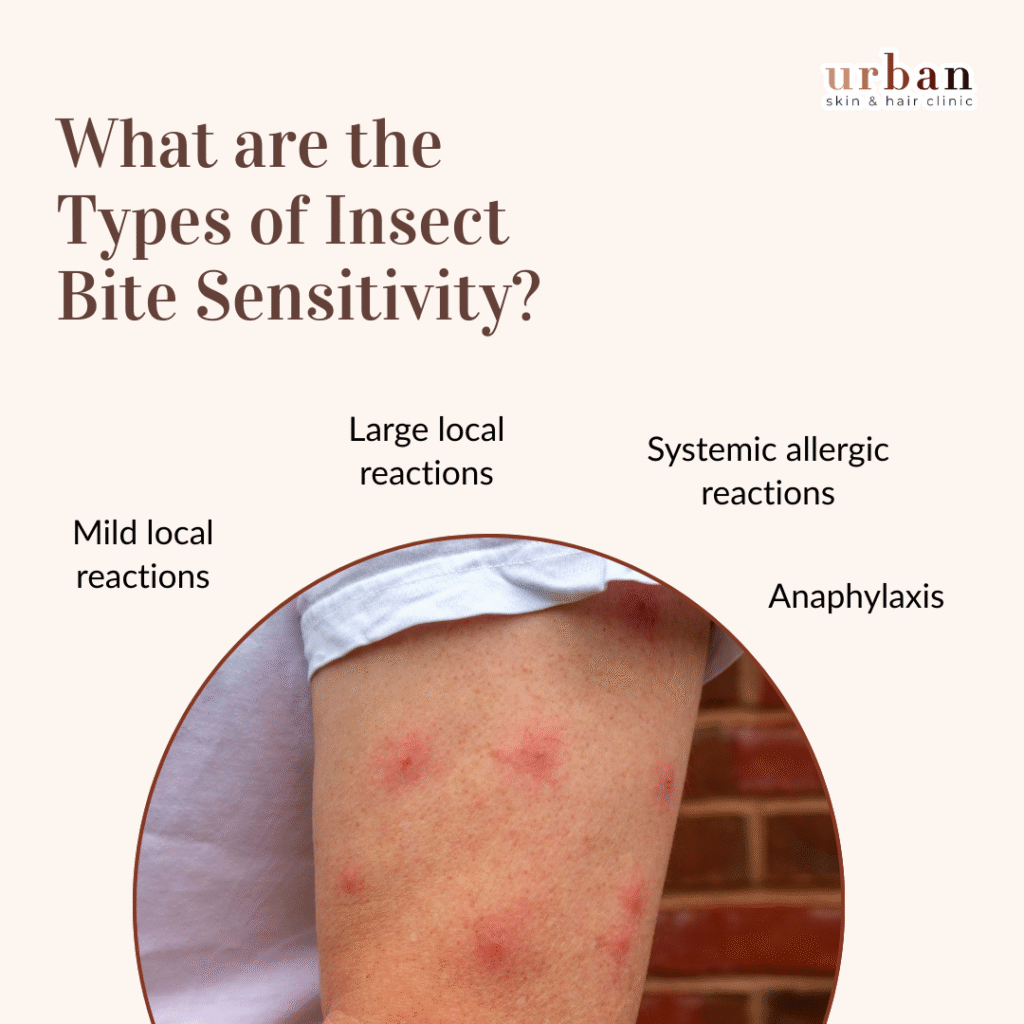
What are the Types of Insect Bite Sensitivity?
When discussing insect bite sensitivity, it’s important to note that people can react differently to insect bites based on their individual immune responses and other factors. While there isn’t a specific classification system for “types” of insect bite sensitivity.
- Mild local reactions: Many people experience mild local reactions to insect bites. These reactions are characterized by redness, swelling, itching.
- Large local reactions: Some individuals may develop more significant local reactions. The area around the bite may swell considerably, extending beyond the immediate site of the bite.
- Systemic allergic reactions: In some cases, individuals can have an allergic reaction to insect bites. These systemic reactions can involve symptoms beyond the immediate bite area and may include hives, itching in other parts of the body.
- Anaphylaxis: Anaphylaxis is a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction that can occur after an insect bite. It involves a rapid and systemic response that affects multiple body systems.
Treatment for Of Insect Bite Sensitivity
Effective treatment of fungal infections involves a combination of antifungal medications, proper hygiene practices, and lifestyle adjustments. Seeking professional medical evaluation and treatment at Urban Skin & Hair Clinic is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored management. Here are the common approaches to treating fungal infections:
Wash the affected area with mild soap and water to remove any insect venom or saliva that may still be on the skin.
Applying a cold compress or ice wrapped in a cloth to the bite site can help reduce swelling and alleviate itching.
Over-the-counter creams or ointments containing hydrocortisone or calamine can help relieve itching and inflammation.
Taking oral antihistamines (e.g., cetirizine, loratadine) can help reduce itching and allergic reactions.
Try to avoid scratching the affected area, as it can lead to further irritation and increase the risk of infection.
If the bite is on an arm or leg, elevating the limb can help reduce swelling. For more severe reactions, especially those with systemic symptoms or signs of anaphylaxis, immediate medical attention is crucial. Emergency treatment may include:
- Epinephrine Injection: For severe allergic reactions or anaphylaxis, an epinephrine auto-injector (e.g., EpiPen) may be administered as the first-line treatment. This medication helps counteract the life-threatening effects of the allergic reaction.
- Emergency Medical Care: If anaphylaxis occurs, call for emergency medical help immediately. An individual experiencing anaphylaxis may require further medical interventions, such as IV fluids, oxygen, and other medications to stabilize their condition.
For individuals with recurrent or severe insect bite sensitivity, an allergist or immunologist can be consulted for a comprehensive evaluation. Allergy testing can be conducted to identify specific allergens responsible for the reactions.
It’s important to note that not everyone will develop insect bite sensitivity, even after multiple exposures
Insect Bite Sensitivity Treatment Results Before & After


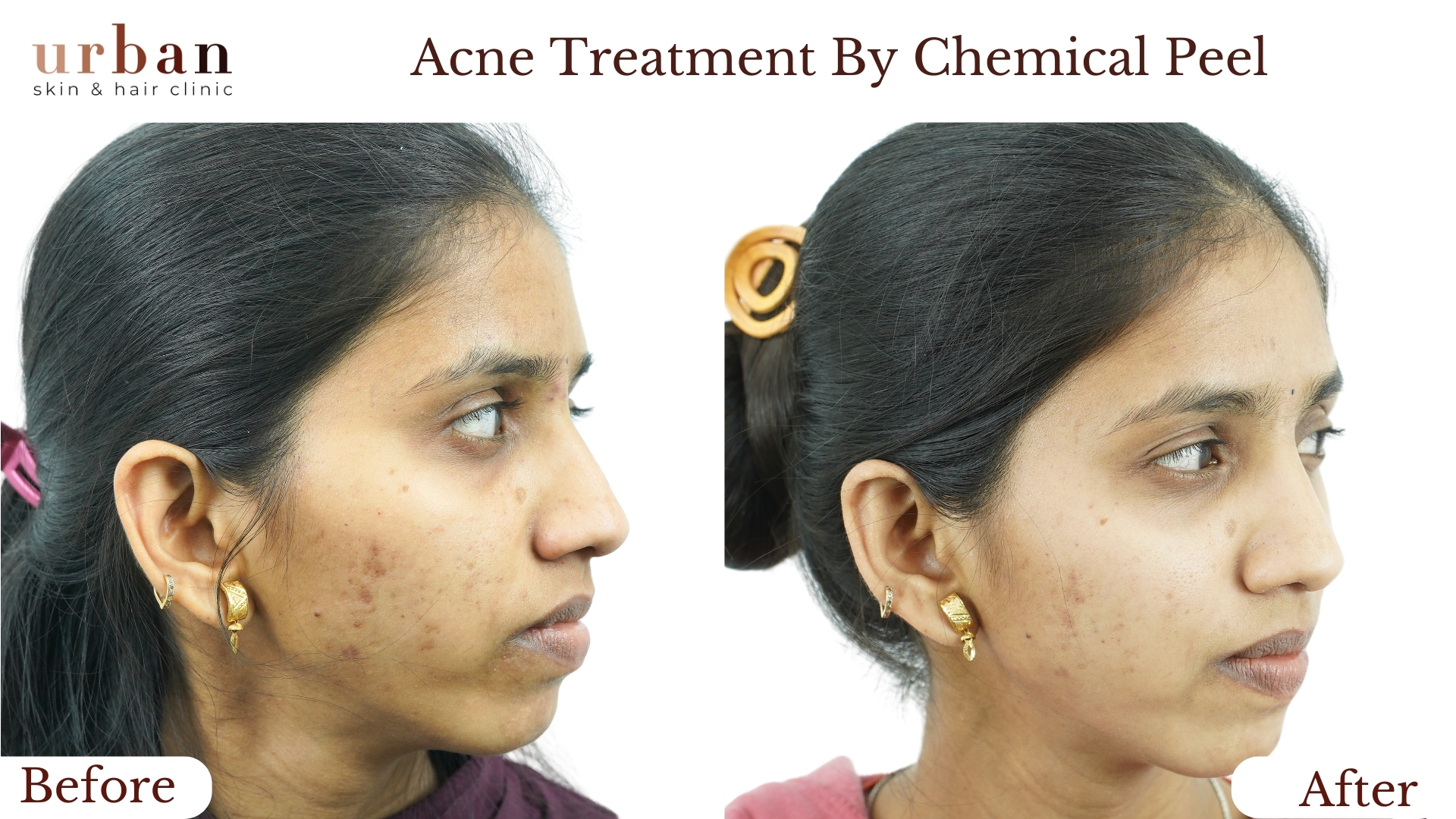
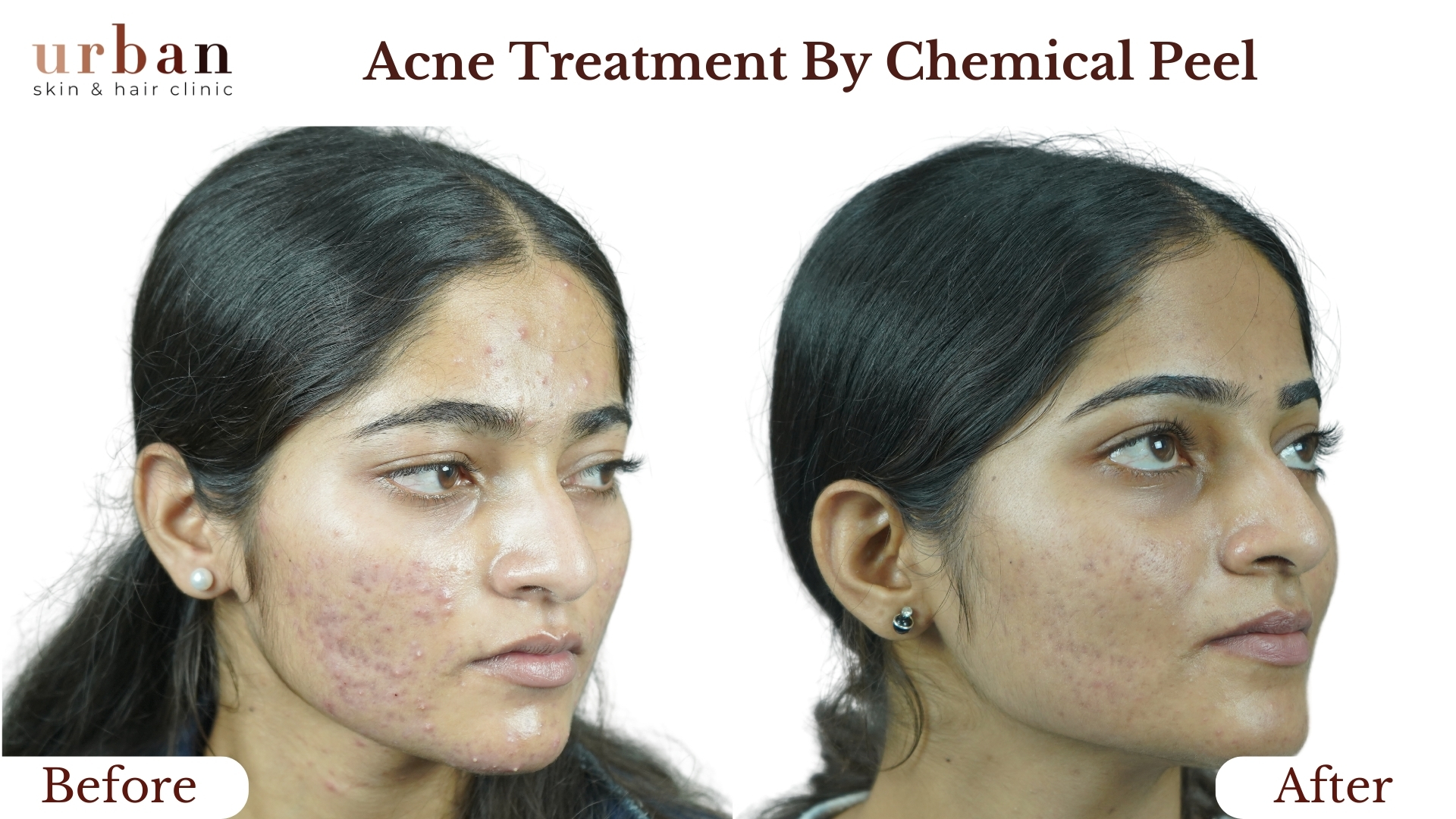
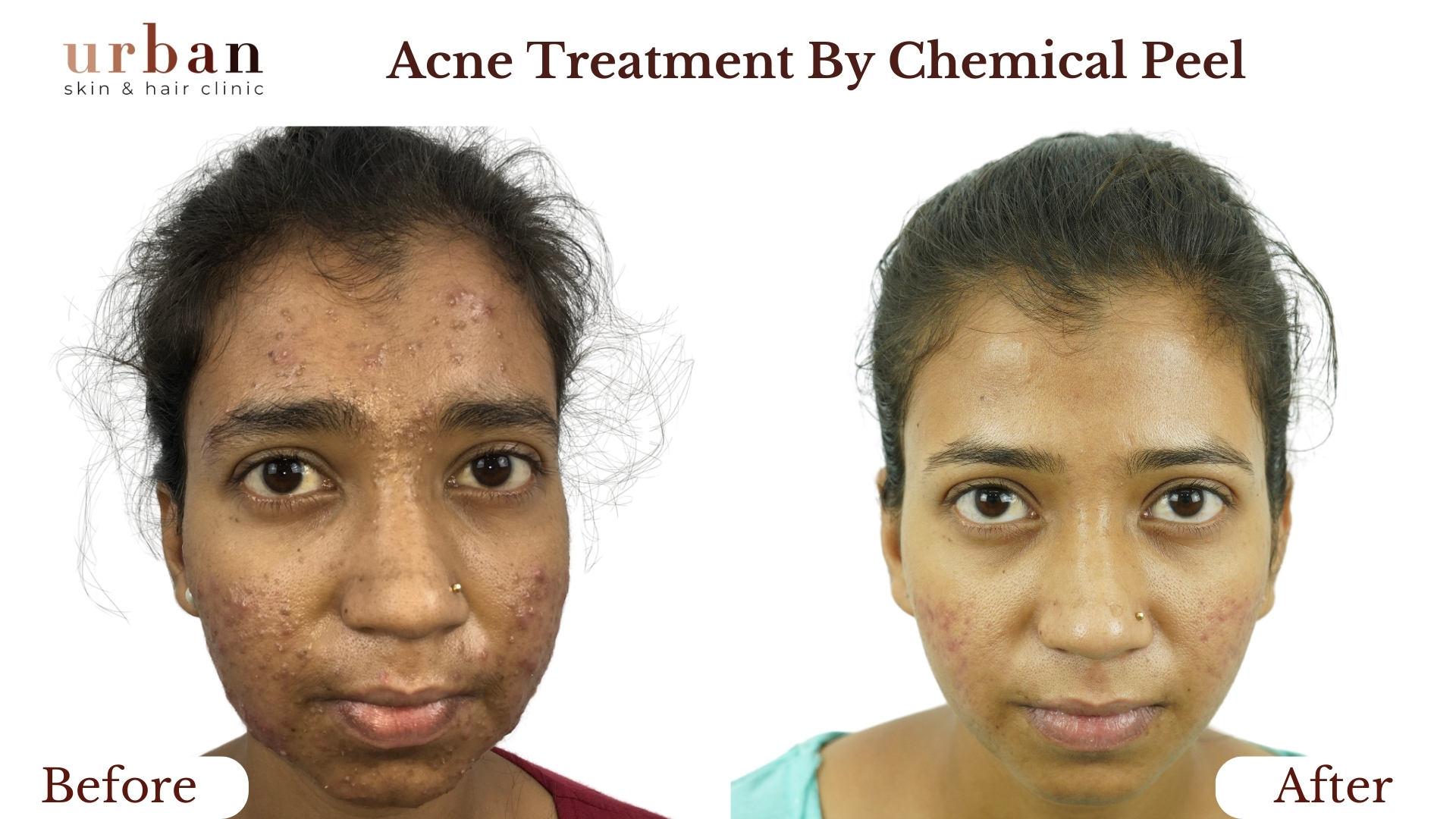
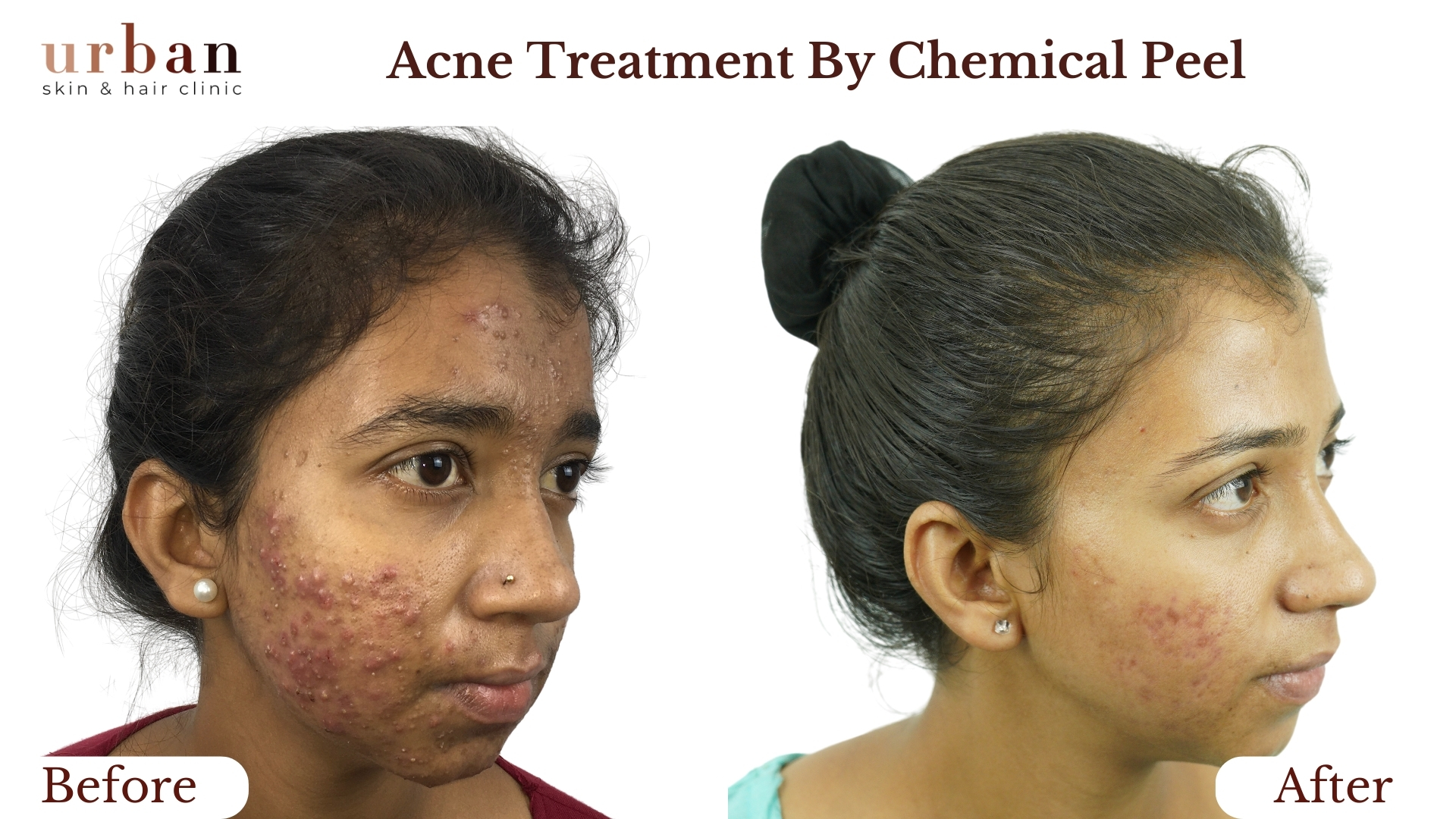
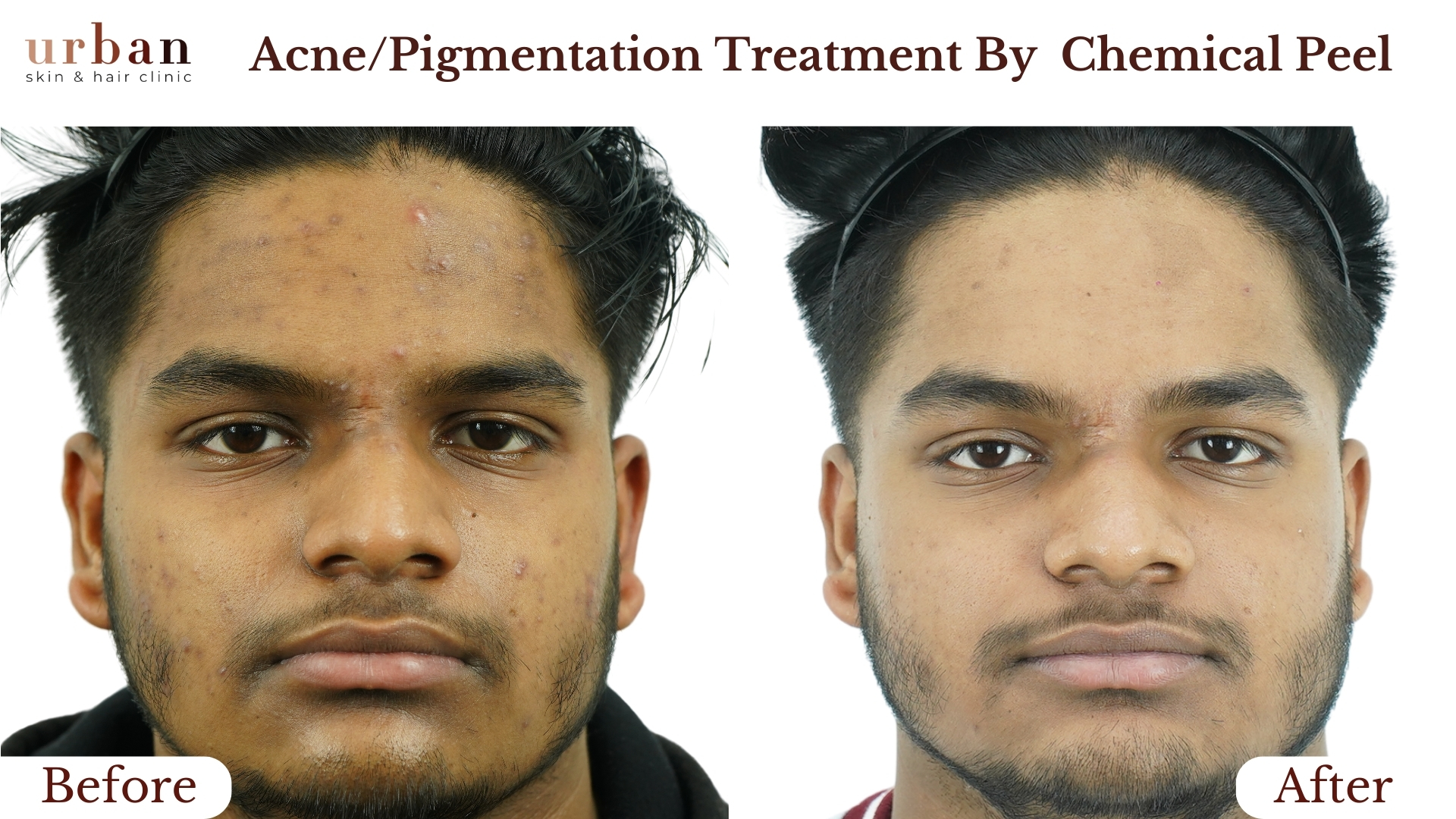
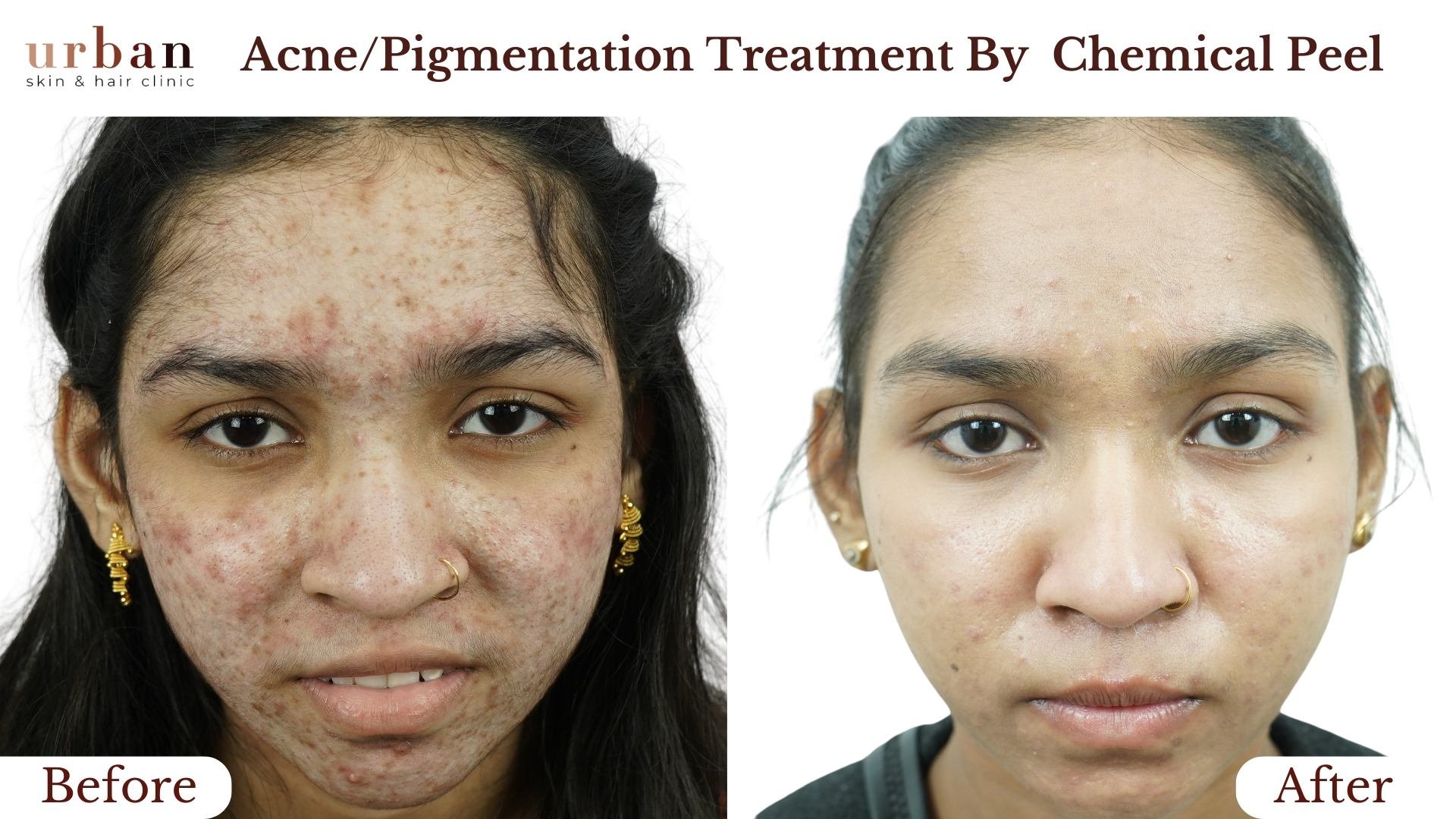

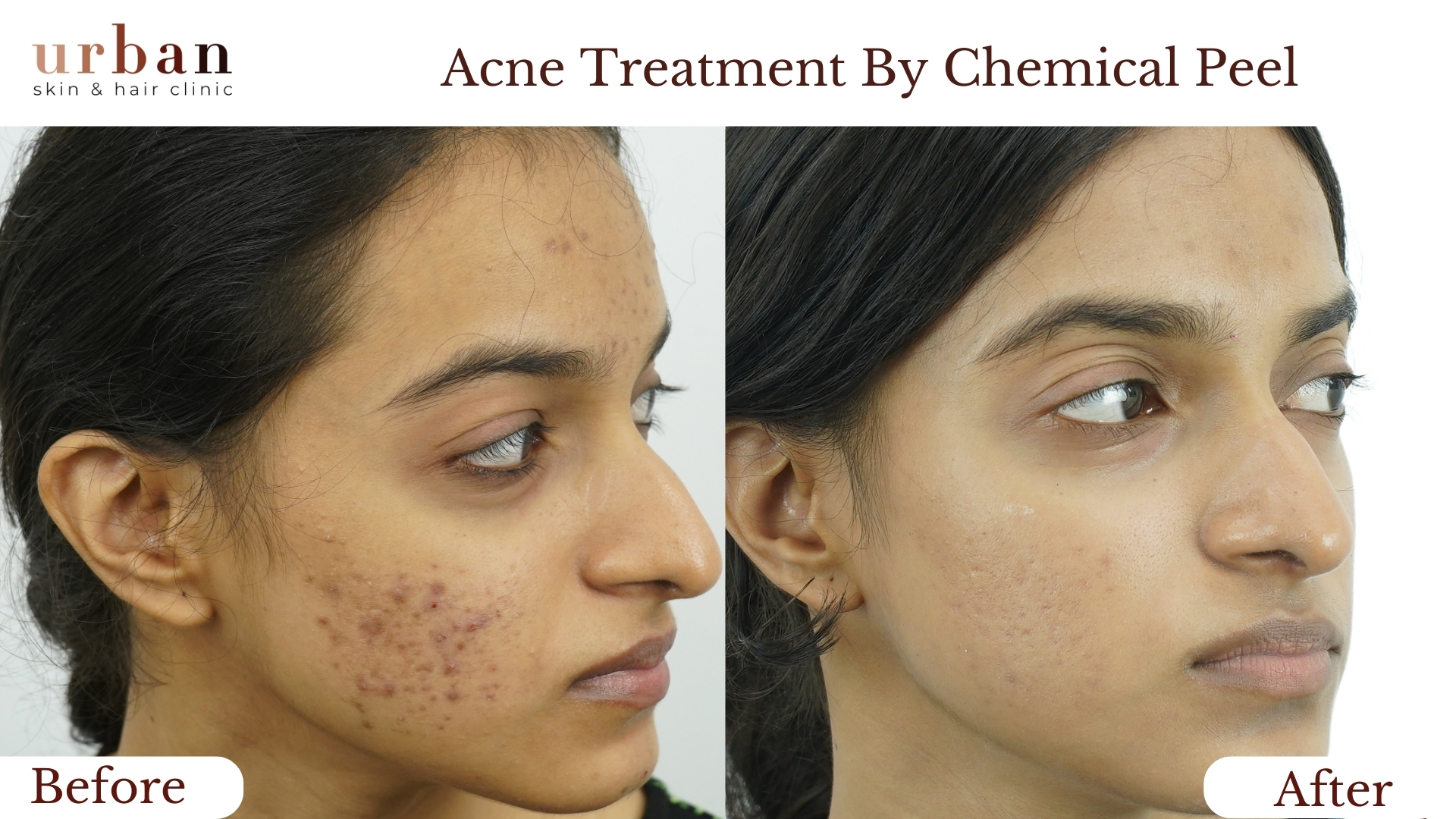
Benefits of Insect Bite Sensitivity Treatment
Insect bite sensitivity treatment alleviates exaggerated allergic responses to bites or stings, reducing symptoms and preventing severe outcomes like anaphylaxis.
Symptom Relief
Topical corticosteroids and antihistamines quickly reduce itching, swelling, and pain in large local reactions within hours to days.
Anaphylaxis Prevention
Epinephrine auto-injectors halt life-threatening reactions immediately, stabilizing breathing and circulation during severe episodes.
Long-Term Desensitization
Venom immunotherapy protects 80-90% of patients from anaphylaxis for years by retraining the immune system over 3-5 years.
Infection Risk Reduction
Early anti-inflammatory treatments like hydrocortisone dry weeping lesions, minimizing secondary bacterial complications.

Popular Treatments for Insect Bite Sensitivity
How To Prevent Insect Bite Sensitivity?
Insect bite sensitivity prevention centers on avoiding bites through repellents and barriers, as well as medical desensitization for severe cases.
Insect Repellents
Apply EPA-registered repellents with 20-30% DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus to exposed skin and clothing, reapplying as directed.
Protective Clothing
Wear long sleeves, pants, socks, and closed shoes in insect-prone areas; tuck pants into socks and pre-treat clothes with permethrin.
Environmental Controls
Use screened windows, air conditioning, and bed nets treated with pyrethroids; eliminate standing water weekly to reduce mosquito breeding.
Allergy Management
For known sensitivity, carry epinephrine auto-injectors and consider venom immunotherapy to reduce reaction severity over time.
Consult a Specialist Today
Many of the techniques for preventing pimples may also be used to cure them. Eating well, avoiding stress, and not popping pimples may help manage zits and reduce their length. If your acne continues despite your best efforts, you may need prescription acne treatment. Consult your dermatologist if you’re uncertain about treatment.
FAQ's
Sensitivity arises from IgE-mediated allergic reactions to insect saliva or venom proteins, common with mosquitoes, bees, wasps, or fire ants.
Mild cases show large hives, swelling, and itching beyond the bite site; severe ones include anaphylaxis with throat swelling, breathing difficulty, or shock.
No, normal reactions are localized redness and pain; sensitivity involves exaggerated swelling (>10 cm) or systemic symptoms lasting days.
Topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines relieve mild symptoms; epinephrine auto-injectors manage anaphylaxis, followed by immunotherapy for prevention.
Yes, repeated exposures may increase severity; allergy testing and venom shots desensitize 80-90% of patients long-term.